Chapter 12 - FIU Faculty Websites
... The protein clathrin helps to internalize receptors bound to their cargo. Fusion of internal membranes with the plasma membrane allows the release of molecules, such as neurotransmitters, from the cell. The internalization of iron-bound transferrin in association with the transferrin receptor is a e ...
... The protein clathrin helps to internalize receptors bound to their cargo. Fusion of internal membranes with the plasma membrane allows the release of molecules, such as neurotransmitters, from the cell. The internalization of iron-bound transferrin in association with the transferrin receptor is a e ...
Induction of Sequence-Specific DNA
... There are a family of proteins called Stat (signal transducers and activators of transcription) proteins, which include Statl and Stat2, that have been identified through the study of transcriptional regulation in response to stimulation by interferon-a (IFN-a) and IFN-y.’”*’ There are an increasing ...
... There are a family of proteins called Stat (signal transducers and activators of transcription) proteins, which include Statl and Stat2, that have been identified through the study of transcriptional regulation in response to stimulation by interferon-a (IFN-a) and IFN-y.’”*’ There are an increasing ...
DNA-Bound Fos Proteins Activate Transcription in Yeast
... and possess an affinity for DNA (Donner et al., 1982; Watt et al., 1985; Renz et al., 1987). One plausible idea for the Fos proteins is that they exert their effects by altering gene expression (see, for example, Varmus, 1987). Similarly, it is possible that Myc proteins might exert some of their ef ...
... and possess an affinity for DNA (Donner et al., 1982; Watt et al., 1985; Renz et al., 1987). One plausible idea for the Fos proteins is that they exert their effects by altering gene expression (see, for example, Varmus, 1987). Similarly, it is possible that Myc proteins might exert some of their ef ...
Matching Terms Test
... pocket folds for large molecules to enter the cell basic substance for life produces, stores & packages secretion for discharge from the cell cell structures that help with function creates even cell division allows for transport of materials forms chromosomes contain digestive enzymes that destroy ...
... pocket folds for large molecules to enter the cell basic substance for life produces, stores & packages secretion for discharge from the cell cell structures that help with function creates even cell division allows for transport of materials forms chromosomes contain digestive enzymes that destroy ...
Meiosis: Its Origin According to the Viral
... lated organisms. These three organisms were, an archaeal ancestor of the eukaryotic cyto‐ plasm, an alpha-proteobacterial ancestor of the mitochondria and a viral ancestor of the nucleus. [20] Although it is now widely accepted that the eukaryotic mitochondria is descend‐ ed from an endosymbiotic ba ...
... lated organisms. These three organisms were, an archaeal ancestor of the eukaryotic cyto‐ plasm, an alpha-proteobacterial ancestor of the mitochondria and a viral ancestor of the nucleus. [20] Although it is now widely accepted that the eukaryotic mitochondria is descend‐ ed from an endosymbiotic ba ...
Avoidance of Four-way Junctions and
... 1987; Lloyd and Traas, 1988). Although actin filaments, like the MTs, seem to disappear from the PPB by metaphase, the nucleus-radiating actin filaments in the phragmosomal plane remain. In the present paper, we examine the relationship between the nucleus-radiating MTs and the cortical MTs of the P ...
... 1987; Lloyd and Traas, 1988). Although actin filaments, like the MTs, seem to disappear from the PPB by metaphase, the nucleus-radiating actin filaments in the phragmosomal plane remain. In the present paper, we examine the relationship between the nucleus-radiating MTs and the cortical MTs of the P ...
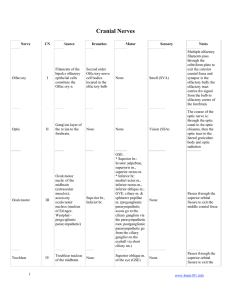
Cranial Nerves
... Exits the posterior cranial fossa by passing through the hypoglossal canal; the superior root of the ansa cervicalis travels with the hypoglossal n. for a short distance ...
... Exits the posterior cranial fossa by passing through the hypoglossal canal; the superior root of the ansa cervicalis travels with the hypoglossal n. for a short distance ...
Latrunculin A Induced Perturbation of the Actin Cytoskeleton
... 1998, Chen et al. 2003, Zuin et al. 2005, Belfield et al. 2014, Biswas and Ghosh, 2015). The pap1 gene encodes a bZIP domain containing transcription factor that shares similarity with the mammalian c-Jun protein (a component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex involved in cell growth, differen ...
... 1998, Chen et al. 2003, Zuin et al. 2005, Belfield et al. 2014, Biswas and Ghosh, 2015). The pap1 gene encodes a bZIP domain containing transcription factor that shares similarity with the mammalian c-Jun protein (a component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex involved in cell growth, differen ...
Cell Membrane - WasmundScience
... external fluid is engulfed. Receptor-mediated endocytosis occurs when the material to be transported binds to certain specific molecules in the membrane. Examples include the transport of insulin and cholesterol into animal cells. ...
... external fluid is engulfed. Receptor-mediated endocytosis occurs when the material to be transported binds to certain specific molecules in the membrane. Examples include the transport of insulin and cholesterol into animal cells. ...
Cell Membrane
... external fluid is engulfed. Receptor-mediated endocytosis occurs when the material to be transported binds to certain specific molecules in the membrane. Examples include the transport of insulin and cholesterol into animal cells. ...
... external fluid is engulfed. Receptor-mediated endocytosis occurs when the material to be transported binds to certain specific molecules in the membrane. Examples include the transport of insulin and cholesterol into animal cells. ...
Microbial Discovery Activity
... cytoplasm and ribosomes. For example, if there are 24 students in your class, with 8 groups of 3 students, then one must prepare 8 cards that say “DNA”, 8 cards that say “cytoplasm”, etc. Prepare multiple copies of other cells parts, as multiple groups may wish to have “pilus” or “LPS”. The teacher ...
... cytoplasm and ribosomes. For example, if there are 24 students in your class, with 8 groups of 3 students, then one must prepare 8 cards that say “DNA”, 8 cards that say “cytoplasm”, etc. Prepare multiple copies of other cells parts, as multiple groups may wish to have “pilus” or “LPS”. The teacher ...
7-3 Cell Boundaries - River Dell Regional School District
... b. remain in high concentration outside the cell. c. move by diffusion from outside to inside the cell. d. cause water to enter the cell by osmosis. Slide 30 of 47 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... b. remain in high concentration outside the cell. c. move by diffusion from outside to inside the cell. d. cause water to enter the cell by osmosis. Slide 30 of 47 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Ch. 27 & 28 Notes
... 27.1 ~ Structural, functional, and genetic adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success ...
... 27.1 ~ Structural, functional, and genetic adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success ...
Cell Membranes
... or more positive than the outside of the cell? If there is a glycocalyx (sugar bundle) on the outside of the cell, what does it do to the charge on the OUTSIDE of the cell membrane? What are the three types of Carbohydrates? What are the functions of the Carbohyrates? ...
... or more positive than the outside of the cell? If there is a glycocalyx (sugar bundle) on the outside of the cell, what does it do to the charge on the OUTSIDE of the cell membrane? What are the three types of Carbohydrates? What are the functions of the Carbohyrates? ...
Targeted Stimuli-Responsive Dextran Conjugates for Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocytes
... types or organs via proteins, specifically, lectinmediated targeting holds potential due to the high specificity and affinity of receptor-ligand interactions, rapid internalization, and relative ease of processing. Dextran, a commercially available, biodegradable polymer has been conjugated to doxor ...
... types or organs via proteins, specifically, lectinmediated targeting holds potential due to the high specificity and affinity of receptor-ligand interactions, rapid internalization, and relative ease of processing. Dextran, a commercially available, biodegradable polymer has been conjugated to doxor ...
Motor Components of the Cranial Nerves
... The ascending fibers from the RF end in the intralaminar thalamic nuclei. Some fibers also end in the hypothalamus. The ascending reticular connections are of particular importance for the general level of activity of the cerebral cortex. Afferents. Spinoreticular fibers. They ascend in the ventral ...
... The ascending fibers from the RF end in the intralaminar thalamic nuclei. Some fibers also end in the hypothalamus. The ascending reticular connections are of particular importance for the general level of activity of the cerebral cortex. Afferents. Spinoreticular fibers. They ascend in the ventral ...
In Plant and Animal Cells, Detergent-Resistant
... postulated to explain the difference in plasma membrane organization of polarized epithelial cells and differential targeting of lipids and proteins to their apical and baso-lateral sides (Simons and van Meer, 1988; Brown and Rose, 1992). Rafts, areas enriched in certain lipids (cholesterol and sphi ...
... postulated to explain the difference in plasma membrane organization of polarized epithelial cells and differential targeting of lipids and proteins to their apical and baso-lateral sides (Simons and van Meer, 1988; Brown and Rose, 1992). Rafts, areas enriched in certain lipids (cholesterol and sphi ...
S-layer and cytoplasmic membrane – exceptions from the typical
... cell wall polymers and structures. Members of the Thermoplasmatales like Ferroplasma acidophilum completely lack a cell wall, despite growing under harsh conditions like elevated temperatures and low pH. It is therefore thought that a glycocalyx, lipoglycans, or membrane-associated glycoproteins sub ...
... cell wall polymers and structures. Members of the Thermoplasmatales like Ferroplasma acidophilum completely lack a cell wall, despite growing under harsh conditions like elevated temperatures and low pH. It is therefore thought that a glycocalyx, lipoglycans, or membrane-associated glycoproteins sub ...
Biological Membranes and Transport
... Polymerization is driven by ATP hydrolysis and occurs at the (+) end of the filament. Microfilaments are involved in cytoplasmic streaming, ameboid movement, and muscle contraction. 2. The second type of fibers are the INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS. There are six different types of intermediate filament pr ...
... Polymerization is driven by ATP hydrolysis and occurs at the (+) end of the filament. Microfilaments are involved in cytoplasmic streaming, ameboid movement, and muscle contraction. 2. The second type of fibers are the INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS. There are six different types of intermediate filament pr ...
Ribosomal proteins L5 and L15 Ivailo Simoff in vivo
... Protein synthesis is a complex, highly regulated and energy consuming process, during which a large ribonucleoprotein particle called the ribosome, synthesizes new proteins, according to the specification laid down in the genes. The eukaryotic ribosome consists of two unequal parts called: small and ...
... Protein synthesis is a complex, highly regulated and energy consuming process, during which a large ribonucleoprotein particle called the ribosome, synthesizes new proteins, according to the specification laid down in the genes. The eukaryotic ribosome consists of two unequal parts called: small and ...
HIF-2α phosphorylation by CK1δ promotes erythropoietin secretion
... cause any significant change in the in vitro phosphorylation by CK1δ (Fig. S2A). Taken together, our analysis identified residues Ser383 and Thr528 as the predominant CK1δ in vitro phosphorylation sites of human HIF-2α. The fact that these sites are also subjected to modification by the kinases pres ...
... cause any significant change in the in vitro phosphorylation by CK1δ (Fig. S2A). Taken together, our analysis identified residues Ser383 and Thr528 as the predominant CK1δ in vitro phosphorylation sites of human HIF-2α. The fact that these sites are also subjected to modification by the kinases pres ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.