What Is a Cell? - Avery County Schools
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things. A cell is the smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions that keep the thing alive. Some living things are made of only one cell-they are unicellular. People are multicellular. The human body is made of more than one hundred trillion ...
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things. A cell is the smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions that keep the thing alive. Some living things are made of only one cell-they are unicellular. People are multicellular. The human body is made of more than one hundred trillion ...
Name - Belle Vernon Area School District
... eubacteria cells cell theory enzymes deoxyribosenucleic acid adenosine triphosphate amino acids ...
... eubacteria cells cell theory enzymes deoxyribosenucleic acid adenosine triphosphate amino acids ...
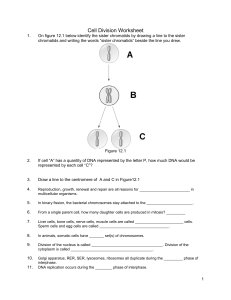
Cell Division Worksheet PDF
... C. If a somatic cell of this animal divided by mitosis, how many chromosomes would each daughter cell contain? 14. Which cell division process would normally be associated with 2n → 2n? A. Mitosis B. Meiosis Identify the process for Figure 12.3 ...
... C. If a somatic cell of this animal divided by mitosis, how many chromosomes would each daughter cell contain? 14. Which cell division process would normally be associated with 2n → 2n? A. Mitosis B. Meiosis Identify the process for Figure 12.3 ...
True or False. The cells in your body are Eukaryotic. Explain. A: True
... 17. This cell structure controls what passes in and out of the cell. A: Cell membranes are porous and allow various gasses, water, waster, food to pass into and out of the cell. 18. One way plant cells are different from animal cells is the presence of chloroplasts. Why does a plant contain these or ...
... 17. This cell structure controls what passes in and out of the cell. A: Cell membranes are porous and allow various gasses, water, waster, food to pass into and out of the cell. 18. One way plant cells are different from animal cells is the presence of chloroplasts. Why does a plant contain these or ...
Glossary of Scientific Terms
... An individual organism which contains cell populations mixed from different genetic backgrounds; can occur spontaneously (certain type of twins) or artificially (where the organism is derived from combined embryos; or embryos with introduced cells) ...
... An individual organism which contains cell populations mixed from different genetic backgrounds; can occur spontaneously (certain type of twins) or artificially (where the organism is derived from combined embryos; or embryos with introduced cells) ...
Different Kinds of Building Blocks
... together. There is the large vacuole, which is like a large bubble that holds extra water, in case it does not rain for while, or if someone forgets to water the plants. Then finally plant cells have chloroplasts that soak in sunlight, which the cell uses to make sugar. That is why plants cannot gro ...
... together. There is the large vacuole, which is like a large bubble that holds extra water, in case it does not rain for while, or if someone forgets to water the plants. Then finally plant cells have chloroplasts that soak in sunlight, which the cell uses to make sugar. That is why plants cannot gro ...
Reading Guide
... 5. Describe what a membrane receptor is and how it transmits messages across membranes. Section 3.4 – Diffusion and Osmosis 1. Describe what passive transport is. Is diffusion a form of passive transport? Explain. ...
... 5. Describe what a membrane receptor is and how it transmits messages across membranes. Section 3.4 – Diffusion and Osmosis 1. Describe what passive transport is. Is diffusion a form of passive transport? Explain. ...
Amber Hess - Magnolia High School
... electrolyte is ammonium chloride paste (DK Science 150). Ordinary dry cells are used in most flashlight batteries. These dry cells use ammonium chloride as the electrolyte. "Cells needed to supply heavier currents use zinc chloride. Alkaline cells, which last longer and can supply even heavier curre ...
... electrolyte is ammonium chloride paste (DK Science 150). Ordinary dry cells are used in most flashlight batteries. These dry cells use ammonium chloride as the electrolyte. "Cells needed to supply heavier currents use zinc chloride. Alkaline cells, which last longer and can supply even heavier curre ...
A-10209A: Enumeration of Mitotic Cells with Dual
... DNA binding dyes such as 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD), Propidium Iodide or DAPI have been commonly used in flow cytometry to measure the change in DNA content of a cell population as it transitions from G0, G1, S, G2 and M. The use of a DNA binding dye alone can only resolve the 5 Phases into 3 grou ...
... DNA binding dyes such as 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD), Propidium Iodide or DAPI have been commonly used in flow cytometry to measure the change in DNA content of a cell population as it transitions from G0, G1, S, G2 and M. The use of a DNA binding dye alone can only resolve the 5 Phases into 3 grou ...
ORGANELLE LOCATION DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
... * Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates, waste products and toxic waste.. *store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) ...
... * Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates, waste products and toxic waste.. *store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) ...
Cell Biology
... vesicles” transport materials from outside the cell to the plasma membrane to be imported) ...
... vesicles” transport materials from outside the cell to the plasma membrane to be imported) ...
File
... nucleus, and you don’t! Because of these differences I am sorry to tell you that I think we need to break up. I hope you understand. Best, Eukaryotic Cell ...
... nucleus, and you don’t! Because of these differences I am sorry to tell you that I think we need to break up. I hope you understand. Best, Eukaryotic Cell ...
Mitosis
... Why Would a Cell Divide? As cells absorb nutrients and get larger, the volume of the cell increases faster than the surface area ...
... Why Would a Cell Divide? As cells absorb nutrients and get larger, the volume of the cell increases faster than the surface area ...
... To Teacher: The students will decide on their own to implement the plans, along with the specific procedures for building the model. The students will then exchange procedures/plans with another group (two students maximum). Allow the students have total creativity for choosing the materials they wi ...
Host Defence
... tissue (or organs) for individuals, the use of autologous cells would avoid any potential immunological complications. Various classifications of cells used in tissue engineering applications: ...
... tissue (or organs) for individuals, the use of autologous cells would avoid any potential immunological complications. Various classifications of cells used in tissue engineering applications: ...
What is the difference in the functioning between rough ER and
... Rough ER is used by animal cells, while smooth ER is only used by plant cells. ...
... Rough ER is used by animal cells, while smooth ER is only used by plant cells. ...
Ecology Vocabulary Words
... surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. Provides strength and support. 15.Cell Membrane—the outside cell boundary that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. 16.Nucleus—the control center of a eukaryotic cell that directs the cell’s activities and contains DNA. 17.Mit ...
... surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. Provides strength and support. 15.Cell Membrane—the outside cell boundary that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. 16.Nucleus—the control center of a eukaryotic cell that directs the cell’s activities and contains DNA. 17.Mit ...
Cellular Hierarchy - Bibb County Schools
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
10. Plasmolysis and the effect of Osmosis on Cells
... water has a higher concentration (because it has fewer solutes) to an area where it has a lower concentration (because it has more solutes). In cells the semi-permeable membrane is the cell or plasma membrane. In plant cells this membrane is normally not seen because it is: very thin and pressed ...
... water has a higher concentration (because it has fewer solutes) to an area where it has a lower concentration (because it has more solutes). In cells the semi-permeable membrane is the cell or plasma membrane. In plant cells this membrane is normally not seen because it is: very thin and pressed ...
first question
... - Mitochondria (with drawing). Mitochondrion is a spherical or rod shaped cell organelle. It has two membranes. The outer membrane is smooth. The inner membrane produces finger like infoldings called cristae. The inner membrane has stalked particles called ATP synthase complex. The mitochondrial cav ...
... - Mitochondria (with drawing). Mitochondrion is a spherical or rod shaped cell organelle. It has two membranes. The outer membrane is smooth. The inner membrane produces finger like infoldings called cristae. The inner membrane has stalked particles called ATP synthase complex. The mitochondrial cav ...
CHAPTER - 8 CELL – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
... The nucleus is a spherical body generally found in the centre of the cell. It has a membrane called nuclear membrane. It has a smaller spherical body called nucleolus and thread like structures called chromosomes. The chromosomes carry genes which transfer characters from the parents to the off spri ...
... The nucleus is a spherical body generally found in the centre of the cell. It has a membrane called nuclear membrane. It has a smaller spherical body called nucleolus and thread like structures called chromosomes. The chromosomes carry genes which transfer characters from the parents to the off spri ...
CHAPTER ONE
... • Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack of _pancakes_____. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of _vesicles____ into the _cytosol → cell membrane_______ ...
... • Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack of _pancakes_____. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of _vesicles____ into the _cytosol → cell membrane_______ ...
John MacDonald: Chemistry & Biochemistry
... Characterizing Photoswitches to Mimic Nerve Cell Repolarization It has been shown that a quaternary ammonium structure (nitrogen bonded to four carbons), such as tetra-ethyl ammonium iodide, can block a potassium channel and therefore inhibit the depolarization of a nerve cell. By attaching this qua ...
... Characterizing Photoswitches to Mimic Nerve Cell Repolarization It has been shown that a quaternary ammonium structure (nitrogen bonded to four carbons), such as tetra-ethyl ammonium iodide, can block a potassium channel and therefore inhibit the depolarization of a nerve cell. By attaching this qua ...
surface area ÷ volume
... • Activator – identify small everyday objects in your life. What are the advantages to being small? Why are these things small? Record the thoughts of your group in your journal. • Key terms: surface area, volume ...
... • Activator – identify small everyday objects in your life. What are the advantages to being small? Why are these things small? Record the thoughts of your group in your journal. • Key terms: surface area, volume ...
slide show on “microorganisms”
... * It is usually found in stagnant water of ponds or pools *Two flagella are present at the anterior end of the cell. *A single large cup shaped chloroplast is also present at the broader end of the chlamydomonas. *Two liquid filled spaces called, contractile vacuole are found at the anterior end of ...
... * It is usually found in stagnant water of ponds or pools *Two flagella are present at the anterior end of the cell. *A single large cup shaped chloroplast is also present at the broader end of the chlamydomonas. *Two liquid filled spaces called, contractile vacuole are found at the anterior end of ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.