Answers to Review Questions Chapter 24 Review Questions Page
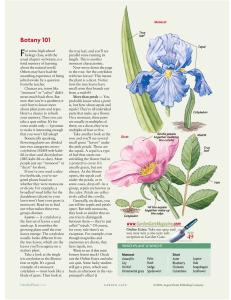
... The arrangement of leaves on a stem is the phyllotaxy. In plants with opposite leaf attachment, such as dogwood and maple, two leaves are attached at each node. In alternate leaf arrangement, such as in poplar and aspen, a single leaf appears at each node. Most plants have the alternate leaf arrange ...
... The arrangement of leaves on a stem is the phyllotaxy. In plants with opposite leaf attachment, such as dogwood and maple, two leaves are attached at each node. In alternate leaf arrangement, such as in poplar and aspen, a single leaf appears at each node. Most plants have the alternate leaf arrange ...
Angiosperms - OpenStax CNX
... found in monocots. In palm trees, vascular and parenchyma tissues produced by the primary and secondary thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern mono ...
... found in monocots. In palm trees, vascular and parenchyma tissues produced by the primary and secondary thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern mono ...
Diversity and Evolution of Monocots
... of monocots in shady understory conditions (T. Givnish, 1984, 1999, 2002) ...
... of monocots in shady understory conditions (T. Givnish, 1984, 1999, 2002) ...
Chapter 23a-Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from
... Nymphaea odorata subsp. odorata [syn. N. odorata] ...
... Nymphaea odorata subsp. odorata [syn. N. odorata] ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily Opuntioideae
... reversals with net-venation!] – sheathing base ...
... reversals with net-venation!] – sheathing base ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... Significant features: leaves 3-ranked, sheaths usually open Special uses: leaves used to weave rush baskets; ...
... Significant features: leaves 3-ranked, sheaths usually open Special uses: leaves used to weave rush baskets; ...
SEED PLANTS: ANGIOSPERMS First land plants appeared
... The paleoherbs are a small group of flowering plants which have traditionally been classified as dicots, but which have many characters in common with monocots. “Even after the general acceptance of Monocots and Dicots as the primary groups of flowering plants, botanists did not always agree upon th ...
... The paleoherbs are a small group of flowering plants which have traditionally been classified as dicots, but which have many characters in common with monocots. “Even after the general acceptance of Monocots and Dicots as the primary groups of flowering plants, botanists did not always agree upon th ...
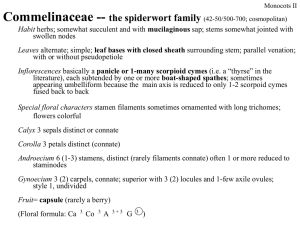
Commelinaceae -- the spiderwort family (42-50/500-700
... vegetatively for years (up to 150 yrs), flower, and then die. This has caused problems in the past (particularly for pandas) because clones can spread over large areas of land, and when it is time for that plant to flower all the clones simultaneously flower and die. Ornamental uses for grasses incl ...
... vegetatively for years (up to 150 yrs), flower, and then die. This has caused problems in the past (particularly for pandas) because clones can spread over large areas of land, and when it is time for that plant to flower all the clones simultaneously flower and die. Ornamental uses for grasses incl ...
Comp 6a-2 Plant Packet
... monocots start out with one seed leaf, while dicots have two. The technical word for seed leaf is cotyledon: you can find it on the coloring sheet; it is the first leaf to emerge from a developing seed. As a seed, both monocots and dicots are covered by a seed coat. The seed consists of the outside ...
... monocots start out with one seed leaf, while dicots have two. The technical word for seed leaf is cotyledon: you can find it on the coloring sheet; it is the first leaf to emerge from a developing seed. As a seed, both monocots and dicots are covered by a seed coat. The seed consists of the outside ...
owen BOTANY - Kowenscience.com
... have numerous roots of near equal size growing in many directions(Monocots) ...
... have numerous roots of near equal size growing in many directions(Monocots) ...
owen BOTANY - Kowenscience.com
... Occurs when a grain of pollen lands on the stigma. If the pollen is from the right kind of plant, and lands on the flower, the pollen grain will break open and its content produce a tube that grows down through the style into the ovule. ...
... Occurs when a grain of pollen lands on the stigma. If the pollen is from the right kind of plant, and lands on the flower, the pollen grain will break open and its content produce a tube that grows down through the style into the ovule. ...
BROMELIACEAE
... HABITAT: prominent epiphytes, but also terrestial plants CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC OF MONOCOTS: herbaceous, sympodial plants; vascular bundles in stem scattered, closed [no interfascicular cambium developing]; tertiary veins without free endings, leaf base sh eathing; pollen monosulcate, gynoecium three ...
... HABITAT: prominent epiphytes, but also terrestial plants CHARACTERS DIAGNOSTIC OF MONOCOTS: herbaceous, sympodial plants; vascular bundles in stem scattered, closed [no interfascicular cambium developing]; tertiary veins without free endings, leaf base sh eathing; pollen monosulcate, gynoecium three ...
Chapter 5 Section 3:
... Pollen falls from anther into stigma, pollen falls after an animal brushes against anther, pollen can travel with insects of animals as they pass by 10. What is fertilization? Once pollen is on stigma, it travels down the style to the ovary where pollen meets the egg (ovule) and form the zygote that ...
... Pollen falls from anther into stigma, pollen falls after an animal brushes against anther, pollen can travel with insects of animals as they pass by 10. What is fertilization? Once pollen is on stigma, it travels down the style to the ovary where pollen meets the egg (ovule) and form the zygote that ...
Comparing Monocot and Dicot Pants
... • Find out what a monocot plant and a dicot plant is. • Create a table to compare the structures of these two classes of plant. • In your table you should compare seeds (cotyledons), stem (vascular bundles), flower, leaf (vein pattern) and ...
... • Find out what a monocot plant and a dicot plant is. • Create a table to compare the structures of these two classes of plant. • In your table you should compare seeds (cotyledons), stem (vascular bundles), flower, leaf (vein pattern) and ...
Grasses and Forbs: A Major Difference
... Student Page 1: The Two Great Classes of Angiosperms (Flowering Plants) When studying a prairie, we must be able to identify the plants that are found there. Any method of identification that allows us to narrow the possibilities as we look at an unknown plant in the field is extremely useful. Two ...
... Student Page 1: The Two Great Classes of Angiosperms (Flowering Plants) When studying a prairie, we must be able to identify the plants that are found there. Any method of identification that allows us to narrow the possibilities as we look at an unknown plant in the field is extremely useful. Two ...
Hesperaloe red yucca
... The leaves of monocots are almost always long and slender, much longer than they are wide. The veins are parallel to the leaf edges. Grasses, agave, and yucca are monocots. In contrast, the leaves ...
... The leaves of monocots are almost always long and slender, much longer than they are wide. The veins are parallel to the leaf edges. Grasses, agave, and yucca are monocots. In contrast, the leaves ...
Comparing Monocot and Dicot Pants
... two classes of plant. • In your table you should compare seeds, stem, flower, leaf and root. • Page 397 in your text book will help you. • There are other pages that may be helpful as well. You will need to look these up. • The micro-slide-viewer contains a slides with some great images of monocot a ...
... two classes of plant. • In your table you should compare seeds, stem, flower, leaf and root. • Page 397 in your text book will help you. • There are other pages that may be helpful as well. You will need to look these up. • The micro-slide-viewer contains a slides with some great images of monocot a ...
origin of Angiosperms
... Paleoherb Hypothesis: primitive angiosperms with short life cycle and mixed monocot- / dicot-traits as origin (Taylor und Hickey). Pro: 18S, flower morphology Woody Magnoliid Hypothese: Magnolia like trees as origin (Doyle und Donoghue). Pro: non-fused petals, no sepals, whorls of flower organs, liv ...
... Paleoherb Hypothesis: primitive angiosperms with short life cycle and mixed monocot- / dicot-traits as origin (Taylor und Hickey). Pro: 18S, flower morphology Woody Magnoliid Hypothese: Magnolia like trees as origin (Doyle und Donoghue). Pro: non-fused petals, no sepals, whorls of flower organs, liv ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily Opuntioideae
... Significant features: among the most specialized of all angiosperm flowers Special uses: many ornamentals; Vanilla ...
... Significant features: among the most specialized of all angiosperm flowers Special uses: many ornamentals; Vanilla ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... Fruit type is the achene: very important in the taxonomy of the family. ...
... Fruit type is the achene: very important in the taxonomy of the family. ...
Plant Kingdom
... How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. ...
... How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. ...
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (/ˈmɒnɵˈkɒtɪˈliːdən/), also known as monocots, are plants whose seeds typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which flowering plants (or angiosperms) have traditionally been divided, the rest of the flowering plants having two cotyledons and being classed as dicotyledons, or dicots. However, molecular phylogenetic research has shown that the monocots form a monophyletic group – a clade – since they comprise all the descendants of a common ancestor, but that dicots do not form a monophyletic group. Monocots have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called ""monocots"" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank.According to the IUCN there are 59,300 species of monocots. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses, Poaceae, who are economically the most important family of monocots: in agriculture the majority of the biomass produced comes from monocots. These include not only major grains (rice, wheat, maize, etc.), but also forage grasses, sugar cane, and the bamboos. Other economically important monocot cultures include various palms (Arecaceae), bananas (Musaceae), gingers and their relatives, turmeric and cardamom (Zingiberaceae) and onions (Amaryllidaceae), which includes such ubiquitously used vegetables as onions and garlic. Additionally, plants cultivated for their blooms are also from the monocot group, notably lilies, daffodils, irises, amaryllis, cannas, bluebells and tulips.