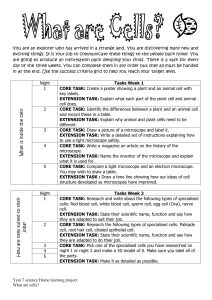
Year 7 science Home learning project What are cells? You are an
... are going to produce an information pack detailing your finds. There is a task for every day of the three weeks. You can complete them in any order but they all must be handed in at the end. Use the success criteria grid to help you reach your target level. ...
... are going to produce an information pack detailing your finds. There is a task for every day of the three weeks. You can complete them in any order but they all must be handed in at the end. Use the success criteria grid to help you reach your target level. ...
Cell Keywords - No Brain Too Small
... 38. Golgi body 39. Guanine 40. Induced Fit Model 41. Ion Exchange Pump 42. Lactic Acid ...
... 38. Golgi body 39. Guanine 40. Induced Fit Model 41. Ion Exchange Pump 42. Lactic Acid ...
Scavenger Hunt
... 6. This organelle is sometimes referred to as the packaging center of the cell. It accepts vesicles from the ER containing proteins, modifies the proteins then repackages them into new vesicles for transport. 7. This organelle has its own double layer membrane surrounding it as the most importa ...
... 6. This organelle is sometimes referred to as the packaging center of the cell. It accepts vesicles from the ER containing proteins, modifies the proteins then repackages them into new vesicles for transport. 7. This organelle has its own double layer membrane surrounding it as the most importa ...
Chapter 3 Study Outline
... concentration. Requires ____________ proteins: (pumps). Also requires energy in the form of _______________. Why would the body want to spend energy to acquire (or get rid of) something? Endocytosis and Exocytosis: In ________________ molecules that are too large to be transported by other means are ...
... concentration. Requires ____________ proteins: (pumps). Also requires energy in the form of _______________. Why would the body want to spend energy to acquire (or get rid of) something? Endocytosis and Exocytosis: In ________________ molecules that are too large to be transported by other means are ...
Cellular Transport
... o Engulfing – cell membrane surrounds a particle, engulfs it, and a vacuole forms o Transport protein – ‘picks up’ molecules from outside the cell Concentration – the amount of molecules in a specified area Concentration gradient – a difference in amount of molecules between two areas Equilibr ...
... o Engulfing – cell membrane surrounds a particle, engulfs it, and a vacuole forms o Transport protein – ‘picks up’ molecules from outside the cell Concentration – the amount of molecules in a specified area Concentration gradient – a difference in amount of molecules between two areas Equilibr ...
Plant Tissues-PPT
... Meristems, Simple Tissues, & Complex Tissues Many of the figures found in this presentation are from the internet site http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/130/ and a CD entitled “Plant Anatomy” by Richard Crang & Andrey Vassilyev published by McGraw Hill. ...
... Meristems, Simple Tissues, & Complex Tissues Many of the figures found in this presentation are from the internet site http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/130/ and a CD entitled “Plant Anatomy” by Richard Crang & Andrey Vassilyev published by McGraw Hill. ...
Cell Powerpoint
... A group of cells working together A group of tissues working together A group of systems working together A group of organs working together ...
... A group of cells working together A group of tissues working together A group of systems working together A group of organs working together ...
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
... 2. External regulators direct ells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. ...
... 2. External regulators direct ells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. ...
Microlife
... removal (Osmosis and Diffusion) Cells can become specialized to perform certain tasks Multicellular animals have better survival chance; (If you are single celled organism with cell flaw or cell damaged you die: Prokaryote/bacteria) In multicellular organisms cells can replaced when damaged: However ...
... removal (Osmosis and Diffusion) Cells can become specialized to perform certain tasks Multicellular animals have better survival chance; (If you are single celled organism with cell flaw or cell damaged you die: Prokaryote/bacteria) In multicellular organisms cells can replaced when damaged: However ...
Cell Transport Review Worksheet
... Integral proteins with carbohydrates (sugars) attached that stick out on the exterior surface of cell membranes help recognize “self” and are called _______________________. A. amino acids B. lipoproteins C. glycoproteins D. monosaccharides One difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that _ ...
... Integral proteins with carbohydrates (sugars) attached that stick out on the exterior surface of cell membranes help recognize “self” and are called _______________________. A. amino acids B. lipoproteins C. glycoproteins D. monosaccharides One difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that _ ...
File
... Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
... Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
Cell Keywords - No Brain Too Small
... g) anchored in the cell membrane and extending outside the cell used for motility h) Involved in water regulation. i) Energy required to get reactions started j) Site for substrate to bind to k) Requires energy & against concentration gradient l) Complimentary to thymine m) Energy molecule n) Reacti ...
... g) anchored in the cell membrane and extending outside the cell used for motility h) Involved in water regulation. i) Energy required to get reactions started j) Site for substrate to bind to k) Requires energy & against concentration gradient l) Complimentary to thymine m) Energy molecule n) Reacti ...
Cell Structure
... 1. Different cells have different specialized structures and different specialized functions. The specialized function of the cell depends on the unique environment of the cell. Ex. Fresh water vs. salt water ...
... 1. Different cells have different specialized structures and different specialized functions. The specialized function of the cell depends on the unique environment of the cell. Ex. Fresh water vs. salt water ...
The Basic Structure of Cells
... Cell theory: The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of living things. There are many different types of cells but they are similar in their basic ...
... Cell theory: The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of living things. There are many different types of cells but they are similar in their basic ...
8 active studying tips for the Cell Structure and
... 8. Get together with a friend. One person reads the characteristics of one of the organelles in the first person singular, one at a time: “I have a double membrane.” After each fact, the other person tries to guess what the cell part is. Make this harder by starting with more general characteristics ...
... 8. Get together with a friend. One person reads the characteristics of one of the organelles in the first person singular, one at a time: “I have a double membrane.” After each fact, the other person tries to guess what the cell part is. Make this harder by starting with more general characteristics ...
The Cell as a System - Center for Science of Information
... • How will we define and characterize a biological system? • How can we obtain the information on components of the system (qualitative and quantitative; static and dynamical)? Technologies and computational methods? • What mechanisms can we infer from the system behavior? • What are realistic model ...
... • How will we define and characterize a biological system? • How can we obtain the information on components of the system (qualitative and quantitative; static and dynamical)? Technologies and computational methods? • What mechanisms can we infer from the system behavior? • What are realistic model ...
plasma membrane
... have no organelles & no nucleus. All the cell chemistry is carried on in the cells cytoplasm. DNA floats in the cytoplasm in long strings or coils. Eukaryotes: have internal membrane covered organelles. Also have a nucleus where DNA is found during most of the cells life. Kingdom Plantae, Animal ...
... have no organelles & no nucleus. All the cell chemistry is carried on in the cells cytoplasm. DNA floats in the cytoplasm in long strings or coils. Eukaryotes: have internal membrane covered organelles. Also have a nucleus where DNA is found during most of the cells life. Kingdom Plantae, Animal ...
Cell Functions Test Review
... • Nucleus: control center of a cell; contains DNA • Nuclear membrane: surrounds nucleus – determines what goes in/out of nucleus ...
... • Nucleus: control center of a cell; contains DNA • Nuclear membrane: surrounds nucleus – determines what goes in/out of nucleus ...
Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell.
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. Organisms share the following characteristics: • organization • ability to grow and develop • ability to respond • ability to reproduce ...
... All living things are made up of one or more cells. Organisms share the following characteristics: • organization • ability to grow and develop • ability to respond • ability to reproduce ...
docs/DatatoBiology - Center for Science of Information
... • How will we define and characterize a biological system? • How can we obtain the information on components of the system (qualitative and quantitative; static and dynamical)? Technologies and computational methods? • What mechanisms can we infer from the system behavior? • What are realistic model ...
... • How will we define and characterize a biological system? • How can we obtain the information on components of the system (qualitative and quantitative; static and dynamical)? Technologies and computational methods? • What mechanisms can we infer from the system behavior? • What are realistic model ...
Notch 1 and pre-T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T
... • First discovered in Drosophila but is highly conserved • Homologs have been found in C.Elegans and in humans ...
... • First discovered in Drosophila but is highly conserved • Homologs have been found in C.Elegans and in humans ...
Life Science Review
... • 4. Recognize that within cells, many of the basic functions of organisms (e.g., extracting energy from food and getting rid of waste) are carried out. The way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms. • 6. Identify the general functions of the major systems of the human body (dig ...
... • 4. Recognize that within cells, many of the basic functions of organisms (e.g., extracting energy from food and getting rid of waste) are carried out. The way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms. • 6. Identify the general functions of the major systems of the human body (dig ...
pogil 9
... mitochondria or chloroplasts. In the nucleus you find two circular chromosomes. Propose a series of events that led to evolution of this organism. ...
... mitochondria or chloroplasts. In the nucleus you find two circular chromosomes. Propose a series of events that led to evolution of this organism. ...
REPRODUCTION Part 1
... When an organism passes all of its DNA onto its offspring and the offspring are identical to the parent, it is called asexual reproduction. One-celled organisms usually reproduce asexually. Their cells divide to form two identical cells. Protists, fungi, and some plants and animals can reprodu ...
... When an organism passes all of its DNA onto its offspring and the offspring are identical to the parent, it is called asexual reproduction. One-celled organisms usually reproduce asexually. Their cells divide to form two identical cells. Protists, fungi, and some plants and animals can reprodu ...
Website #1: http://sheppardsoftware.com/health/anatomy/cell/index
... 8. Nucleus is called the ______________________ of the cell. It is a large __________ spot in eukaryotic cells. It ___________________ all cell activity. The nuclear membrane has many _________________. The thick ropy strands are the _______________________. The large solid spot is the _____________ ...
... 8. Nucleus is called the ______________________ of the cell. It is a large __________ spot in eukaryotic cells. It ___________________ all cell activity. The nuclear membrane has many _________________. The thick ropy strands are the _______________________. The large solid spot is the _____________ ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.























