Since your team has the advantage of having THREE people to pull
... Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a bacterial cell. The three primary shapes in bacteria are coccus (spherical), bacillus (rodshaped) and spirillum (spiral). Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definit ...
... Composed of peptidoglycan (polysaccharides + protein), the cell wall maintains the overall shape of a bacterial cell. The three primary shapes in bacteria are coccus (spherical), bacillus (rodshaped) and spirillum (spiral). Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definit ...
Slide 1
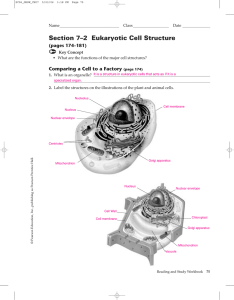
... Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis, made up of rRNA Golgi apparatus – folded membranes that store and transports enzymes and hormones, also produces the cell wall in plants Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Sit ...
... Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis, made up of rRNA Golgi apparatus – folded membranes that store and transports enzymes and hormones, also produces the cell wall in plants Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Sit ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a ...
Cell City Analogy Directions: Match the important parts of the city
... 2. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible envelope that surrounds the cell. It allows the cell to change shape and controls what goes into and out of the cell. What does the cell membrane resembl ...
... 2. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible envelope that surrounds the cell. It allows the cell to change shape and controls what goes into and out of the cell. What does the cell membrane resembl ...
Plant Structure and Function
... We shall begin the study of this unit by reviewing the structure of the different parts of a plant cell and how the structures of those parts are suited to the function they perform. As we have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function. A good understanding of cell struct ...
... We shall begin the study of this unit by reviewing the structure of the different parts of a plant cell and how the structures of those parts are suited to the function they perform. As we have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function. A good understanding of cell struct ...
Basic Biological SA Questions
... cell structure, of even the simplest kind. There was no membrane, no nucleus, and no ribosomes. They determined that a virus was nothing more than a strand of nucleic acid, DNA or RNA, protected by a protein shell. Scientists also believed that viruses lacked the mechanisms necessary for metabolic f ...
... cell structure, of even the simplest kind. There was no membrane, no nucleus, and no ribosomes. They determined that a virus was nothing more than a strand of nucleic acid, DNA or RNA, protected by a protein shell. Scientists also believed that viruses lacked the mechanisms necessary for metabolic f ...
Class Notes
... that are joined together. The proteins form a framework inside a cell. This framework gives a cell its shape and helps it move. 7. The genetic material in a prokaryotic cell is not surrounded by a membrane. Most prokaryotic ...
... that are joined together. The proteins form a framework inside a cell. This framework gives a cell its shape and helps it move. 7. The genetic material in a prokaryotic cell is not surrounded by a membrane. Most prokaryotic ...
Cell Membranes - Lovejoy High School
... Diffusion Diffusion - the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. Passive Transport-requires no energy ...
... Diffusion Diffusion - the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. Passive Transport-requires no energy ...
BSC 2020
... matter and energy • Structure and function are correlated at all levels. • Cells are the basic functional and structural unit of life • Continuity of life is based on heritable information contained within DNA ...
... matter and energy • Structure and function are correlated at all levels. • Cells are the basic functional and structural unit of life • Continuity of life is based on heritable information contained within DNA ...
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... chromatin that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next. ...
... chromatin that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next. ...
Brief Summary of Life on Earth
... replicate themselves (not perfectly, but making mistakes (mutations) is important for life!) o Lipid membranes can form spontaneously (drop of oil on water) o Possibly, this is how life began. Oldest known fossils of cells on Earth are 3.465 billion years old! They are very similar to anaerobic phot ...
... replicate themselves (not perfectly, but making mistakes (mutations) is important for life!) o Lipid membranes can form spontaneously (drop of oil on water) o Possibly, this is how life began. Oldest known fossils of cells on Earth are 3.465 billion years old! They are very similar to anaerobic phot ...
Cell City - CAC
... Cell City!! UFOs!! UFOs!! I see them: Unidentified Floating Objects! They’re taking over your cells, and it’s up to you to figure out what they are!! Just like the first scientists studying cells, you need to identify the names and functions of each of the “UFO’s” (a.k.a. organelles) that are foun ...
... Cell City!! UFOs!! UFOs!! I see them: Unidentified Floating Objects! They’re taking over your cells, and it’s up to you to figure out what they are!! Just like the first scientists studying cells, you need to identify the names and functions of each of the “UFO’s” (a.k.a. organelles) that are foun ...
5.1 The Cell Cycle
... • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. ...
... • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. ...
Mitosis PPT
... A cell’s genetic material is called its genome - prokaryote = single long DNA strand - eukaryote = number of DNA molecules ...
... A cell’s genetic material is called its genome - prokaryote = single long DNA strand - eukaryote = number of DNA molecules ...
Lec.3
... 2-A viable cell count curve measures only living (viable) cells (capable of growing and producing a colony on a suitable growth medium). The typical phases of a standard growth curve are (Figure 2): 1- Lag phase: during vigorous metabolic activity occurs but cells do not divide. This can last for a ...
... 2-A viable cell count curve measures only living (viable) cells (capable of growing and producing a colony on a suitable growth medium). The typical phases of a standard growth curve are (Figure 2): 1- Lag phase: during vigorous metabolic activity occurs but cells do not divide. This can last for a ...
Chp 4 Notes
... 1. Cells are the smallest unit that can carry on life functions 2. Robert Hooke: discovered and named the cell in 1665 i. Looked at Cork (dead plant cells) ii. Described them as looking like cells in a monastery 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek: observed the first living cells in 1673 i. observed algae and ...
... 1. Cells are the smallest unit that can carry on life functions 2. Robert Hooke: discovered and named the cell in 1665 i. Looked at Cork (dead plant cells) ii. Described them as looking like cells in a monastery 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek: observed the first living cells in 1673 i. observed algae and ...
Biology Name: Block: ____ Learning Targets: Membrane
... Knowledge Targets “What I need to know!” Reasoning Targets “What I can do with what I know.” ...
... Knowledge Targets “What I need to know!” Reasoning Targets “What I can do with what I know.” ...
The Importance of Vacuoles - LS-Biology
... higher the turgor pressure. This affects the rigidity of the cell wall, furthermore supporting the shape and structure of plants, helping them maintain an upright position. If a vacuole contains too much liquid, then it is able to export this material to avoid cytolysis or the bursting of the cell. ...
... higher the turgor pressure. This affects the rigidity of the cell wall, furthermore supporting the shape and structure of plants, helping them maintain an upright position. If a vacuole contains too much liquid, then it is able to export this material to avoid cytolysis or the bursting of the cell. ...
The Cell Theory
... Letter e, stained and unstained cells, electron microscope http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/ISR/equip/micro.gif&imgrefurl=http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/ISR/equip/equip4.htm&h=441& w=472&sz=44&tbnid=IBLNc48P3MC_rM:&tbnh=121&tbnw=129&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dcompou ...
... Letter e, stained and unstained cells, electron microscope http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/ISR/equip/micro.gif&imgrefurl=http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/ISR/equip/equip4.htm&h=441& w=472&sz=44&tbnid=IBLNc48P3MC_rM:&tbnh=121&tbnw=129&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dcompou ...
Chapter 4
... • compartments specialized for specific metabolic pathways (each has a particular kind of enzymes) ...
... • compartments specialized for specific metabolic pathways (each has a particular kind of enzymes) ...
Prokaryotics and Eukaryotic Cells
... Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the most common organisms today. ...
... Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria. Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes. They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the most common organisms today. ...