Lymphatic Vessels
... Flow of lymph through nodes o Lymph enters the convex side through afferent lymphatic vessels o Lymph flows through a number of sinuses inside the node o Lymph exits through efferent lymphatic vessels o Because there are fewer efferent than afferent vessels, flow is slowed Other Lymphoid Organs ...
... Flow of lymph through nodes o Lymph enters the convex side through afferent lymphatic vessels o Lymph flows through a number of sinuses inside the node o Lymph exits through efferent lymphatic vessels o Because there are fewer efferent than afferent vessels, flow is slowed Other Lymphoid Organs ...
comaneanu r - Revista de Chimie
... 5. GOLOMB G., WAGNER D., Biomaterials, 12, nr. 4, 1991, p. 397 6. WILLIAMS D.F., The Williams Dictionary of Biomaterials, 1999. 7. STROSCIO M.A., DUTTA M., Biological Nanostructures and Applications of Nanostructures in Biology - Electrical, Mechanical, and Optical Properties, Springer Science-Busin ...
... 5. GOLOMB G., WAGNER D., Biomaterials, 12, nr. 4, 1991, p. 397 6. WILLIAMS D.F., The Williams Dictionary of Biomaterials, 1999. 7. STROSCIO M.A., DUTTA M., Biological Nanostructures and Applications of Nanostructures in Biology - Electrical, Mechanical, and Optical Properties, Springer Science-Busin ...
7 Colon CASEbook FINAL2.pmd
... Colon cancer starts on the inside of the intestinal tube, called the lumen, a cavity/channel within a tube and grows outward through the bowel wall where it can spread to adjacent structures and the regional lymph nodes. Staging of colon cancer and prognosis are based on the depth of invasion of the ...
... Colon cancer starts on the inside of the intestinal tube, called the lumen, a cavity/channel within a tube and grows outward through the bowel wall where it can spread to adjacent structures and the regional lymph nodes. Staging of colon cancer and prognosis are based on the depth of invasion of the ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... seed growing into a plant A small child growing into a human A caterpillar growing into a butterfly ...
... seed growing into a plant A small child growing into a human A caterpillar growing into a butterfly ...
Print this article
... after myocardial infarction (MI), combined with the absence of endogenous repair mechanisms, is a causative factor in progression to heart failure. A pathologic ventricular remodeling ensues as damaged myocardium is replaced by a fibrous scar composed of extracellular matrix produced by nonmyocytic ...
... after myocardial infarction (MI), combined with the absence of endogenous repair mechanisms, is a causative factor in progression to heart failure. A pathologic ventricular remodeling ensues as damaged myocardium is replaced by a fibrous scar composed of extracellular matrix produced by nonmyocytic ...
C – E – L – L – O
... “typical” animal and plant cells, and many of the organelles are identical. However, there are a few organelles in both the typical animal and plant cells that are only in one or the other that perform functions that are unique to that type of cell. ...
... “typical” animal and plant cells, and many of the organelles are identical. However, there are a few organelles in both the typical animal and plant cells that are only in one or the other that perform functions that are unique to that type of cell. ...
Diffusion - Net Texts
... movement of molecules from an area where there is a higher concentration (larger amount) of the substance to an area where there is a lower concentration (lower amount) of the substance ( Figure 1.1). The amount of a ...
... movement of molecules from an area where there is a higher concentration (larger amount) of the substance to an area where there is a lower concentration (lower amount) of the substance ( Figure 1.1). The amount of a ...
Cell Structure and Function
... suited for a specific function; students exchange cells and attempt to guess function. 15 minutes • Mini-lecture: Give real life examples of how cell structure aids with function; clarify misconceptions revealed during activities. 10 minutes • Summation: Leave students with a thought-provoking quest ...
... suited for a specific function; students exchange cells and attempt to guess function. 15 minutes • Mini-lecture: Give real life examples of how cell structure aids with function; clarify misconceptions revealed during activities. 10 minutes • Summation: Leave students with a thought-provoking quest ...
Dr - UTCOM2013
... a nucleus (1 or 2) located in the center of the cell. is striated involuntary muscle. intercalated discs which hold cardiac cells together at their adjacent ends. branching fibers consisting of cells tightly adherent to one another at their ...
... a nucleus (1 or 2) located in the center of the cell. is striated involuntary muscle. intercalated discs which hold cardiac cells together at their adjacent ends. branching fibers consisting of cells tightly adherent to one another at their ...
vitroandremaintumorigenic. However, late
... primary tumor; (b) adherence and attachment of tumor cells to the basement membrane; (c) invasion of tumor cells through the basement membrane, with local proteolysis associated with the breakdown of the basement membrane components; and (d) migration of tumor cells through the defect in the extrace ...
... primary tumor; (b) adherence and attachment of tumor cells to the basement membrane; (c) invasion of tumor cells through the basement membrane, with local proteolysis associated with the breakdown of the basement membrane components; and (d) migration of tumor cells through the defect in the extrace ...
Anatomy of Cells
... nuclear pores penetrating them Nuclear pores allow mRNA to leave the nucleus to go to the cytoplasm Also contains the nucleolus where ribosomal subunits are produced ...
... nuclear pores penetrating them Nuclear pores allow mRNA to leave the nucleus to go to the cytoplasm Also contains the nucleolus where ribosomal subunits are produced ...
in follicle cells
... ca. 2% of all genes involved in embryo pattern formation (ca. 100 of >15.000 protein-encoding genes, only 5.000 essential genes) ...
... ca. 2% of all genes involved in embryo pattern formation (ca. 100 of >15.000 protein-encoding genes, only 5.000 essential genes) ...
Ultrastructural, Cell Membrane, and Cytogenetic Characteristics of B
... cytes from peripheral blood and spleen were obtained. The strated that, following LPS stimulation, the BCL, cells undergo cap-forming ability of the lymphocytes with F-Con A (100 /¿g/ further proliferation and differentiation into larger cells that ml) was determined and compared to that of normal ...
... cytes from peripheral blood and spleen were obtained. The strated that, following LPS stimulation, the BCL, cells undergo cap-forming ability of the lymphocytes with F-Con A (100 /¿g/ further proliferation and differentiation into larger cells that ml) was determined and compared to that of normal ...
Anat2_06_Lymphatic
... Edema & Lymph Flow Edema – excessive accumulation of interstitial fluid. Edema can be caused by obstruction of lymph flow due to an infected lymph node or blocked lymphatic vessel. Increased capillary blood pressure can cause edema by producing accumulation of interstitial fluid faster than ...
... Edema & Lymph Flow Edema – excessive accumulation of interstitial fluid. Edema can be caused by obstruction of lymph flow due to an infected lymph node or blocked lymphatic vessel. Increased capillary blood pressure can cause edema by producing accumulation of interstitial fluid faster than ...
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)
... three true tissue layers; mesoderm forms longitudinal muscle layer lining the body wall no muscle tissue associated with intestine gastrodermal cells line intestine Body Organization: round, nonsegmented, tubular body tapering at both ends no distinct head apparent characteristic "S" - like movement ...
... three true tissue layers; mesoderm forms longitudinal muscle layer lining the body wall no muscle tissue associated with intestine gastrodermal cells line intestine Body Organization: round, nonsegmented, tubular body tapering at both ends no distinct head apparent characteristic "S" - like movement ...
Exploring Animal and Plant Cells Desired Outcomes
... S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, singlecelled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell ( ...
... S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, singlecelled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell ( ...
Vaginitis
... discharge. Women with classic vaginal itch who have a history of yeast vaginitis or are at risk (such as from recent antibiotic therapy) may reasonably treat themselves empirically without further testing, but empiric treatment should be avoided under other circumstances. Severe or recurrrent Candid ...
... discharge. Women with classic vaginal itch who have a history of yeast vaginitis or are at risk (such as from recent antibiotic therapy) may reasonably treat themselves empirically without further testing, but empiric treatment should be avoided under other circumstances. Severe or recurrrent Candid ...
Lab Exercises Part 3a: Poriferans and Cnidarians
... represented in Figure One. Although biologists identify approximately 35 extant phyla within the ...
... represented in Figure One. Although biologists identify approximately 35 extant phyla within the ...
The tetrazolium reduction method for assessing the viability of
... duplicate samples prepared according to our process and the standard process (Table I)..This suggests that cells are immersed essentially in DAPI solution rather than in oil and explains why formazan dissolution on the membrane is slow (Fig. 3). This also suggest that 0.1 pm pore size Millipore filt ...
... duplicate samples prepared according to our process and the standard process (Table I)..This suggests that cells are immersed essentially in DAPI solution rather than in oil and explains why formazan dissolution on the membrane is slow (Fig. 3). This also suggest that 0.1 pm pore size Millipore filt ...
The Muscular System - Chaparral Middle School
... Strengthens the skeletal muscles somewhat, but Click on most effective in the image to play a developing the heart movie ...
... Strengthens the skeletal muscles somewhat, but Click on most effective in the image to play a developing the heart movie ...
Revision summary 2. Movement, Molecules and Enzymes File
... Understand how the functioning of enzymes can be affected by changes in temperature All enzymes have an optimum temperature where they work fastest Low temperatures: less kinetic energy means fewer collisions between enzyme ...
... Understand how the functioning of enzymes can be affected by changes in temperature All enzymes have an optimum temperature where they work fastest Low temperatures: less kinetic energy means fewer collisions between enzyme ...
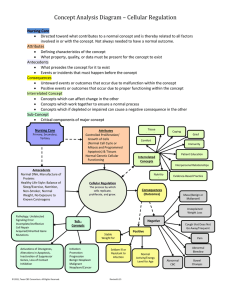
Concept Analysis Diagram * Cellular Regulation
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
Spermatogenesis overview
... types of spermatocytes that range in size from cells smaller than a red blood cell (preleptotene) to very large cells (pachytene) that occupy portions of every cross section of seminiferous tubules. Reduction-division is a biological mechanism by which a single germ cell can increase its DNA content ...
... types of spermatocytes that range in size from cells smaller than a red blood cell (preleptotene) to very large cells (pachytene) that occupy portions of every cross section of seminiferous tubules. Reduction-division is a biological mechanism by which a single germ cell can increase its DNA content ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.