BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW - G. Holmes Braddock High School
... contained dissolve minerals and gases • Most scientists agree that the origin of life simple organic molecules, polymers, protocells and cells. • Other theories of the origin of life are creationism, spontaneous generation, and a meteorite from outer space. ...
... contained dissolve minerals and gases • Most scientists agree that the origin of life simple organic molecules, polymers, protocells and cells. • Other theories of the origin of life are creationism, spontaneous generation, and a meteorite from outer space. ...
In the early 1900s, many children had a disease called rickets
... 16. Which of these correctly matches the molecule with its function? 1. lipid—stores genetic information 3. enzyme—speeds up chemical reactions 2. vitamin—supplies energy to cells 4. carbohydrate—manufactures cell membranes 17. Most carbohydrates in the human body are used for ______________________ ...
... 16. Which of these correctly matches the molecule with its function? 1. lipid—stores genetic information 3. enzyme—speeds up chemical reactions 2. vitamin—supplies energy to cells 4. carbohydrate—manufactures cell membranes 17. Most carbohydrates in the human body are used for ______________________ ...
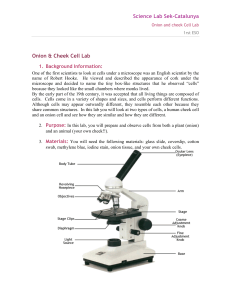
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chamb ...
... One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chamb ...
Applications and skills
... Go through the learning resources that follow, and address the inquiry questions written at the top of each page. Pay attention to the understandings, applications and skills that have been cut and pasted from the IB DP Biology syllabus. You are not required to turn in any notes or written answers t ...
... Go through the learning resources that follow, and address the inquiry questions written at the top of each page. Pay attention to the understandings, applications and skills that have been cut and pasted from the IB DP Biology syllabus. You are not required to turn in any notes or written answers t ...
Why are bones hard and muscles soft?
... All organisms are made up of cells. A cell is the smallest unit of living matter. Cells grow, reproduce, use energy, and produce waste. Nearly all the cells in your body have the same three parts. The first is the cell membrane, which surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the cell and the ...
... All organisms are made up of cells. A cell is the smallest unit of living matter. Cells grow, reproduce, use energy, and produce waste. Nearly all the cells in your body have the same three parts. The first is the cell membrane, which surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the cell and the ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
pdf full text
... Cell-produced functional biomaterials Escherichia coli produce an extracellular amyloid material called curli that is involved in biofilm formation. The secreted major curli subunit, CsgA, self-assembles to form fibrils with great mechanical strength. Chen et al. harnessed control over this system t ...
... Cell-produced functional biomaterials Escherichia coli produce an extracellular amyloid material called curli that is involved in biofilm formation. The secreted major curli subunit, CsgA, self-assembles to form fibrils with great mechanical strength. Chen et al. harnessed control over this system t ...
Chapter 9: movement of material in and out of cell
... Movement of material in and out of cell: The basics & Passive Transport: *How does stuff move in and out of an animal cell? Cell membrane -Selectively permeable - things can go in and out of cell dependent on pore size. - this is done to maintain homeostasis or equilibrium. ...
... Movement of material in and out of cell: The basics & Passive Transport: *How does stuff move in and out of an animal cell? Cell membrane -Selectively permeable - things can go in and out of cell dependent on pore size. - this is done to maintain homeostasis or equilibrium. ...
L3.b Spiral Review
... a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Tuesday 5. The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. b. c. d. ...
... a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Tuesday 5. The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. b. c. d. ...
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(RER)
... contraction of muscle cells. Similarly , cells of the ovaries and testes, which produce the lipid-containing hormones estrogen and testosterone, contain large amounts of SER. Another function of SER is the control the movement of newly synthesized proteins to their proper location in the cell or to ...
... contraction of muscle cells. Similarly , cells of the ovaries and testes, which produce the lipid-containing hormones estrogen and testosterone, contain large amounts of SER. Another function of SER is the control the movement of newly synthesized proteins to their proper location in the cell or to ...
Tead4 triggers trophectoderm
... pathways involved in the formation of adherens and tight junctions, cell polarity and various forms of signaling, they found no abnormalities that could account for the blastocoel failure. They turned next to the trophectoderm, as this tissue is also a critical requirement for normal blastocyst deve ...
... pathways involved in the formation of adherens and tight junctions, cell polarity and various forms of signaling, they found no abnormalities that could account for the blastocoel failure. They turned next to the trophectoderm, as this tissue is also a critical requirement for normal blastocyst deve ...
Cells and Structures ppt
... Mitochondria – Description of Function Mitochondria function in the process of aerobic cellular respiration. They produce ATP energy for the cell. ...
... Mitochondria – Description of Function Mitochondria function in the process of aerobic cellular respiration. They produce ATP energy for the cell. ...
Biology Exam One You can write on this exam. Please put a W on
... a. Bacteria and Archaea b. Plantae and Animalia c. Eukarya and Archaea d. Archaea and Plantae e. Fungi and Bacteria ...
... a. Bacteria and Archaea b. Plantae and Animalia c. Eukarya and Archaea d. Archaea and Plantae e. Fungi and Bacteria ...
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES
... may be TTAGGG In the replication of DNA, after removal of the RNA primer at the 5’ end of a strand by RNAseH activity, conventional DNA polymerases can not fill in the gap. This problem can be solved by the telomerase enzyme. Telomerase consists of RNA and protein. The RNA hybridizes with the 3’ end ...
... may be TTAGGG In the replication of DNA, after removal of the RNA primer at the 5’ end of a strand by RNAseH activity, conventional DNA polymerases can not fill in the gap. This problem can be solved by the telomerase enzyme. Telomerase consists of RNA and protein. The RNA hybridizes with the 3’ end ...
life science– cell membrane
... It is harder to pull in particles when they are abundant inside the cell and scarce outside the cell. An area with a high concentration is more likely to want to travel to a low concentration._ ...
... It is harder to pull in particles when they are abundant inside the cell and scarce outside the cell. An area with a high concentration is more likely to want to travel to a low concentration._ ...
Transactivation Assay Introduction Regulation of gene expression at
... reduce intracellular accumulation of drugs by pumping them out of the cell. In yeast this can be achieved by upregulating expression of a variety of ABC transporters which act as drug pumps. Many such ABC transporters have a broad specificity in terms of the substrates they can move across membranes ...
... reduce intracellular accumulation of drugs by pumping them out of the cell. In yeast this can be achieved by upregulating expression of a variety of ABC transporters which act as drug pumps. Many such ABC transporters have a broad specificity in terms of the substrates they can move across membranes ...
Cells Unit
... causing cell shrinkage or crenation • Hypotonic - term used when the extracellular solute concentration is less than the cell resulting in movement of water into the cell causing cell swelling ...
... causing cell shrinkage or crenation • Hypotonic - term used when the extracellular solute concentration is less than the cell resulting in movement of water into the cell causing cell swelling ...
File
... Red blood cells released by immune cells cause increased blood flow to the infection site; this increased blood flow brings other red blood cells to the area more quickly. ...
... Red blood cells released by immune cells cause increased blood flow to the infection site; this increased blood flow brings other red blood cells to the area more quickly. ...
Time Course of the Primary Immune Response
... 6. Fc receptors come in two basic types: activating (ITAM-associated) and inhibitory (ITIM-associated). 7. The relative expression of activating and inhibitory Fc receptors determines the outcome of a given engagement of Fc receptors. 8. Fc receptor-driven pathology includes formation and deposition ...
... 6. Fc receptors come in two basic types: activating (ITAM-associated) and inhibitory (ITIM-associated). 7. The relative expression of activating and inhibitory Fc receptors determines the outcome of a given engagement of Fc receptors. 8. Fc receptor-driven pathology includes formation and deposition ...
Organelle Functions Organelle Function Sketch Nucleus Control
... Recognition –identify cells as normal or abnormal ...
... Recognition –identify cells as normal or abnormal ...
ws flip cell parts - Renton School District
... On a separate piece of paper, draw and label a large cell membrane that is approximately the size of the whole sheet. You will be filling it with sketches of organelles so make it big. In the corner of your paper, draw a close-up of section of the membrane showing the ...
... On a separate piece of paper, draw and label a large cell membrane that is approximately the size of the whole sheet. You will be filling it with sketches of organelles so make it big. In the corner of your paper, draw a close-up of section of the membrane showing the ...
Anatomy of wood
... parts contain lignin. The precursors for lignin are the three aromatic compounds: coumaryl, coniferyl and sinapyl alcohols. The alcohols form large complexes and give rise to coumaryl-, guiacyl- and sinapylresidues in the polymer. In addition to lignin, many plants contain ferulic acid, which is est ...
... parts contain lignin. The precursors for lignin are the three aromatic compounds: coumaryl, coniferyl and sinapyl alcohols. The alcohols form large complexes and give rise to coumaryl-, guiacyl- and sinapylresidues in the polymer. In addition to lignin, many plants contain ferulic acid, which is est ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.