The organization of animal and plant cells
... Golgi apparatus, vesicles and other organelles derived from them, and the plasma membrane. Many materials are moved around the cell by the endomembrane system, including some proteins. ...
... Golgi apparatus, vesicles and other organelles derived from them, and the plasma membrane. Many materials are moved around the cell by the endomembrane system, including some proteins. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
... – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
Modern cell theory
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
... surface of the cell which separates the cell from the environment. The cytoplasm is the aqueous content within the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane : It is like any other membrane in the cell but it plays a very important function. It forms the border of a cell, so it is also called the cell membra ...
IMMS 1 Revision
... ● Hydrophobic forces - as uncharged and non-polar side chain repel water, they tend toward a protein core. ● Ionic bonds - between fully/partially charged groups ...
... ● Hydrophobic forces - as uncharged and non-polar side chain repel water, they tend toward a protein core. ● Ionic bonds - between fully/partially charged groups ...
TEKS 5 - Online Learning Exchange
... surrounded by a thin flexible barrier called a cell membrane. There are two basic categories of cells based on whether they contain a nucleus. The nucleus (plural: nuclei) is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains DNA. Eukaryotes are cells that enclose their DNA in nuclei. Prokaryotes are ...
... surrounded by a thin flexible barrier called a cell membrane. There are two basic categories of cells based on whether they contain a nucleus. The nucleus (plural: nuclei) is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains DNA. Eukaryotes are cells that enclose their DNA in nuclei. Prokaryotes are ...
Mitosis – PowerPoint
... History of Understanding Cancer Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) – First to recognize ...
... History of Understanding Cancer Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) – First to recognize ...
Slide 1
... Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Site of ribosome synthesis Nuclear Membrane – Surrounds the nucleus. Cell Membrane – Membrane surrounding the organelles and the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
... Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Site of ribosome synthesis Nuclear Membrane – Surrounds the nucleus. Cell Membrane – Membrane surrounding the organelles and the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
2.-6 Lipid Bilayer of the Cell Membrane
... proteins is found in the DNA (your genes) – transcribe that information onto a messenger RNA molecule • each sequence of 3 nucleotides in DNA is called base triplet • each base triplet is transcribed as 3 RNA nucleotides (codon) ...
... proteins is found in the DNA (your genes) – transcribe that information onto a messenger RNA molecule • each sequence of 3 nucleotides in DNA is called base triplet • each base triplet is transcribed as 3 RNA nucleotides (codon) ...
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
... made out of nucleic acids that carries the genetic information for the organism i. Definite number of chromosomes per organism -->Example: Humans have 23 pair or 46 total c. Nucleolus: Small, single-membraned organelle located inside of the nucleus that produces ribosomes (ribosomes manufacture prot ...
... made out of nucleic acids that carries the genetic information for the organism i. Definite number of chromosomes per organism -->Example: Humans have 23 pair or 46 total c. Nucleolus: Small, single-membraned organelle located inside of the nucleus that produces ribosomes (ribosomes manufacture prot ...
CELL FEATURES (SECTION 3-2)
... -no _________________, no internal compartments -Early prokaryotes lived __________________ years ago -Modern prokaryotes are ________________ -Bacteria cell parts cell wall (composed of ____________________ & _________________) plasma membrane Flagella – enables __________________ DNA – in ________ ...
... -no _________________, no internal compartments -Early prokaryotes lived __________________ years ago -Modern prokaryotes are ________________ -Bacteria cell parts cell wall (composed of ____________________ & _________________) plasma membrane Flagella – enables __________________ DNA – in ________ ...
A Robust Approach for In Vitro Generation of Functional Beta Cells
... i.e. in vitro generated cells that can secrete insulin properly in response to physiological levels of glucose. The production of such cells represents the best hope of curing diabetes. Accordingly, methods for obtaining fully functional beta cells and using such cells for the treatment of diabetes ...
... i.e. in vitro generated cells that can secrete insulin properly in response to physiological levels of glucose. The production of such cells represents the best hope of curing diabetes. Accordingly, methods for obtaining fully functional beta cells and using such cells for the treatment of diabetes ...
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
... The fermentation-only archaeon has taken in a bacterial cell and a cyanobacterial cell as endosymbionts By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbi ...
... The fermentation-only archaeon has taken in a bacterial cell and a cyanobacterial cell as endosymbionts By not digesting them completely, but removing the cell wall, the archaeon has gained two gigantic biochemical pathways: respiration and photosynthesis By moving critical genes from each endosymbi ...
Cells
... Golgi bodies: These help package products in the cell and then give them out around the cell. Look at it like this, you wrap a present and then give it to your friend. Well, that is what golgi bodies do. ...
... Golgi bodies: These help package products in the cell and then give them out around the cell. Look at it like this, you wrap a present and then give it to your friend. Well, that is what golgi bodies do. ...
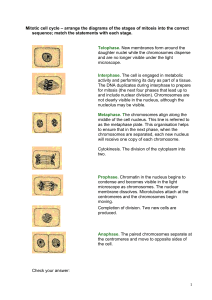
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into the correct sequence; match the statements with each stage. ...
... Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into the correct sequence; match the statements with each stage. ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... Both cilia and flagella are hair-like organelles which extend from the surface of many animal cells. the structure is identical in both, except that flagella are longer and whiplike and cilia are shorter. There are usually only a few flagella on a cell, while cilia may cover the entire surface of a ...
... Both cilia and flagella are hair-like organelles which extend from the surface of many animal cells. the structure is identical in both, except that flagella are longer and whiplike and cilia are shorter. There are usually only a few flagella on a cell, while cilia may cover the entire surface of a ...
Biography - Comtecmed
... The bone marrow is the natural niche of normal and malignant plasma cells. Mainly through tight cellular contacts and secretion of cytokines The Bone marrow niche appear essential for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of malignant Multiple Myeloma (MM) cells. Via interactions through ...
... The bone marrow is the natural niche of normal and malignant plasma cells. Mainly through tight cellular contacts and secretion of cytokines The Bone marrow niche appear essential for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of malignant Multiple Myeloma (MM) cells. Via interactions through ...
cell membrane - McEachern High School
... • Hydrophobic (nonpolar) • form inner layer of cell membrane ...
... • Hydrophobic (nonpolar) • form inner layer of cell membrane ...
Biology_Plant & Animal Cell Notes_06
... Changes chemical energy in food to compounds more convenient for cell to use Has 2 membranes Outer- surrounds the organelle Inner- increases surface area because of folds; this is where cellular respiration takes place; folds are called cristae ...
... Changes chemical energy in food to compounds more convenient for cell to use Has 2 membranes Outer- surrounds the organelle Inner- increases surface area because of folds; this is where cellular respiration takes place; folds are called cristae ...
food proteins
... • modifying the texture of low-fat milk and meat products • restructuring fresh meat and fish • enhancing the sensory quality and storage stability of high-fibre and ...
... • modifying the texture of low-fat milk and meat products • restructuring fresh meat and fish • enhancing the sensory quality and storage stability of high-fibre and ...
Unit 2 pairs test answer key True/False 1. T 2. T 3. F
... In prophase, the cell’s chromatin tightens into chromosomes. Near the end of this stage, the nuclear envelope breaks down and disappears. Finally, the spindle starts to form. 29. C If a cell continues to grow, the ratio of surface area to volume will decrease will decrease and have difficulty supply ...
... In prophase, the cell’s chromatin tightens into chromosomes. Near the end of this stage, the nuclear envelope breaks down and disappears. Finally, the spindle starts to form. 29. C If a cell continues to grow, the ratio of surface area to volume will decrease will decrease and have difficulty supply ...
GENOME GENE EXPRESSION
... activators (transcription factors) eukaryotic genes have one or more enhancers (DNA sequences associated with the gene being regulated, responsible for increasing "enhancing" transcription levels, and for regulating cell- or tissueAnimation of transcription: specific transcription) http://bcs.whfre ...
... activators (transcription factors) eukaryotic genes have one or more enhancers (DNA sequences associated with the gene being regulated, responsible for increasing "enhancing" transcription levels, and for regulating cell- or tissueAnimation of transcription: specific transcription) http://bcs.whfre ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... cheese, the body breaks down the proteins into smaller molecules. What is supplied to cells when the body breaks down proteins? A. amino acids B. nucleic acids C. phospholipids D. carbohydrates 10. What type of cell has membrane-bound organelles? A. eukaryotic cells B. prokaryotic cells C. both prok ...
... cheese, the body breaks down the proteins into smaller molecules. What is supplied to cells when the body breaks down proteins? A. amino acids B. nucleic acids C. phospholipids D. carbohydrates 10. What type of cell has membrane-bound organelles? A. eukaryotic cells B. prokaryotic cells C. both prok ...
Document
... • Living things are given a two-part scientific name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never ...
... • Living things are given a two-part scientific name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never ...