Plant Cell Structures
... A third difference between plant and animal cells is that plants have several kinds of organelles called plastids. And there are several different kinds of plastids in plant cells. For example, Chloroplasts are needed for photosynthesis, leucoplasts can store starch or oil, and brightly colored chro ...
... A third difference between plant and animal cells is that plants have several kinds of organelles called plastids. And there are several different kinds of plastids in plant cells. For example, Chloroplasts are needed for photosynthesis, leucoplasts can store starch or oil, and brightly colored chro ...
Cells
... • Selective permeability : a process used to maintain homeostasis allowing some molecules into the cell while keeping others out. ...
... • Selective permeability : a process used to maintain homeostasis allowing some molecules into the cell while keeping others out. ...
Cell Organelle Functions part 1
... d. Inner, folded membrane = CRISTAE Important details: Mitochondrion is called the "Powerhouse". It releases energy when bonds are broken. The production of ribosomes begins in the nucleus, the rough ER takes the proteins from the ribosomes and transports them where the golgi apparatus (golgi bodies ...
... d. Inner, folded membrane = CRISTAE Important details: Mitochondrion is called the "Powerhouse". It releases energy when bonds are broken. The production of ribosomes begins in the nucleus, the rough ER takes the proteins from the ribosomes and transports them where the golgi apparatus (golgi bodies ...
Protoplast >composed of cell`s nucleus and surrounding
... >most plants store chemicals in vacuole that reacts with chemicals in cytosol >if cell is broken, two chemicals react forming toxic chemicals >surrounded by tonoplast >controls movement of molecules between cytosol and sap >separates vacoular content from cell's cytoplasm >regulates movements of ion ...
... >most plants store chemicals in vacuole that reacts with chemicals in cytosol >if cell is broken, two chemicals react forming toxic chemicals >surrounded by tonoplast >controls movement of molecules between cytosol and sap >separates vacoular content from cell's cytoplasm >regulates movements of ion ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... cells use mitochondria for energy production. Plants primarily use chloroplasts to produce energy. ► Animal cells tend to have many small vacuoles. Mature plant cells may have only one large vacuole. ► Animals cells have lysosomes, but plant cells do not. ...
... cells use mitochondria for energy production. Plants primarily use chloroplasts to produce energy. ► Animal cells tend to have many small vacuoles. Mature plant cells may have only one large vacuole. ► Animals cells have lysosomes, but plant cells do not. ...
Cell Parts
... Phospholipid bilayer acts like a fluid The lipids and proteins can move laterally within the bilayer Mosaic- pattern is constantly changing ...
... Phospholipid bilayer acts like a fluid The lipids and proteins can move laterally within the bilayer Mosaic- pattern is constantly changing ...
Cell Organelles
... Living things get energy in one of two ways: from food or from the sun. Mitochondria: Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Enclosed in two membranes They are inherited ...
... Living things get energy in one of two ways: from food or from the sun. Mitochondria: Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. Organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. Enclosed in two membranes They are inherited ...
Goal Two
... Steps of microscope use Communication among cells within an organism o Chemical signals may be released by one cell to influence the activity of another cell. For example, a nerve cell can send a message to a muscle cell or to another nerve cell. 2.03 Investigate and analyze the cell as a living ...
... Steps of microscope use Communication among cells within an organism o Chemical signals may be released by one cell to influence the activity of another cell. For example, a nerve cell can send a message to a muscle cell or to another nerve cell. 2.03 Investigate and analyze the cell as a living ...
Micr-22 Exam 1 Study Guide Revised Fall 2016 Test Preparation
... and what the different gram reactions signify. 18. Explain how bacterial identification makes use of unique features within certain groups (ex: flagella, cell wall types, cell shape, cell arrangement, inclusions). 19. Distinguish among active and passive transport methods, including simple diffusion ...
... and what the different gram reactions signify. 18. Explain how bacterial identification makes use of unique features within certain groups (ex: flagella, cell wall types, cell shape, cell arrangement, inclusions). 19. Distinguish among active and passive transport methods, including simple diffusion ...
A View of a Cell
... Can be unicellular organisms such as algae and yeast Clearly defined nucleus and organelles ...
... Can be unicellular organisms such as algae and yeast Clearly defined nucleus and organelles ...
Chapter 1 - Introduction
... altered in response to changing external conditions. For example, how do cells adapt to increased work load, as in chronically exercising skeletal muscle? How do cells adapt to nutrient limitation, as during starvation or caloric restriction? How do cells adapt to temperature fluctuations? What are ...
... altered in response to changing external conditions. For example, how do cells adapt to increased work load, as in chronically exercising skeletal muscle? How do cells adapt to nutrient limitation, as during starvation or caloric restriction? How do cells adapt to temperature fluctuations? What are ...
Review- Cell Transport
... protein that is located only on one side of the lipid bilayer is called ________________. 7. Draw a cross section of the lipid bilayer, including the two types of proteins named in #6. ...
... protein that is located only on one side of the lipid bilayer is called ________________. 7. Draw a cross section of the lipid bilayer, including the two types of proteins named in #6. ...
Mitosis Notes
... CELL DIVISION • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
... CELL DIVISION • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
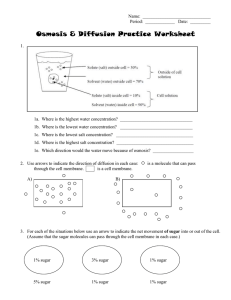
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
Challenges in Morphogenesis and Tissue Engineering
... Progress in Organ-engineering: Current state is analogous to that in late 1970's. Culture primary tissues that grow and undergo morphogenesis. But we do not yet have... Predictive control of cell behaviors, shape changes, and movements to create tissues. Control of tissue formation from the establi ...
... Progress in Organ-engineering: Current state is analogous to that in late 1970's. Culture primary tissues that grow and undergo morphogenesis. But we do not yet have... Predictive control of cell behaviors, shape changes, and movements to create tissues. Control of tissue formation from the establi ...
1. Cell Structure - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... Called the basic unit of life because it is the simplest unit capable of independent existence and reproduction All organisms are constructed out of cells - unicellular organism = 1 cell - multicellular organism = more than 1 cell Cells of all organisms contain organelles which carry out certain ...
... Called the basic unit of life because it is the simplest unit capable of independent existence and reproduction All organisms are constructed out of cells - unicellular organism = 1 cell - multicellular organism = more than 1 cell Cells of all organisms contain organelles which carry out certain ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum
... – Both gave the larger cell an advantage (make food and energy) – Predator cell provided each protection • Over time, these cells could not survive without the mitochondria ...
... – Both gave the larger cell an advantage (make food and energy) – Predator cell provided each protection • Over time, these cells could not survive without the mitochondria ...
Document
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
ZOOMING DOWN THE TREE OF LIFE TO LIFE`S BUILDING BLOCKS
... ZOOMING DOWN THE TREE OF LIFE TO LIFE'S BUILDING BLOCKS Student Worksheet All key components of every living cell are made of macromolecules. These are very large molecules that determine the structural and functional properties of living cells. There are four different kinds of macromolecules -- ca ...
... ZOOMING DOWN THE TREE OF LIFE TO LIFE'S BUILDING BLOCKS Student Worksheet All key components of every living cell are made of macromolecules. These are very large molecules that determine the structural and functional properties of living cells. There are four different kinds of macromolecules -- ca ...
221_ exam_1_2004
... _____ Antiviral drug therapy ideally should target viral activities that are unique to the virus. One of these targets is the process or attachment. A fairly new anti-influenza drug targets _____ a protein on the surface of the influenza virus which is associated with the attachment process. A. B. C ...
... _____ Antiviral drug therapy ideally should target viral activities that are unique to the virus. One of these targets is the process or attachment. A fairly new anti-influenza drug targets _____ a protein on the surface of the influenza virus which is associated with the attachment process. A. B. C ...
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell CONTENT I. The Microscopic world of
... b.Freshwater protists: contractile vacuoles pump water out the cell c. Plant cells: central vacuole stores 90-98% water (turgor pressure), organic nutrients, may contain pigments & poisons. D. Chloroplasts & Mitochondria: Existence explained by endosymbiotic theory: a smaller simpler cell became an ...
... b.Freshwater protists: contractile vacuoles pump water out the cell c. Plant cells: central vacuole stores 90-98% water (turgor pressure), organic nutrients, may contain pigments & poisons. D. Chloroplasts & Mitochondria: Existence explained by endosymbiotic theory: a smaller simpler cell became an ...
Key Unit 3 (Cell membrane)
... 3. What is the difference between a channel protein and a transport protein? Channel protein lets any molecule through it (like a bridge) whereas transport proteins are specific to certain molecules (only let some things across) ...
... 3. What is the difference between a channel protein and a transport protein? Channel protein lets any molecule through it (like a bridge) whereas transport proteins are specific to certain molecules (only let some things across) ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.









![Name: Date: Period: Cell Organelles Worksheet[1].doc Organelle](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014152553_1-fd24a25ff154c0312a2390f004444c80-300x300.png)