
Chapter 31: Page 304
... In addition to protecting the cell, the cell wall also gives an organism the ability to remain stiff, like the trunk of a tree! Cell walls connect to each other just like a brick wall! This gives plants and fungi a strong body that does not break in half during a windstorm and can straighten up when ...
... In addition to protecting the cell, the cell wall also gives an organism the ability to remain stiff, like the trunk of a tree! Cell walls connect to each other just like a brick wall! This gives plants and fungi a strong body that does not break in half during a windstorm and can straighten up when ...
Environ-X - NanoServices
... is supposed to be used in indoor antisepsis and sterilization, water treatment, water pollution comprehensive management and photodynamic therapy. Actually, photocatalytic sterilization is supposed to constantly work between bacteria and titanium dioxide instead of simple surface reaction as photoca ...
... is supposed to be used in indoor antisepsis and sterilization, water treatment, water pollution comprehensive management and photodynamic therapy. Actually, photocatalytic sterilization is supposed to constantly work between bacteria and titanium dioxide instead of simple surface reaction as photoca ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... Chief Systems of the World - Ptolemaic and Copernican the Inquisition banned its sale and ordered Galileo to appear in Rome before them. Illness prevented him from travelling to Rome until 1633. Galileo's accusation at the trial which followed was that he had breached the conditions laid down by the ...
... Chief Systems of the World - Ptolemaic and Copernican the Inquisition banned its sale and ordered Galileo to appear in Rome before them. Illness prevented him from travelling to Rome until 1633. Galileo's accusation at the trial which followed was that he had breached the conditions laid down by the ...
Cell-a-bration Project
... c) Cell parts: Cell Wall(Plant Cell Only), Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Chloroplasts(Plant Cell Only), Vacuole, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, and Mitochondria. 4. Key - Make a table that contains the following on a separate paper either handwritten or on computer: (See example of table bel ...
... c) Cell parts: Cell Wall(Plant Cell Only), Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Chloroplasts(Plant Cell Only), Vacuole, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, and Mitochondria. 4. Key - Make a table that contains the following on a separate paper either handwritten or on computer: (See example of table bel ...
Cells and Systems Quiz – Section 1 and 2 – Study Guide
... Know the major parts/organs of each system. Describe the function of villa. What is the difference between the small and large intestine. Know where gas exchange occurs. How does oxygen get into our circulatory system? Explain two ways in which veins and arteries are different. List four parts of bl ...
... Know the major parts/organs of each system. Describe the function of villa. What is the difference between the small and large intestine. Know where gas exchange occurs. How does oxygen get into our circulatory system? Explain two ways in which veins and arteries are different. List four parts of bl ...
I. Evolution from unicellular to multicellular organisms II. Evolution
... The orchid mantis drastically changes its appearance during post-hatching development. The first-instar nymph of the mantis is colored red and black and is believed to mimic other unpalatable insects like ants. A flower-like appearance emerges after molting into the 2nd-instar nymph. We aim to compa ...
... The orchid mantis drastically changes its appearance during post-hatching development. The first-instar nymph of the mantis is colored red and black and is believed to mimic other unpalatable insects like ants. A flower-like appearance emerges after molting into the 2nd-instar nymph. We aim to compa ...
Amphibians and Mammals
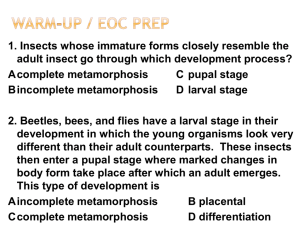
... hatch into swimming, fish like organisms called tadpoles. Tadpoles breathe with gills and after a period of growth, the body of the tadpole changes into a frog body. This dramatic physical change in which a frog develops is called metamorphosis. ...
... hatch into swimming, fish like organisms called tadpoles. Tadpoles breathe with gills and after a period of growth, the body of the tadpole changes into a frog body. This dramatic physical change in which a frog develops is called metamorphosis. ...
Kingdom Notes - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Makes Its Own Food? Some do by photosynthesis, autotrophs others are heterotrophs Main Type of Reproduction: binary fission, conjugation, mitosis, meiosis (Sexual and Asexual) Examples: paramecium, amoeba, algae, malaria Fun Fact: Sometimes referred to as the “junk” Kingdom, because if it is not a f ...
... Makes Its Own Food? Some do by photosynthesis, autotrophs others are heterotrophs Main Type of Reproduction: binary fission, conjugation, mitosis, meiosis (Sexual and Asexual) Examples: paramecium, amoeba, algae, malaria Fun Fact: Sometimes referred to as the “junk” Kingdom, because if it is not a f ...
Diversity of Life - BPS Science Weebly
... Standard: 2 - Recognize that all organisms are composed of cells, and that many organisms are single-celled (unicellular), e.g., bacteria, yeast. In these single-celled organisms, one cell must carry out all of the basic functions of life. Standard: 3 - Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, i ...
... Standard: 2 - Recognize that all organisms are composed of cells, and that many organisms are single-celled (unicellular), e.g., bacteria, yeast. In these single-celled organisms, one cell must carry out all of the basic functions of life. Standard: 3 - Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, i ...
Chapter : 6: A Tour of the Cell
... a) Microtubules are hollow tubes of protein that provide structural support. b) Microfilaments are chains of proteins that resist stretching. c) Intermediate filaments are more permanent structures in cells compared to microfilaments and microtubules. d) Components of the cytoskeleton are often invo ...
... a) Microtubules are hollow tubes of protein that provide structural support. b) Microfilaments are chains of proteins that resist stretching. c) Intermediate filaments are more permanent structures in cells compared to microfilaments and microtubules. d) Components of the cytoskeleton are often invo ...
Respiratory System
... Intermingled w/ small alveolar cells & joined by O.Z. Same # of cells as Type I, but cover 5% of surface Able to proliferate & give rise to both Type I & II Lamellar body secretions: Surfactant components: o Multilamellar bodies or (10%) Rich in phospholipids Discharged into lumen Fx ...
... Intermingled w/ small alveolar cells & joined by O.Z. Same # of cells as Type I, but cover 5% of surface Able to proliferate & give rise to both Type I & II Lamellar body secretions: Surfactant components: o Multilamellar bodies or (10%) Rich in phospholipids Discharged into lumen Fx ...
function - mselder
... from the parent cell coils and condenses to form pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same gen ...
... from the parent cell coils and condenses to form pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same gen ...
cell membrane
... - CELL AND ORGAN CULTURE - cells or fragments of tissue are removed aseptically, transferred to a physiological medium and kept at a temperature normal for animal from which the sample was taken. The cultures are placed in thin glass vessels or in hanging drops on a coverglas mounted over a hollow s ...
... - CELL AND ORGAN CULTURE - cells or fragments of tissue are removed aseptically, transferred to a physiological medium and kept at a temperature normal for animal from which the sample was taken. The cultures are placed in thin glass vessels or in hanging drops on a coverglas mounted over a hollow s ...
Lesion - BioMed Central
... “soap bubble appearance” type. Giant cells are attached to the periphery of the clustered spindle cells. Ewing’s sarcoma ...
... “soap bubble appearance” type. Giant cells are attached to the periphery of the clustered spindle cells. Ewing’s sarcoma ...
Slide 1
... “Molecular and network modeling in synthetic and systems biology” Protein Engineering III Prof. Dane Wittrup MIT “Protein engineering in biomedicine” Targeted Delivery of Proteins and Nucleotides I Extracellular and Intracellular Delivery ...
... “Molecular and network modeling in synthetic and systems biology” Protein Engineering III Prof. Dane Wittrup MIT “Protein engineering in biomedicine” Targeted Delivery of Proteins and Nucleotides I Extracellular and Intracellular Delivery ...
Click4Biology: 2.1 Cell Theory
... The approach of the physical sciences is to reduce an inanimate phenomenon to its constituent parts and that knowledge of these will explain the phenomena as a whole. The parts do not vary (otherwise there would be more parts) and these are predictable within the laws and principles that describe th ...
... The approach of the physical sciences is to reduce an inanimate phenomenon to its constituent parts and that knowledge of these will explain the phenomena as a whole. The parts do not vary (otherwise there would be more parts) and these are predictable within the laws and principles that describe th ...
South Warren High School Science Department 2011
... Course description: The goal of this course is to develop scientifically literate students who are able to understand the influence of science on technology and society and are able to use this knowledge to enhance critical thinking skills and daily decision making. Students will investigate, throug ...
... Course description: The goal of this course is to develop scientifically literate students who are able to understand the influence of science on technology and society and are able to use this knowledge to enhance critical thinking skills and daily decision making. Students will investigate, throug ...
Worksheet - Moore Public Schools
... bacteria; serves as a barrier against white blood cells D. internal “soup” of cell that is bounded by the cell envelope; mostly water, but within it are the bacterial inclusions E. region within bacteria visible in transmission electron micrographs. Most of the bacterial DNA is found here, along wit ...
... bacteria; serves as a barrier against white blood cells D. internal “soup” of cell that is bounded by the cell envelope; mostly water, but within it are the bacterial inclusions E. region within bacteria visible in transmission electron micrographs. Most of the bacterial DNA is found here, along wit ...
File - Hawk Nation Biology
... Of the four different types of biomolecules, which of them can contain phosphorous in their structure? A. Nucleic acid and lipids C . Protein and carbohydrate B. Nucleic acid and carbohydrate D. Lipid and carbohydrate ...
... Of the four different types of biomolecules, which of them can contain phosphorous in their structure? A. Nucleic acid and lipids C . Protein and carbohydrate B. Nucleic acid and carbohydrate D. Lipid and carbohydrate ...
1 IMMUNE SYSTEM WORKSHEET KEY CONCEPT: The immune
... 5. __ Basophil cells ___ and ____ mast cells _____ are white blood cells that release chemical signals that attract other white cells to the site of an infection. 6. ____ Eosinophils ____ are white blood cells that help rid the body of parasites by injecting them with toxic substances. 7. __ Antibod ...
... 5. __ Basophil cells ___ and ____ mast cells _____ are white blood cells that release chemical signals that attract other white cells to the site of an infection. 6. ____ Eosinophils ____ are white blood cells that help rid the body of parasites by injecting them with toxic substances. 7. __ Antibod ...
Summary: Function and Structure of Cell Parts
... • free ribosomes make proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, for example, for the cytoskeleton • ribosomes that are attached to the ER make proteins which must be kept separate from the cytoplasm, either because they are going to be secreted by the cell (for example, polypeptide hormones like insu ...
... • free ribosomes make proteins that are used in the cytoplasm, for example, for the cytoskeleton • ribosomes that are attached to the ER make proteins which must be kept separate from the cytoplasm, either because they are going to be secreted by the cell (for example, polypeptide hormones like insu ...
Cell Physiology [PPT]
... Long rigid shape - which enables microtubules to support other structures within the cell Ability to generate movement - various kinds of movements in all eukaryotic cells. both within cells (conveyer belts) and of the whole cells themselves ( microtubules that form structures such as cilia and ...
... Long rigid shape - which enables microtubules to support other structures within the cell Ability to generate movement - various kinds of movements in all eukaryotic cells. both within cells (conveyer belts) and of the whole cells themselves ( microtubules that form structures such as cilia and ...
Corning® Cell Culture Supplements
... in culture. These supplements include essential biological molecules such as proteins or fatty acids, trace elements, metals or other essential nutrients. Media supplemented with animal serum does not always require additional growth factors because animal serum contains these necessary compounds. G ...
... in culture. These supplements include essential biological molecules such as proteins or fatty acids, trace elements, metals or other essential nutrients. Media supplemented with animal serum does not always require additional growth factors because animal serum contains these necessary compounds. G ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.





















![Cell Physiology [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000836372_1-f01c4ac0aa1884121950a80d4cb7cd49-300x300.png)
