The Body in Motion
... Centrifugal force separates extract Pellet – heavier cell organelles Supernatant – liquid poured off ...
... Centrifugal force separates extract Pellet – heavier cell organelles Supernatant – liquid poured off ...
Microscope and Cells
... with light microscopes. Most of their size ranges from 1-100 µm. The cells are small, because they have to be able to carry materials from one side of the cell to the next in a short period of time. Cells must have a large enough surface area to be able to take in nutrients and oxygen and release wa ...
... with light microscopes. Most of their size ranges from 1-100 µm. The cells are small, because they have to be able to carry materials from one side of the cell to the next in a short period of time. Cells must have a large enough surface area to be able to take in nutrients and oxygen and release wa ...
Course Specifications
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
File
... Randomly located throughout the cell, this organelle is often called the cell’s garbage disposal because it digests worn out organelles, food molecules, viruses and bacteria ...
... Randomly located throughout the cell, this organelle is often called the cell’s garbage disposal because it digests worn out organelles, food molecules, viruses and bacteria ...
Cellular Functions
... By slide #: 2- carbohydrates, 3- energy, 4-lipids, 5proteins, 6-nucleic acids, 7- many of the chemical reactions take place in water, 8chains of carbon atoms, 9-chemical energy, 10photosynthesis, 11- glucose, 12-cellular respiration, 13-mitochondria, 14-fermentation, 15-concentration, 16-diffusion, ...
... By slide #: 2- carbohydrates, 3- energy, 4-lipids, 5proteins, 6-nucleic acids, 7- many of the chemical reactions take place in water, 8chains of carbon atoms, 9-chemical energy, 10photosynthesis, 11- glucose, 12-cellular respiration, 13-mitochondria, 14-fermentation, 15-concentration, 16-diffusion, ...
NVC3_5 - Napa Valley College
... threat to the cell • Containing waste products • Maintaining internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor within the cell • Maintaining an acidic internal pH • Containing small molecules (anthocyanins for color) • Exporting unwanted substances from the cell • Allows plants to support structures such as l ...
... threat to the cell • Containing waste products • Maintaining internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor within the cell • Maintaining an acidic internal pH • Containing small molecules (anthocyanins for color) • Exporting unwanted substances from the cell • Allows plants to support structures such as l ...
Mitosis - edl.io
... 2) Pick a stage of the cell cycle. Name 2 things that happen in this stage. 3) Review the picture slides. Identify the stages based on the ...
... 2) Pick a stage of the cell cycle. Name 2 things that happen in this stage. 3) Review the picture slides. Identify the stages based on the ...
1. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through a. a
... d. the nucleus. e. the plasma membrane. 2. Bacterial cell are prokaryotic; in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell they would a. be smaller. b. have a smaller nucleus. c. lack a plasma membrane. d. have fewer internal membranous compartments. e. have a greater variety of organelles. 3. The maximu ...
... d. the nucleus. e. the plasma membrane. 2. Bacterial cell are prokaryotic; in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell they would a. be smaller. b. have a smaller nucleus. c. lack a plasma membrane. d. have fewer internal membranous compartments. e. have a greater variety of organelles. 3. The maximu ...
CELLS
... Every living thing is made of cells Cells complete different functions in different parts of organisms. Muscle cells help us move Fat cells store energy ...
... Every living thing is made of cells Cells complete different functions in different parts of organisms. Muscle cells help us move Fat cells store energy ...
John MacDonald: Chemistry & Biochemistry
... Characterizing Photoswitches to Mimic Nerve Cell Repolarization It has been shown that a quaternary ammonium structure (nitrogen bonded to four carbons), such as tetra-ethyl ammonium iodide, can block a potassium channel and therefore inhibit the depolarization of a nerve cell. By attaching this qua ...
... Characterizing Photoswitches to Mimic Nerve Cell Repolarization It has been shown that a quaternary ammonium structure (nitrogen bonded to four carbons), such as tetra-ethyl ammonium iodide, can block a potassium channel and therefore inhibit the depolarization of a nerve cell. By attaching this qua ...
THE CELL – Chapter 3
... b. hypertonic-when the solution has less water than the cell-water leaves the cell and the cell shrinks c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movemen ...
... b. hypertonic-when the solution has less water than the cell-water leaves the cell and the cell shrinks c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movemen ...
Unit 1 Post Test: Structure and Function of Cells
... The cellular process in which materials move across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to area of low concentration is called A. ...
... The cellular process in which materials move across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to area of low concentration is called A. ...
The Cell Cycle and Development
... implying that the DNA damage checkpoint is activated at this stage.1 The early mouse embryo also receives some attention, with focus on the cell cycle transitions undergone during the first mitotic cleavages. Probably the most striking example of the degree to which the cell cycle can be altered to ...
... implying that the DNA damage checkpoint is activated at this stage.1 The early mouse embryo also receives some attention, with focus on the cell cycle transitions undergone during the first mitotic cleavages. Probably the most striking example of the degree to which the cell cycle can be altered to ...
ExamView Pro - Final Exam review sheet #3.tst
... d. ribosomes. ____ 13. When compared to a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell a. has more types of organelles. b. has DNA that is linear rather than circular. c. stores its DNA in a nucleus rather than in the cytoplasm. d. All of the above ____ 14. Which of the following best describes the character ...
... d. ribosomes. ____ 13. When compared to a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell a. has more types of organelles. b. has DNA that is linear rather than circular. c. stores its DNA in a nucleus rather than in the cytoplasm. d. All of the above ____ 14. Which of the following best describes the character ...
Cells
... the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is not surrounded by a membrane, but sits in the nucleus. The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
... the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is not surrounded by a membrane, but sits in the nucleus. The nucleolus makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
Question Report
... that becomes activated by a receptor protein C. a membrane bound enzyme that converts ATP to ...
... that becomes activated by a receptor protein C. a membrane bound enzyme that converts ATP to ...
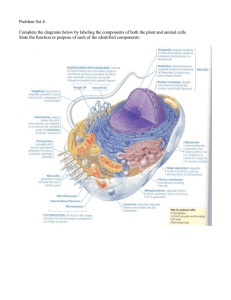
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
EdibleCellLessonPlan
... 1. The teacher will ask 1 student per group to fill out a chart on the board relating to each cell and the organelles within. 2. The teacher will ask guiding questions: a. If you had to separate these 4 types of cells into 2 groups, what would the 2 groups be? b. Which organelles are unique to each ...
... 1. The teacher will ask 1 student per group to fill out a chart on the board relating to each cell and the organelles within. 2. The teacher will ask guiding questions: a. If you had to separate these 4 types of cells into 2 groups, what would the 2 groups be? b. Which organelles are unique to each ...
Section: 2.4 Name:
... with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell. Color and label the vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infol ...
... with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell. Color and label the vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infol ...
Cell Analogy Project : DUE___________________ Introduction
... Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some similar parts and some parts that a ...
... Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some similar parts and some parts that a ...
PDF
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.