Unit 1 Study Guide
... a. Haploid a cell containing ½ information - n b. Diploid 2 complete haploid sets - 2n c. Homologous chromosomes pairs of like chromosomes (1 from mom & 1 from dad) d. Tetrad 2 homologous pairs of chromosomes (2 chromosomes = 4 sister chromatids) ...
... a. Haploid a cell containing ½ information - n b. Diploid 2 complete haploid sets - 2n c. Homologous chromosomes pairs of like chromosomes (1 from mom & 1 from dad) d. Tetrad 2 homologous pairs of chromosomes (2 chromosomes = 4 sister chromatids) ...
Minimal Essential Medium Non-Essential Amino Acids (100X Solution)
... Acids (100X Solution) In many cell culture applications using defined media for the in vitro cultivation of cells, the addition of supplemental nutrients and reagents is required. Additives such as antibiotics, buffers, and stains are frequently used to prevent bacterial contamination, control pH, a ...
... Acids (100X Solution) In many cell culture applications using defined media for the in vitro cultivation of cells, the addition of supplemental nutrients and reagents is required. Additives such as antibiotics, buffers, and stains are frequently used to prevent bacterial contamination, control pH, a ...
Cell theory states: living things are composed of one or
... things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory. Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as the method for cell origination, but spontaneous generatio ...
... things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory. Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as the method for cell origination, but spontaneous generatio ...
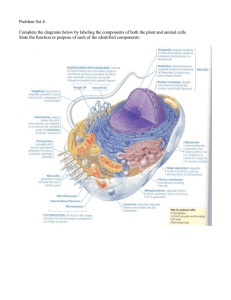
Problem Set 4:
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
... 8.6 What osmotic problems do fresh water protists face? Hypertonic protests will gain water from their hypotonic environment. What adaptations may help them osmoregulate? Some have membranes that are less permeable to water and contractile vacuoles that expel excess water. 8.7 The ideal osmotic env ...
Plant Cell
... The rough ER appears rough due to the presence of ribosomes on the membrane surface Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
... The rough ER appears rough due to the presence of ribosomes on the membrane surface Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
bio12_sm_02_1
... (d) Many plastids like chloroplasts and chromoplasts contain pigments. 3. The nuclear envelope is a double-layered membrane that contains pores and many other specialized proteins—some are receptors and others are transporters. These membrane proteins work with the lipid bilayer to transport molecul ...
... (d) Many plastids like chloroplasts and chromoplasts contain pigments. 3. The nuclear envelope is a double-layered membrane that contains pores and many other specialized proteins—some are receptors and others are transporters. These membrane proteins work with the lipid bilayer to transport molecul ...
2-Inside-a-cell
... 1.All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. Cells can only be produced by other living cells. ...
... 1.All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. Cells can only be produced by other living cells. ...
Cells - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... allowed people to see cells for the first time. Hand ...
... allowed people to see cells for the first time. Hand ...
Linking metabolism and cell identity: a voyage from the Arabidopsis
... Linking metabolism and cell identity: a voyage from the Arabidopsis root to embryonic stem cells Living organisms are defined by their metabolic activity. Metabolic processes are involved in every aspect of cell function, thereby enabling the characterization and quantification of cellular processes ...
... Linking metabolism and cell identity: a voyage from the Arabidopsis root to embryonic stem cells Living organisms are defined by their metabolic activity. Metabolic processes are involved in every aspect of cell function, thereby enabling the characterization and quantification of cellular processes ...
Cell cycle and mitosis PowerPoint
... Why is there a limit on cell size? If a cell continues to grow, the surface area of the membrane might not be able to transport enough nutrients and waste. Transport of substances within the cell is also more difficult in larger cells. ...
... Why is there a limit on cell size? If a cell continues to grow, the surface area of the membrane might not be able to transport enough nutrients and waste. Transport of substances within the cell is also more difficult in larger cells. ...
A counter-example to Paul`s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
... A counter-example to Paul’s premise 2 is a human cancer cell, as Marquis points out. When a human cancer cell appears in my body, it is a human individual according to the criterion in premise 1: “a life is begun which is neither that of the father nor the mother; it is rather new human life with it ...
CLASSIFYING LIVING THINGS
... Choose ONE living thing. Choose ONE life function-Write ONE paragraph explaining how the function applies to the organism. How are they related? ...
... Choose ONE living thing. Choose ONE life function-Write ONE paragraph explaining how the function applies to the organism. How are they related? ...
Biology
... 9) Define each of the properties of life and give an example. Property of Life Definition Example Cellular Organization All living things are made Cells are compartmentalized. They make up tissues, up of one or more cells & which make up organs, which make up organ are organized in such a systems, w ...
... 9) Define each of the properties of life and give an example. Property of Life Definition Example Cellular Organization All living things are made Cells are compartmentalized. They make up tissues, up of one or more cells & which make up organs, which make up organ are organized in such a systems, w ...
TEST REVIEW- Cells ANSWERS 15
... 2. Name three objects that are made of cells. Answers may vary humans, plants, bacteria ...
... 2. Name three objects that are made of cells. Answers may vary humans, plants, bacteria ...
Advanced Biology
... Cytoplasm fills the interior of the cell, exclusive of the nucleus, and a plasma membrane encloses the cell and separates it from its surroundings. The plasma membrane contains several types of proteins that allow the cell to interact with its environment. ...
... Cytoplasm fills the interior of the cell, exclusive of the nucleus, and a plasma membrane encloses the cell and separates it from its surroundings. The plasma membrane contains several types of proteins that allow the cell to interact with its environment. ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... -outside of nucleus, studded with pores Nucleolus: -circular structure within nucleus -makes ribosomes Nucleoplasm: -cytoplasm inside the nucleus ...
... -outside of nucleus, studded with pores Nucleolus: -circular structure within nucleus -makes ribosomes Nucleoplasm: -cytoplasm inside the nucleus ...
PDF
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
PDF
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
... Embryonic stem cells achieve XEN state Early mammalian embryogenesis is characterised by a gradual restriction in the developmental potential of embryonic cells. By the blastocyst stage, embryonic and extra-embryonic cells have diverged in their fate and function. However, on p. 2866, Kathy Niakan a ...
[email protected]
... Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis in Brain Repair Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology University of Coimbra ...
... Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis in Brain Repair Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology University of Coimbra ...
Anchorage, cell density, and chemical growth factors affect cell
... timing of the cell division in different parts of the body in order to grow and develop normally. EX. Cells in the digestive tract and skins cells need to be replaced frequently to replace cells that have flaked off. Liver cells usually do not divide unless the liver is damaged. -Most animal cells e ...
... timing of the cell division in different parts of the body in order to grow and develop normally. EX. Cells in the digestive tract and skins cells need to be replaced frequently to replace cells that have flaked off. Liver cells usually do not divide unless the liver is damaged. -Most animal cells e ...
Cell Theory
... • Wrote the first two parts of the cell theory –1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells –2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things ...
... • Wrote the first two parts of the cell theory –1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells –2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things ...
Transport
... gases, salts and other materials necessary for life. B. Circulation – the second stage of transport. 1. When absorbed materials are moved from one area to another within an organism. 2. Materials may be moved by diffusion, and in more complex organisms, a vascular system is needed. ...
... gases, salts and other materials necessary for life. B. Circulation – the second stage of transport. 1. When absorbed materials are moved from one area to another within an organism. 2. Materials may be moved by diffusion, and in more complex organisms, a vascular system is needed. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.