![Anti-GABA antibody [5A9] ab86186 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008296205_1-9b8206993c446f240db0ef9ab99a7030-300x300.png)
Anti-GABA antibody [5A9] ab86186 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 1 Image
... Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab86186 in the following tested applications. The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab86186 in the following tested applications. The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
Aug31-Sept11
... using Frayer Model Finish Characteristics of Living Things HW assignment that is ...
... using Frayer Model Finish Characteristics of Living Things HW assignment that is ...
Osmosis Diffusion Notes
... transport) and do not use energy to go with concentration (passive transport) 2. Receptor Protein- receives chemical signals from the blood and communicates them to the inside of the cell. 3. Glycoprotein + Carbohydrate- identifies the cell so it will not be destroyed. ...
... transport) and do not use energy to go with concentration (passive transport) 2. Receptor Protein- receives chemical signals from the blood and communicates them to the inside of the cell. 3. Glycoprotein + Carbohydrate- identifies the cell so it will not be destroyed. ...
CH 3 Part 2 - Catherine Huff`s Site
... •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. •Are assembled ...
... •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. •Are assembled ...
SIOP Lesson Plan
... 4. Students will use a spoon to dig a hole into the cytoplasm. Just pushing the jello will cause it to crack and come apart. Place the large marshmallow into the animal cell and the small marshmallow into the plant cell. 5 Using your spoon to make spaces and your Venn diagram as a guide place your o ...
... 4. Students will use a spoon to dig a hole into the cytoplasm. Just pushing the jello will cause it to crack and come apart. Place the large marshmallow into the animal cell and the small marshmallow into the plant cell. 5 Using your spoon to make spaces and your Venn diagram as a guide place your o ...
CH # 10-4
... Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
... Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
Document
... antifibronectin antibody, or with preimmune serum as a control, prior to gastrulation. Cell movements were then monitored photographically. ...
... antifibronectin antibody, or with preimmune serum as a control, prior to gastrulation. Cell movements were then monitored photographically. ...
CELLS: The Living Units
... Facilitated diffusion 2. Carrier Proteins • Are integral transmembrane proteins • Show specificity for certain polar molecules like sugars and amino acids • Molecules too large to pass so they are carried through by transport receptor carriers ...
... Facilitated diffusion 2. Carrier Proteins • Are integral transmembrane proteins • Show specificity for certain polar molecules like sugars and amino acids • Molecules too large to pass so they are carried through by transport receptor carriers ...
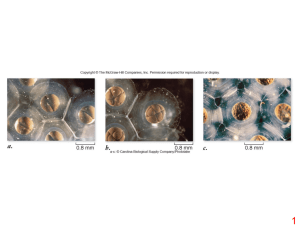
Characteristics of normal cell division Primary culture of normal cells
... 3. Solid tumor in situ: cells are even more malformed and de-differentiated. Growth extends from original mass into the tissue. 4. Malignancy (cancer): cells detach and penetrate basal lamina into other tissues. May enter lymphatic or circulatory system and reach other organs to start new tumors. ...
... 3. Solid tumor in situ: cells are even more malformed and de-differentiated. Growth extends from original mass into the tissue. 4. Malignancy (cancer): cells detach and penetrate basal lamina into other tissues. May enter lymphatic or circulatory system and reach other organs to start new tumors. ...
1.3 Diffusion, Osmosis, and the Cell Membrane • Diffusion is the
... • One way that substances can move through the cell membrane is by diffusion. • When the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same, it is called equilibrium. ...
... • One way that substances can move through the cell membrane is by diffusion. • When the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same, it is called equilibrium. ...
chapter 10 section 4 notes
... Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
... Adult cells generally reach a point at which their differentiation is complete and they can no longer become other types of cells. ...
Discovering Cells
... center of the cell and directs all of the cell’s activities. The nucleus is protected by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. ...
... center of the cell and directs all of the cell’s activities. The nucleus is protected by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. ...
Cell Theory, Structure and Transport Chapter 7 PAP Guided Reading
... The nucleus contains DNA and controls the activity of a cell. Organelles That Store, Clean Up, and Support These structures include: vacuoles: membrane-enclosed saclike structures that store water, salts, and organic molecules lysosomes: organelles filled with enzymes that break down large mol ...
... The nucleus contains DNA and controls the activity of a cell. Organelles That Store, Clean Up, and Support These structures include: vacuoles: membrane-enclosed saclike structures that store water, salts, and organic molecules lysosomes: organelles filled with enzymes that break down large mol ...
Meristematic tissue/meristems
... of shells and peach pits 2. Fibers- used to manufacture textile goods, ropes, string, canvas ...
... of shells and peach pits 2. Fibers- used to manufacture textile goods, ropes, string, canvas ...
General Biology – Chapter 5 Notes on Active Transport Systems
... facilitated diffusion in conjunction with a carrier protein. The difference is that Sodium and potassium move against the concentration gradients so that for every three sodium ions being pump outside the cell, there are two potassium ions being pumped into the cell. Because these ions are being pum ...
... facilitated diffusion in conjunction with a carrier protein. The difference is that Sodium and potassium move against the concentration gradients so that for every three sodium ions being pump outside the cell, there are two potassium ions being pumped into the cell. Because these ions are being pum ...
The cytoskeleton The cell surface and junctions
... Young cells first construct thin primary walls. Stronger secondary walls are added to the inside of the primary wall when growth ceases. A sticky middle lamella cements adjacent cells together. The walls do not isolate the cells: the cytoplasm of one cell is continuous with the cytoplasm of its neig ...
... Young cells first construct thin primary walls. Stronger secondary walls are added to the inside of the primary wall when growth ceases. A sticky middle lamella cements adjacent cells together. The walls do not isolate the cells: the cytoplasm of one cell is continuous with the cytoplasm of its neig ...
No Slide Title
... Channels may be open all the time, or gated (closed randomly or as “directed”) How might channels be regulated? Name one stimulus to “open” . ...
... Channels may be open all the time, or gated (closed randomly or as “directed”) How might channels be regulated? Name one stimulus to “open” . ...
How things get in and out of a Cell HOMEOSTASIS
... - usually moves stuff in or out AGAINST the diffusion gradient (a.k.a. - the concentration gradient). * The diffusion gradient refers to the different levels of concentration inside and outside of the cell ...
... - usually moves stuff in or out AGAINST the diffusion gradient (a.k.a. - the concentration gradient). * The diffusion gradient refers to the different levels of concentration inside and outside of the cell ...
Lecture 6 eukaryote
... • Delivery of materials to be digested by route that does not involve endocytosis ...
... • Delivery of materials to be digested by route that does not involve endocytosis ...
File
... 4) A mitochondrion contains two distinct internal compartments so that the reactions of cellular respiration occur in separate locations. Explain the structure and function of the following mitochondrial components: a) cristae: ...
... 4) A mitochondrion contains two distinct internal compartments so that the reactions of cellular respiration occur in separate locations. Explain the structure and function of the following mitochondrial components: a) cristae: ...
The impact of a limited supply of stem cell lines on
... cells lines, one of which is whether an embryo is considered a human. The alternative methods for deriving stem cell lines that have been uncovered are discussed along with how they have contributed to and the impact they have had on recent research efforts. In conclusion, alternative methods to ove ...
... cells lines, one of which is whether an embryo is considered a human. The alternative methods for deriving stem cell lines that have been uncovered are discussed along with how they have contributed to and the impact they have had on recent research efforts. In conclusion, alternative methods to ove ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • Diffusion depends on random particle movements so substances diffuse across membranes without using energy • Equilibrium- when the concentration of the solute is the same throughout a system ...
... • Diffusion depends on random particle movements so substances diffuse across membranes without using energy • Equilibrium- when the concentration of the solute is the same throughout a system ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.