Interactive Review CHAPTER REVIEW Reviewing
... Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across a membrane. Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against a concentration gradient. The processes of endocytosis and exocytosis move s ...
... Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across a membrane. Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against a concentration gradient. The processes of endocytosis and exocytosis move s ...
Cell Organelles
... Living things get energy in one of two ways: from food or from the sun. Mitochondria: Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Enclosed in two membranes They are inherited ...
... Living things get energy in one of two ways: from food or from the sun. Mitochondria: Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Enclosed in two membranes They are inherited ...
make more cells
... Proteins do all the work! one of the major job of cells is to make proteins, ...
... Proteins do all the work! one of the major job of cells is to make proteins, ...
Types of Transport Passive Transport Active Transport diffusion
... Diffusion can be explained by the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration . Diffusion rates increase with increasing temperature, pressure and concentration. When molecules are finally distributed equally, then equilibrium is reached. ...
... Diffusion can be explained by the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration . Diffusion rates increase with increasing temperature, pressure and concentration. When molecules are finally distributed equally, then equilibrium is reached. ...
Chapter 5
... 1. A common form of anchoring junction, desmosomes, are points of attachment between some animal cells a) Desmosomes hold cells subject to mechanical stresses together b) Desmosomes are composed of intermediate filaments, which span the gap between two cells B. Adhering junctions cement cells togeth ...
... 1. A common form of anchoring junction, desmosomes, are points of attachment between some animal cells a) Desmosomes hold cells subject to mechanical stresses together b) Desmosomes are composed of intermediate filaments, which span the gap between two cells B. Adhering junctions cement cells togeth ...
Implantation
... sperm capacitation which render them capable of fertilization in vivo does not occur until they are removed from the seminal plasma after ejaculation. Those sperm that do penetrate the cervical os are directed along channels of lower viscosity mucus into the cervical crypts where they are stored fo ...
... sperm capacitation which render them capable of fertilization in vivo does not occur until they are removed from the seminal plasma after ejaculation. Those sperm that do penetrate the cervical os are directed along channels of lower viscosity mucus into the cervical crypts where they are stored fo ...
Sodium-Potassium pumps
... resting potential, assists transport and regulates cellular volume. In order to maintain the cell’s resting potential, cells must keep a low concentration of ↓ sodium ions & high levels of ↑ potassium ions within the cell. ...
... resting potential, assists transport and regulates cellular volume. In order to maintain the cell’s resting potential, cells must keep a low concentration of ↓ sodium ions & high levels of ↑ potassium ions within the cell. ...
Link
... fast growing cancer cells, and CSCs, due to their stem cell-like properties, divide more slowly.2 After surviving treatment, CSCs are able to regenerate the original tumour and/or produce invasive cancer cells that are able to colonise distant organs. For these reasons, CSCs are widely thought to be ...
... fast growing cancer cells, and CSCs, due to their stem cell-like properties, divide more slowly.2 After surviving treatment, CSCs are able to regenerate the original tumour and/or produce invasive cancer cells that are able to colonise distant organs. For these reasons, CSCs are widely thought to be ...
CHAPTER SUMMARY
... 3. Plays an important role during cell division 4. The general location of the centrosome is identified by the centrioles D. Cell extensions 1. Cytoskeleton forms projections that extend the plasma membrane outward to form tiny, fingerlike processes 2. There are three types of these processes; each ...
... 3. Plays an important role during cell division 4. The general location of the centrosome is identified by the centrioles D. Cell extensions 1. Cytoskeleton forms projections that extend the plasma membrane outward to form tiny, fingerlike processes 2. There are three types of these processes; each ...
Knowles_Evans_NCR3s_Studentship
... can replace a major proportion of such animal use. Studies of other tissue types demonstrate that normal and tumour-derived human cells can be maintained for long periods as three-dimensional organoids that are suitable for rapid in vitro drug screening and can be modified to provide paired isogenic ...
... can replace a major proportion of such animal use. Studies of other tissue types demonstrate that normal and tumour-derived human cells can be maintained for long periods as three-dimensional organoids that are suitable for rapid in vitro drug screening and can be modified to provide paired isogenic ...
document
... 6. Bundles of skeletal muscle cells are called ________________. 7. The connective tissue which immediately surrounds a muscle is called _______________ and the connective tissue around the fascicles is called ________________. ...
... 6. Bundles of skeletal muscle cells are called ________________. 7. The connective tissue which immediately surrounds a muscle is called _______________ and the connective tissue around the fascicles is called ________________. ...
Biology, 8th Edition
... As small as it is, the micrometer is actually too large to measure most cell components. For this purpose biologists use the nanometer (nm), which is 1/1,000,000,000 (one billionth) of a meter, or 1/1000 of a micrometer. To mentally move down to the world of the nanometer, recall that a millimeter i ...
... As small as it is, the micrometer is actually too large to measure most cell components. For this purpose biologists use the nanometer (nm), which is 1/1,000,000,000 (one billionth) of a meter, or 1/1000 of a micrometer. To mentally move down to the world of the nanometer, recall that a millimeter i ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... iii. Transport Protein/Protein Transport: structure that allows substances to go in and out of the cell ***Selectively permeable: allows certain molecules to pass in or out of the cell iv. Receptor Molecules: structures on the outer surface of the cell membrane; specific in shape and function; recei ...
... iii. Transport Protein/Protein Transport: structure that allows substances to go in and out of the cell ***Selectively permeable: allows certain molecules to pass in or out of the cell iv. Receptor Molecules: structures on the outer surface of the cell membrane; specific in shape and function; recei ...
Read each statement carefully
... Level I Directions: Read each statement carefully. Using your textbook, decide if the statement is true or false. If the statement is true, place a checkmark in the first blank and the page number in the second blank. If the statement is false, put a “0” in the first blank and the page number un the ...
... Level I Directions: Read each statement carefully. Using your textbook, decide if the statement is true or false. If the statement is true, place a checkmark in the first blank and the page number in the second blank. If the statement is false, put a “0” in the first blank and the page number un the ...
Read each statement carefully
... Level I Directions: Read each statement carefully. Using your textbook, decide if the statement is true or false. If the statement is true, place a checkmark in the first blank and the page number in the second blank. If the statement is false, put a “0” in the first blank and the page number un the ...
... Level I Directions: Read each statement carefully. Using your textbook, decide if the statement is true or false. If the statement is true, place a checkmark in the first blank and the page number in the second blank. If the statement is false, put a “0” in the first blank and the page number un the ...
PDF Steady State of Living Cells and Donnan Equilibrium
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
... The previous PDF handout points out that since the Nernst potential, Vi Nernst ≠ ΔV is ...
Osmosis and diffusion webquest
... Now click on “Add salt” and observe what happens. After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
... Now click on “Add salt” and observe what happens. After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
Chapter 7 Section 7_3 Cell Transport
... • If a substance is in higher concentration on either side of cell membrane, the particles will diffuse to the other side where they are less concentrated. • Once the concentration of a substance is equal on both side of the cell membrane, equilibrium is reached. ...
... • If a substance is in higher concentration on either side of cell membrane, the particles will diffuse to the other side where they are less concentrated. • Once the concentration of a substance is equal on both side of the cell membrane, equilibrium is reached. ...
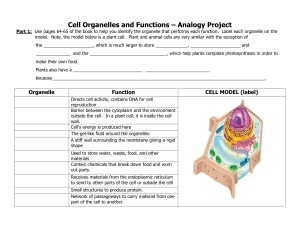
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
investigation of the in-vitro metabolites of etodolac using
... Nanak Institute of Research and Development, G. N. Khalsa College, Matunga, Mumbai-400019, Maharashtra, India. (2) Shimadzu Analytical (India) Pvt. Ltd., 1 A/B Rushabh Chambers, Makwana Road, Marol, Andheri (E), Mumbai-400059, Maharashtra, India. ...
... Nanak Institute of Research and Development, G. N. Khalsa College, Matunga, Mumbai-400019, Maharashtra, India. (2) Shimadzu Analytical (India) Pvt. Ltd., 1 A/B Rushabh Chambers, Makwana Road, Marol, Andheri (E), Mumbai-400059, Maharashtra, India. ...
2.-6 Lipid Bilayer of the Cell Membrane
... Generalized Cell Structures • Plasma membrane = cell membrane • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific ...
... Generalized Cell Structures • Plasma membrane = cell membrane • Nucleus = genetic material of cell • Cytoplasm = everything between the membrane and the nucleus – cytosol = intracellular fluid – organelles = subcellular structures with specific ...
Diffusion/Osmosis/Homeostasis
... 14. What is osmotic pressure? 15. Which way water will move in each of the following situations: a. Salt inside the cell 65% and outside the cell 40%. ___________________________________ b. Sugar inside the cell 27% and outside 80%. ...
... 14. What is osmotic pressure? 15. Which way water will move in each of the following situations: a. Salt inside the cell 65% and outside the cell 40%. ___________________________________ b. Sugar inside the cell 27% and outside 80%. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.