Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
Cells, Mitosis-Meiosis, Photosynthesis
... down and later reforms. The chromosomes are also sorted and separated to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. • The second major step is cytokinesis. As in prokaryotic cells, during this step the cytoplasm divides and two daughter cells form. The Cell Cycle Cell div ...
... down and later reforms. The chromosomes are also sorted and separated to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. • The second major step is cytokinesis. As in prokaryotic cells, during this step the cytoplasm divides and two daughter cells form. The Cell Cycle Cell div ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... Eukaryotic cells are generally more complex than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are generally quite a bit bigger than prokaryotic cells. ...
... Eukaryotic cells are generally more complex than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are generally quite a bit bigger than prokaryotic cells. ...
Lecture 4 - A tour through the cell
... organized form of DNA in the nucleus = chromatin described as “beads on a string” model DNA helix is wrapped around complexes of proteins called histones the histone-DNA complex is called a nucleosome described by Roger Kornberg – Nobel Prize 2006 ...
... organized form of DNA in the nucleus = chromatin described as “beads on a string” model DNA helix is wrapped around complexes of proteins called histones the histone-DNA complex is called a nucleosome described by Roger Kornberg – Nobel Prize 2006 ...
Chapter 4: The Characteristics of Prokaryotic and
... Flagella, Cilia, Pseudopodia(Amoeboid Movement), Cell Wall ...
... Flagella, Cilia, Pseudopodia(Amoeboid Movement), Cell Wall ...
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
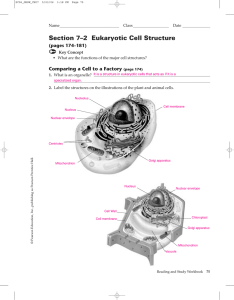
... chromatin that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next. ...
... chromatin that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next. ...
Chapter 7 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... Two basic cell types 1. Prokaryotes: Cells that do not contain any membrane bound organelles. 2. Eukaryotes: Contains a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Can be one cell or multicellular. ...
... Two basic cell types 1. Prokaryotes: Cells that do not contain any membrane bound organelles. 2. Eukaryotes: Contains a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Can be one cell or multicellular. ...
Cells Cell Theory Cell size is limited Surface area Surface area
... Series of membranes throughout the cytoplasm Divides cell into compartments where different cellular functions occur One of the fundamental distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes ...
... Series of membranes throughout the cytoplasm Divides cell into compartments where different cellular functions occur One of the fundamental distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes ...
Use ALL notes, lab, hand-outs to prepare! This is only a guide, do
... 20. Be able to draw and label the 2 energy organelles in detail. 21. Explain why Cell Theory still very important to biology today. 22. Be able to describe the types of movement for single celled organisms. 23. Describe the fluid mosaic model. 24. Know the components of a solution and give an exampl ...
... 20. Be able to draw and label the 2 energy organelles in detail. 21. Explain why Cell Theory still very important to biology today. 22. Be able to describe the types of movement for single celled organisms. 23. Describe the fluid mosaic model. 24. Know the components of a solution and give an exampl ...
Cells are the basic unit of life.
... sunlight to produce sugar (food) and O2 as a waste product. ...
... sunlight to produce sugar (food) and O2 as a waste product. ...
Lesson Plan
... Model other ways of expressing the similarities and differences between two objects. It is really common in our daily life that we always have to compare things. We therefore have to learn more ways of expressing similarities and differences between two objects. ...
... Model other ways of expressing the similarities and differences between two objects. It is really common in our daily life that we always have to compare things. We therefore have to learn more ways of expressing similarities and differences between two objects. ...
Cell Parts
... • Small, roughly spherical organelles that are responsible for making proteins. • Ribosomes do not have a membrane • Some are found freely floating in the cytosol • Others are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
... • Small, roughly spherical organelles that are responsible for making proteins. • Ribosomes do not have a membrane • Some are found freely floating in the cytosol • Others are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
Keystone Study Points Answer Key
... The cells of multicellular organisms become specialized for particular tasks and communicate with one another to maintain homeostasis ...
... The cells of multicellular organisms become specialized for particular tasks and communicate with one another to maintain homeostasis ...
Chp 7 Study Guide File
... 36. Label the diagrams below (isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic) …hint: the dots are the solute & they will not pass through the membrane. ...
... 36. Label the diagrams below (isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic) …hint: the dots are the solute & they will not pass through the membrane. ...
Chp 7 Study Guide File
... 23. How do you carry a microscope? 24. What are three practices you use when putting away a microscope? A. B. C. 25. What happens to magnification when power is increased? 26. What happens to the brightness of the image when magnification is increased? 27. What happens to resolution (image sharpnes ...
... 23. How do you carry a microscope? 24. What are three practices you use when putting away a microscope? A. B. C. 25. What happens to magnification when power is increased? 26. What happens to the brightness of the image when magnification is increased? 27. What happens to resolution (image sharpnes ...
Unit 6 Test Review
... 8. The movement of glucose into cells is achieved by (what process)__________________________. 9. A contractile vacuole can be found in ________________ and used for ____________________ excess ________________. 10. The movement of substances FROM an area of LOW concentration TO an area of HIGH conc ...
... 8. The movement of glucose into cells is achieved by (what process)__________________________. 9. A contractile vacuole can be found in ________________ and used for ____________________ excess ________________. 10. The movement of substances FROM an area of LOW concentration TO an area of HIGH conc ...
BIOL 141: Foundations of Biology: Cells, Energy and
... A. Identify the basic properties of enzymes and describe their function and regulation. B. Explain the fundamentals of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. C. Describe the role of enzymes in the processes of photosynthesis and in cellular energy harvesting pathways. III. Describe the fundamental ...
... A. Identify the basic properties of enzymes and describe their function and regulation. B. Explain the fundamentals of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. C. Describe the role of enzymes in the processes of photosynthesis and in cellular energy harvesting pathways. III. Describe the fundamental ...
1 Supplementary materials and methods Reagents and Western
... buffer with EDTA/ß-mercaptoethanol. Probes were subjected to SDS-PAGE and proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were blocked with 2.5% BSA. Polyclonal anti-YB-1 antibodies raised with recombinant full-length YB-1 protein (kind gift by Capowski and Malter, University of Wisconsi ...
... buffer with EDTA/ß-mercaptoethanol. Probes were subjected to SDS-PAGE and proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were blocked with 2.5% BSA. Polyclonal anti-YB-1 antibodies raised with recombinant full-length YB-1 protein (kind gift by Capowski and Malter, University of Wisconsi ...
PDF
... downregulates Foxj1, a transcription factor that is required for the biosynthesis of motile cilia. KV-specific expression of foxj1a, they report, requires the presence of putative Lef1/Tcf binding sites in the foxj1a enhancer region, which suggests that Wnt signalling activates fox1ja transcription ...
... downregulates Foxj1, a transcription factor that is required for the biosynthesis of motile cilia. KV-specific expression of foxj1a, they report, requires the presence of putative Lef1/Tcf binding sites in the foxj1a enhancer region, which suggests that Wnt signalling activates fox1ja transcription ...
Cells - nimitz126
... cells share this outer boundary This membrane encloses and separates the interior of the cell – the cytoplasm The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves the cell ...
... cells share this outer boundary This membrane encloses and separates the interior of the cell – the cytoplasm The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves the cell ...
4-1: What are cells
... 6. Relate: As microscopes improved, there were more discoveries about cells 7. Apply: Cells do carry out respiration. They break down a simple sugar called glucose to get energy. 8. Apply: New cells could not be produced by the cork that Robert Hooke observed because those cells were no longer livin ...
... 6. Relate: As microscopes improved, there were more discoveries about cells 7. Apply: Cells do carry out respiration. They break down a simple sugar called glucose to get energy. 8. Apply: New cells could not be produced by the cork that Robert Hooke observed because those cells were no longer livin ...
PDF
... downregulates Foxj1, a transcription factor that is required for the biosynthesis of motile cilia. KV-specific expression of foxj1a, they report, requires the presence of putative Lef1/Tcf binding sites in the foxj1a enhancer region, which suggests that Wnt signalling activates fox1ja transcription ...
... downregulates Foxj1, a transcription factor that is required for the biosynthesis of motile cilia. KV-specific expression of foxj1a, they report, requires the presence of putative Lef1/Tcf binding sites in the foxj1a enhancer region, which suggests that Wnt signalling activates fox1ja transcription ...
Ch. 19 GN - Jamestown Public Schools
... - Chemoautotrophs - _________________ that can perform ___________________ o Like photoautotrophs, they make _________ carbon molecules from _______ dioxide o However, they do not require ________ as a __________ source o They use ___________ directly from ___________ reactions involving __________, ...
... - Chemoautotrophs - _________________ that can perform ___________________ o Like photoautotrophs, they make _________ carbon molecules from _______ dioxide o However, they do not require ________ as a __________ source o They use ___________ directly from ___________ reactions involving __________, ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.