... R is a coefficient, called the gas constant. It does not depend on either p, r, or T. The gas constant depends only on the composition of gases that make up the air (every gas has its own gas constant). Since this composition (for dry air) is roughly constant throughout most of the atmosphere R of a ...
09-TempControls
... • Daytime: cloud cover reflects sunlight = colder • Nighttime: cloud cover traps energy = warmer ...
... • Daytime: cloud cover reflects sunlight = colder • Nighttime: cloud cover traps energy = warmer ...
Heat, Temperature and Atmospheric Circulations
... • Radiational Heating – absorption > emission • Radiational Cooling – absorption < emission • Radiational Equilibrium - absorption = emission (blackbody) • In equilibrium temperature is constant, though different parts may be different temperatures ...
... • Radiational Heating – absorption > emission • Radiational Cooling – absorption < emission • Radiational Equilibrium - absorption = emission (blackbody) • In equilibrium temperature is constant, though different parts may be different temperatures ...
Heat Transfer
... An engineer wishes to determine the specific heat of a new metal alloy. A 0.150-kg sample of the alloy is heated to 540°C. It is then quickly placed in 0.400 kg of water at 10.0°C, which is contained in a 0.200-kg aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket si ...
... An engineer wishes to determine the specific heat of a new metal alloy. A 0.150-kg sample of the alloy is heated to 540°C. It is then quickly placed in 0.400 kg of water at 10.0°C, which is contained in a 0.200-kg aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket si ...
cfd investigation of helical coil heat exchanger abstract
... chemical reactors because they can accommodate a large heat transfer area in a small space, with high heat transfer coefficients. This project deals with the analysis of the helical coiled heat exchanger with various correlations given by different papers for specific conditions. Although various co ...
... chemical reactors because they can accommodate a large heat transfer area in a small space, with high heat transfer coefficients. This project deals with the analysis of the helical coiled heat exchanger with various correlations given by different papers for specific conditions. Although various co ...
Heat Transfer - cloudfront.net
... When each glob gets to the top, it falls back down. • What do you think is happening? • Is this a method of heat transfer? © Copyright 2015 – All rights reserved. www.cpalms.org ...
... When each glob gets to the top, it falls back down. • What do you think is happening? • Is this a method of heat transfer? © Copyright 2015 – All rights reserved. www.cpalms.org ...
Convective heat transfer
... saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an external driving energy source to the contrary, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becoming more uniform. In conduction, the heat flow is within and through th ...
... saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an external driving energy source to the contrary, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becoming more uniform. In conduction, the heat flow is within and through th ...
ph607-15-test2ans
... ionised and they are hence unstable to convection. The structure of solar-type stars then consists of a hot radiative core, at the centre of which the nuclear energy is produced, surrounded by a cool convective envelope. The envelope is shallow for stars near the upper-mass limit but becomes gradual ...
... ionised and they are hence unstable to convection. The structure of solar-type stars then consists of a hot radiative core, at the centre of which the nuclear energy is produced, surrounded by a cool convective envelope. The envelope is shallow for stars near the upper-mass limit but becomes gradual ...
Atmospheric circulation
... • Atmosphere is thin, compared to size of the Earth.! • Different amounts of solar energy are absorbed at different latitudes (more in tropics than at poles).! ...
... • Atmosphere is thin, compared to size of the Earth.! • Different amounts of solar energy are absorbed at different latitudes (more in tropics than at poles).! ...
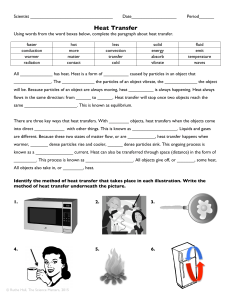
Heat Transfer - Granville County Public Schools
... same _____________________. This is known as equilibrium. There are three key ways that heat transfers. With ________ objects, heat transfers when the objects come into direct ____________ with other things. This is known as __________________. Liquids and gases are different. Because these two stat ...
... same _____________________. This is known as equilibrium. There are three key ways that heat transfers. With ________ objects, heat transfers when the objects come into direct ____________ with other things. This is known as __________________. Liquids and gases are different. Because these two stat ...
Convection

Convection is the concerted, collective movement of groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. Diffusion of heat can take place in solids, but that is called heat conduction. Convection cannot be demonstrated by placing a heat source (e.g. a Bunsen burner) at the side of a glass full of a liquid, and observing the changes in temperature in the glass caused by the warmer ghost fluid moving into cooler areas.Convective heat transfer is one of the major types of heat transfer, and convection is also a major mode of mass transfer in fluids. Convective heat and mass transfer take place both by diffusion – the random Brownian motion of individual particles in the fluid – and by advection, in which matter or heat is transported by the larger-scale motion of currents in the fluid. In the context of heat and mass transfer, the term ""convection"" is used to refer to the sum of advective and diffusive transfer. In common use the term ""convection"" may refer loosely to heat transfer by convection, as opposed to mass transfer by convection, or the convection process in general. Sometimes ""convection"" is even used to refer specifically to ""free heat convection"" (natural heat convection) as opposed to forced heat convection. However, in mechanics the correct use of the word is the general sense, and different types of convection should be qualified for clarity.Convection can be qualified in terms of being natural, forced, gravitational, granular, or thermomagnetic. It may also be said to be due to combustion, capillary action, or Marangoni and Weissenberg effects. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be seen as clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics.









![L 17 - Thermodynamics [2] Thermal Expansion Coefficients of linear](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014728078_1-e88e92f3857e030978e2ede6a9072797-300x300.png)