Question Sheet - Manchester HEP
... electron (b) the centre of mass frame. Check the consistency of these estimates by considering the Lorentz contraction in going between the electron rest frame and the centre of mass frame. e- ...
... electron (b) the centre of mass frame. Check the consistency of these estimates by considering the Lorentz contraction in going between the electron rest frame and the centre of mass frame. e- ...
Rules for Drawing Bohr Rutherford Diagrams and Reading
... One way to convey the mass number and the atomic number of an element is by using Standard Atomic Notation. This notation includes the mass number (placed at the upper left of the chemical symbol) and the atomic number (placed at the lower left of the symbol). For example, the Standard Atomic Notati ...
... One way to convey the mass number and the atomic number of an element is by using Standard Atomic Notation. This notation includes the mass number (placed at the upper left of the chemical symbol) and the atomic number (placed at the lower left of the symbol). For example, the Standard Atomic Notati ...
RENORMALIZATION AND GAUGE INVARIANCE∗
... Unitarity then automatically follows for a scalar field theory generated by a real Lagrangian, provided regularization of the infinities is done by modifications of the prapagator that are such that Eqs. (5.3) are kept intact. The latter is indeed the case for the propagator modifications (3.3), (3. ...
... Unitarity then automatically follows for a scalar field theory generated by a real Lagrangian, provided regularization of the infinities is done by modifications of the prapagator that are such that Eqs. (5.3) are kept intact. The latter is indeed the case for the propagator modifications (3.3), (3. ...
Khatua, Bansal, and Shahar Reply: The preceding
... effect that further reveals the nontrivial topological nature of the vector potential, but the electron acquires an Aharonov-Bohm phase for both Figs. 15–7 and 15–8 of Ref. [3]. The preceding Comment [1] specifically discusses three sentences from our Letter [2]. The sentences in the Abstract, (i) “ ...
... effect that further reveals the nontrivial topological nature of the vector potential, but the electron acquires an Aharonov-Bohm phase for both Figs. 15–7 and 15–8 of Ref. [3]. The preceding Comment [1] specifically discusses three sentences from our Letter [2]. The sentences in the Abstract, (i) “ ...
Solving Classical Field Equations 1. The Klein
... 7. Relation to the quantum theory Looking back at the “Feynman rules” above for the φ4 -theory which describe the allowed graphs we notice that these rule simply describe all graphs with 4-valent vertices (there are in total four lines at each vertex) that do not contain any loops. In quantum field ...
... 7. Relation to the quantum theory Looking back at the “Feynman rules” above for the φ4 -theory which describe the allowed graphs we notice that these rule simply describe all graphs with 4-valent vertices (there are in total four lines at each vertex) that do not contain any loops. In quantum field ...
Document
... Perturbative expansion of S-matrix contains Time ordered product of interaction Hamiltonian. To find transition amplitude one need to find ...
... Perturbative expansion of S-matrix contains Time ordered product of interaction Hamiltonian. To find transition amplitude one need to find ...
QuestionSheet
... electron (b) the centre of mass frame. Check the consistency of these estimates by considering the Lorentz contraction in going between the electron rest frame and the centre of mass frame. ...
... electron (b) the centre of mass frame. Check the consistency of these estimates by considering the Lorentz contraction in going between the electron rest frame and the centre of mass frame. ...
Maxwell`s equations
... We have to make more precise statement over which field configurations we integrate because now also the Dirac fields transform under the gauge transformation (next semester). one arrow in and one out ...
... We have to make more precise statement over which field configurations we integrate because now also the Dirac fields transform under the gauge transformation (next semester). one arrow in and one out ...
PHY 551 - Stony Brook University
... forces are described by exchange of particles primarily applied to Quantum Field Theory mathematical tool for calculating amplitudes for a given process ...
... forces are described by exchange of particles primarily applied to Quantum Field Theory mathematical tool for calculating amplitudes for a given process ...
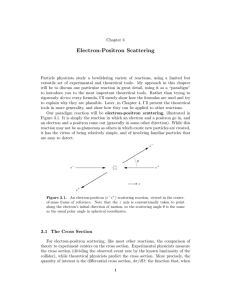
Electron-Positron Scattering
... The first term in Bhabha’s formula comes from the square of the first diagram, the last term comes from the square of the second diagram, and the middle term comes from the cross term (or “interference term”) between the two diagrams. So the diagrams are really a pictorial way of remembering the formu ...
... The first term in Bhabha’s formula comes from the square of the first diagram, the last term comes from the square of the second diagram, and the middle term comes from the cross term (or “interference term”) between the two diagrams. So the diagrams are really a pictorial way of remembering the formu ...
Document
... (2) At point ( x1 , t1 ) an antiparticle-particle pair is produced. The antiparticle moves forward to point ( x2 , t2 ) where it annihilates with another particle producing to two photons. FK7003 ...
... (2) At point ( x1 , t1 ) an antiparticle-particle pair is produced. The antiparticle moves forward to point ( x2 , t2 ) where it annihilates with another particle producing to two photons. FK7003 ...
Field Intensity Lines and Field Potential Lines - ND
... apparatus is set up as shown below, and a bead is suspended between the parallel plates. Evaluate the students' four results. Justify your evaluation of each result. Communicate clearly your understanding of the physics principles that you are using to solve this question. You may communicate this u ...
... apparatus is set up as shown below, and a bead is suspended between the parallel plates. Evaluate the students' four results. Justify your evaluation of each result. Communicate clearly your understanding of the physics principles that you are using to solve this question. You may communicate this u ...
3.6 The Feynman-rules for QED For any given action (Lagrangian
... and denotes the center-of-mass energy squared. In the limit of massless particles and energies are equal to . The total cross section all momenta is obtained by integrating over the solid angle ...
... and denotes the center-of-mass energy squared. In the limit of massless particles and energies are equal to . The total cross section all momenta is obtained by integrating over the solid angle ...
Electric Field Lines
... transistors in electric circuits. 5e. Know charged particles are sources of electric fields and are subject to the forces of the electric fields from other charges. 5h. Know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby conductors. 5i. Know plasmas, a fourth s ...
... transistors in electric circuits. 5e. Know charged particles are sources of electric fields and are subject to the forces of the electric fields from other charges. 5h. Know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby conductors. 5i. Know plasmas, a fourth s ...
Physics 218. Quantum Field Theory. Professor Dine Green`s
... somewhat simpler than the LSZ discussion. But it relies on the identification of the initial and final states with their leading order expansions. We can refine this by thinking about the structure of the perturbation expansion. The LSZ formula systematizes this. LSZ has other virtues. Most importan ...
... somewhat simpler than the LSZ discussion. But it relies on the identification of the initial and final states with their leading order expansions. We can refine this by thinking about the structure of the perturbation expansion. The LSZ formula systematizes this. LSZ has other virtues. Most importan ...
Linear momentum and the impulse
... Next, we contemplate how to change the value of p for a particle. Obviously, the mass can not change and therefore to change p we must do it by changing v, i.e we must accelerate the particle. Newton’s second law gives Fnet = m dv/dt = d [mv]/dt = dp/dt. This becomes for a system of particles, Fextn ...
... Next, we contemplate how to change the value of p for a particle. Obviously, the mass can not change and therefore to change p we must do it by changing v, i.e we must accelerate the particle. Newton’s second law gives Fnet = m dv/dt = d [mv]/dt = dp/dt. This becomes for a system of particles, Fextn ...
FIELD THEORY 1. Consider the following lagrangian1
... with µ ∈ R and λ > 0 1. Find all the symmetries of the above field theoretic model 2. Write the energy momentum tensor as well as the total energy and total momentum for this model and comment about it 3. Determine all the degenerate classical field configurations of minimal energy and specify their ...
... with µ ∈ R and λ > 0 1. Find all the symmetries of the above field theoretic model 2. Write the energy momentum tensor as well as the total energy and total momentum for this model and comment about it 3. Determine all the degenerate classical field configurations of minimal energy and specify their ...
Correlation Functions and Diagrams
... Correlation function of fields are the natural objects to study in the path integral formulation. They contain the physical information we are interested in (e.g. scattering amplitudes) and have a simple expansion in terms of Feynman diagrams. This chapter develops this formalism, which will be the ...
... Correlation function of fields are the natural objects to study in the path integral formulation. They contain the physical information we are interested in (e.g. scattering amplitudes) and have a simple expansion in terms of Feynman diagrams. This chapter develops this formalism, which will be the ...
Feynman Diagrams in Quantum Mechanics
... problem being solved, and then use some Feynman rules to calculate a value for each diagram. The values are then added together, with certain weights, to evaluate the desired expectation. This process may seem a bit arbitrary, but in the second half of the paper we give a natural explanation as to w ...
... problem being solved, and then use some Feynman rules to calculate a value for each diagram. The values are then added together, with certain weights, to evaluate the desired expectation. This process may seem a bit arbitrary, but in the second half of the paper we give a natural explanation as to w ...
Document
... 1. A Feynman diagram consists of external lines (lines which enter or leave the diagram) and internal lines (lines start and end in the diagram). External lines represent physical particles (observable). Internal lines represent virtual particles ( A virtual particle is just like a physical particle ...
... 1. A Feynman diagram consists of external lines (lines which enter or leave the diagram) and internal lines (lines start and end in the diagram). External lines represent physical particles (observable). Internal lines represent virtual particles ( A virtual particle is just like a physical particle ...
Introduction - High Energy Physics Group
... The virtual ee pairs are polarised At large distances the bare electron charge is screened. At shorter distances, screening effect reduced and see a larger effective charge i.e. . ...
... The virtual ee pairs are polarised At large distances the bare electron charge is screened. At shorter distances, screening effect reduced and see a larger effective charge i.e. . ...
Introduction to Feynman Diagrams and Dynamics of Interactions
... The basic vertex shows the coupling of a charged particle (an electron here) to a quantum of the electromagnetic field, the photon. Note that in my convention, time flows to the right. Energy and momentum are conserved at each vertex. Each vertex has a coupling strength characteristic of the interac ...
... The basic vertex shows the coupling of a charged particle (an electron here) to a quantum of the electromagnetic field, the photon. Note that in my convention, time flows to the right. Energy and momentum are conserved at each vertex. Each vertex has a coupling strength characteristic of the interac ...
Numerical Methods Project: Feynman path integrals in quantum
... where L is the langragian, ∆t is assumed to be infinitesimally small and the weight factor w is assumed to be independent of the potential. The expression above is also know as the short time propagator. Richard Feynman is said to have been led to this idea by Paul Dirac who made a similar comment a ...
... where L is the langragian, ∆t is assumed to be infinitesimally small and the weight factor w is assumed to be independent of the potential. The expression above is also know as the short time propagator. Richard Feynman is said to have been led to this idea by Paul Dirac who made a similar comment a ...
Feynman diagram
In theoretical physics, Feynman diagrams are pictorial representations of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles. The scheme is named for its inventor, American physicist Richard Feynman, and was first introduced in 1948. The interaction of sub-atomic particles can be complex and difficult to understand intuitively. Feynman diagrams give a simple visualization of what would otherwise be a rather arcane and abstract formula. As David Kaiser writes, ""since the middle of the 20th century, theoretical physicists have increasingly turned to this tool to help them undertake critical calculations"", and as such ""Feynman diagrams have revolutionized nearly every aspect of theoretical physics"". While the diagrams are applied primarily to quantum field theory, they can also be used in other fields, such as solid-state theory.Feynman used Ernst Stueckelberg's interpretation of the positron as if it were an electron moving backward in time. Thus, antiparticles are represented as moving backward along the time axis in Feynman diagrams.The calculation of probability amplitudes in theoretical particle physics requires the use of rather large and complicated integrals over a large number of variables. These integrals do, however, have a regular structure, and may be represented graphically as Feynman diagrams. A Feynman diagram is a contribution of a particular class of particle paths, which join and split as described by the diagram. More precisely, and technically, a Feynman diagram is a graphical representation of a perturbative contribution to the transition amplitude or correlation function of a quantum mechanical or statistical field theory. Within the canonical formulation of quantum field theory, a Feynman diagram represents a term in the Wick's expansion of the perturbative S-matrix. Alternatively, the path integral formulation of quantum field theory represents the transition amplitude as a weighted sum of all possible histories of the system from the initial to the final state, in terms of either particles or fields. The transition amplitude is then given as the matrix element of the S-matrix between the initial and the final states of the quantum system.