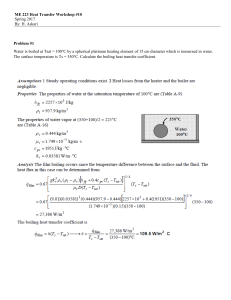
Heat Transfer - Madison County Schools
... liquid or gas (or plasma). The particles of a fluid take heat with them as they move. If you heat the air in one room, the air will heat the next room as the air flows from one room to the next. This is heating by convection. ...
... liquid or gas (or plasma). The particles of a fluid take heat with them as they move. If you heat the air in one room, the air will heat the next room as the air flows from one room to the next. This is heating by convection. ...
Name____________________________
... Convection: Transfer of heat within a liquid or gas. Conduction: Transfer of heat through matter by direct contact. Thermal Radiation: The energy radiated by solids, liquids, and gases in the form of electromagnetic waves as a result of their temperature. Deformation: Alteration of shape, as by pres ...
... Convection: Transfer of heat within a liquid or gas. Conduction: Transfer of heat through matter by direct contact. Thermal Radiation: The energy radiated by solids, liquids, and gases in the form of electromagnetic waves as a result of their temperature. Deformation: Alteration of shape, as by pres ...
Electronics Cooling MEP 635
... • The mechanism of heat transfer by radiation depends on the transfer of energy between surfaces by electromagnetic waves in the wave length interval between 0.1 to 100 μm. • Radiation heat transfer can travel in vacuum such as solar energy. • Radiation heat transfer depends on the surface propertie ...
... • The mechanism of heat transfer by radiation depends on the transfer of energy between surfaces by electromagnetic waves in the wave length interval between 0.1 to 100 μm. • Radiation heat transfer can travel in vacuum such as solar energy. • Radiation heat transfer depends on the surface propertie ...
Heating of the Atmosphere
... a liquid or gas As the cool air sinks it pushes the warm air up The cool air is eventually heated by the ground and again begins to rise This continual process of warm air rising and cool air sinking creates a circular movement of air called a convection ...
... a liquid or gas As the cool air sinks it pushes the warm air up The cool air is eventually heated by the ground and again begins to rise This continual process of warm air rising and cool air sinking creates a circular movement of air called a convection ...
Heat Transfer and Winds
... are caused by differences in air pressure. As air becomes less dense when it is heated, its air pressure decreases. Cool, dense air with a higher pressure forces the warm air to rise. ...
... are caused by differences in air pressure. As air becomes less dense when it is heated, its air pressure decreases. Cool, dense air with a higher pressure forces the warm air to rise. ...
8.5 CONVECTION By convection we mean a motion of material due
... By convection we mean a motion of material due to buoyancy forces resulting from temperature differences. cold hot material is less dense than cold material. It rises hot The theory of convection is too complicated to get into here, but we may still understand the basic ideas. The first one we need ...
... By convection we mean a motion of material due to buoyancy forces resulting from temperature differences. cold hot material is less dense than cold material. It rises hot The theory of convection is too complicated to get into here, but we may still understand the basic ideas. The first one we need ...
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN TURBULENT CONVECTION IN A BUNDLE
... Buoyant, turbulent convective heat transfer around cylindrical rods arranged in bundles is a technically relevant heat transfer configuration which finds application in steam generators, cooling of reactor core fuel assemblies and heat exchangers in general. Most of the research performed so far con ...
... Buoyant, turbulent convective heat transfer around cylindrical rods arranged in bundles is a technically relevant heat transfer configuration which finds application in steam generators, cooling of reactor core fuel assemblies and heat exchangers in general. Most of the research performed so far con ...
POWERPOINT SCIENCE
... temperature to a region of lower temperature, and acts to equalize temperature differences. It is also described as heat energy transferred from one material to another by direct contact. ...
... temperature to a region of lower temperature, and acts to equalize temperature differences. It is also described as heat energy transferred from one material to another by direct contact. ...
Layers of Earth Webquest - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... Tectonic Plates: http://www.sciencemonster.com/earth-science/layers-of-theearth.html –only use the first 3 pages!!! 1. What are tectonic plates? __________________________________________________________ 2. What is something else that you learned from pages 1-3 that helps you understand what is spec ...
... Tectonic Plates: http://www.sciencemonster.com/earth-science/layers-of-theearth.html –only use the first 3 pages!!! 1. What are tectonic plates? __________________________________________________________ 2. What is something else that you learned from pages 1-3 that helps you understand what is spec ...
Convection

Convection is the concerted, collective movement of groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. Diffusion of heat can take place in solids, but that is called heat conduction. Convection cannot be demonstrated by placing a heat source (e.g. a Bunsen burner) at the side of a glass full of a liquid, and observing the changes in temperature in the glass caused by the warmer ghost fluid moving into cooler areas.Convective heat transfer is one of the major types of heat transfer, and convection is also a major mode of mass transfer in fluids. Convective heat and mass transfer take place both by diffusion – the random Brownian motion of individual particles in the fluid – and by advection, in which matter or heat is transported by the larger-scale motion of currents in the fluid. In the context of heat and mass transfer, the term ""convection"" is used to refer to the sum of advective and diffusive transfer. In common use the term ""convection"" may refer loosely to heat transfer by convection, as opposed to mass transfer by convection, or the convection process in general. Sometimes ""convection"" is even used to refer specifically to ""free heat convection"" (natural heat convection) as opposed to forced heat convection. However, in mechanics the correct use of the word is the general sense, and different types of convection should be qualified for clarity.Convection can be qualified in terms of being natural, forced, gravitational, granular, or thermomagnetic. It may also be said to be due to combustion, capillary action, or Marangoni and Weissenberg effects. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be seen as clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics.