Parts of Plant and Animal Cells By
... l o Flagella are long, thread-like single cells with the ability • Bacteria which have flagella are either rod or spiral-shaped l and are known as bacilli. Which is found in the eukaryotic cells. a -Cilia is an organelle found in the eukaryotic cells. There are two a types of cilia: motle cilia and ...
... l o Flagella are long, thread-like single cells with the ability • Bacteria which have flagella are either rod or spiral-shaped l and are known as bacilli. Which is found in the eukaryotic cells. a -Cilia is an organelle found in the eukaryotic cells. There are two a types of cilia: motle cilia and ...
2nd Semester Biology Final Study Guide
... 5. Carbon is cycled throughout the atmosphere through what 3 processes? 6. Distinguish between a food web and food chain. 7. Draw and label the water cycle 8. Define biotic and abiotic factors 9. List and briefly describe the following biomes: a. Tundra b. Desert c. Tropical Rainforest d. Temperate ...
... 5. Carbon is cycled throughout the atmosphere through what 3 processes? 6. Distinguish between a food web and food chain. 7. Draw and label the water cycle 8. Define biotic and abiotic factors 9. List and briefly describe the following biomes: a. Tundra b. Desert c. Tropical Rainforest d. Temperate ...
PROKARYOTIC CELLS - Life is a journey: Mr. T finding his way
... • Nucleoid: Region where the circular chromosome (DNA) is located •Ribosomes: Only ‘organelles’ in a prokaryotic cell - Produce protein ...
... • Nucleoid: Region where the circular chromosome (DNA) is located •Ribosomes: Only ‘organelles’ in a prokaryotic cell - Produce protein ...
Chapter 15 - Evolution
... which an ancestral species adapt to a different environment resulting in a new species. Divergent evolution or ...
... which an ancestral species adapt to a different environment resulting in a new species. Divergent evolution or ...
CELL CITY INTRODUCTION! Floating around in the cytoplasm are
... 7. The chromosomes are rod-shaped bodies found in the nucleus. They are made of DNA and protein. They contain all the information to run the cell. They also pass on the hereditary traits of the cell to new cells. a. What company or place do the chromosomes resemble in a Cell City? __________________ ...
... 7. The chromosomes are rod-shaped bodies found in the nucleus. They are made of DNA and protein. They contain all the information to run the cell. They also pass on the hereditary traits of the cell to new cells. a. What company or place do the chromosomes resemble in a Cell City? __________________ ...
a molecule necessary and complementary to life. What elements are
... This is a phospholipid molecule. Which area is hydrophilic? In terms of its role in the cell membrane, which area would be found inside the membrane? Which area would face the inside of the cell? facing outside of the cell membrane? ...
... This is a phospholipid molecule. Which area is hydrophilic? In terms of its role in the cell membrane, which area would be found inside the membrane? Which area would face the inside of the cell? facing outside of the cell membrane? ...
Genus species
... fertilizer for plants, used in many types of industry, help regulate our bodies (food, industrial, clean-up) Some cause disease: E. coli, salmonella, Staph and many more… Reproduction: binary fission(asexual), conjugation(sexual) Protista: ...
... fertilizer for plants, used in many types of industry, help regulate our bodies (food, industrial, clean-up) Some cause disease: E. coli, salmonella, Staph and many more… Reproduction: binary fission(asexual), conjugation(sexual) Protista: ...
Organelles of the Cell Part I
... 2) Ribosome travels through rough ER making proteins 3) Golgi Body sorts & packages the protein 4) Vesicle releases the protein from the cell ...
... 2) Ribosome travels through rough ER making proteins 3) Golgi Body sorts & packages the protein 4) Vesicle releases the protein from the cell ...
Ch3partB
... Plant cells- outer cell wall in addition to the plasma membrane, which is composed of cellulose for rigidity. Some plant cells have a secondary cell wall which is composed of lignin Eukaryotic cells have: •Organelles - subcellular structures that perform specific life functions •Organelles present ...
... Plant cells- outer cell wall in addition to the plasma membrane, which is composed of cellulose for rigidity. Some plant cells have a secondary cell wall which is composed of lignin Eukaryotic cells have: •Organelles - subcellular structures that perform specific life functions •Organelles present ...
Jeopardy Review
... 10 - What is the diffusion of water through the cell membrane called? _______________. 20 - What would happen to a cell if it was placed in a hypertonic solution? _________________. 30 - A cell membrane is composed of 2 layers of _____________ and one layer of _____________. 40 - _____________is an ...
... 10 - What is the diffusion of water through the cell membrane called? _______________. 20 - What would happen to a cell if it was placed in a hypertonic solution? _________________. 30 - A cell membrane is composed of 2 layers of _____________ and one layer of _____________. 40 - _____________is an ...
Scientific Inquiry
... the “ER” or passed from the inside of the “ER” to the Golgi bodies Golgi bodies – structure looks like flattened sacs and tubes The “mailroom” of the cell Golgi bodies receive proteins and other newly formed materials from the “ER”, package them and distribute them to other parts of the cell o ...
... the “ER” or passed from the inside of the “ER” to the Golgi bodies Golgi bodies – structure looks like flattened sacs and tubes The “mailroom” of the cell Golgi bodies receive proteins and other newly formed materials from the “ER”, package them and distribute them to other parts of the cell o ...
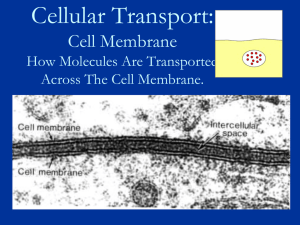
cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
YOU ARE DOING GREAT!
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. All cells are produced from other cells. Only animals are composed of cells. All living things are composed of cells. ...
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. All cells are produced from other cells. Only animals are composed of cells. All living things are composed of cells. ...
The Discovery of the Cell
... Cells come in an amazing variety of shapes and sizes, but all cells contain DNA. All cells are surrounded by a thin flexible barrier called a cell membrane. There are two basic categories of cells based on whether they contain a nucleus. ...
... Cells come in an amazing variety of shapes and sizes, but all cells contain DNA. All cells are surrounded by a thin flexible barrier called a cell membrane. There are two basic categories of cells based on whether they contain a nucleus. ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... LS-B. Explain the characteristics of life as indicated by cellular processes and describe the process of cell division and development. Indictaor: LS-B4. Summarize the general processes of cell division and differentiation, and explain why specialized cells are useful to organisms and explain that c ...
... LS-B. Explain the characteristics of life as indicated by cellular processes and describe the process of cell division and development. Indictaor: LS-B4. Summarize the general processes of cell division and differentiation, and explain why specialized cells are useful to organisms and explain that c ...
AP Biology - Review Sheet for TEST #1 - Chapters 02
... 66. A cell membrane exists to form an inside and an outside of a cell. The presence of an inside and an outside allows the establishment of different environments. In addition, membranes hold integral proteins with a variety of chemical properties and activities. This allows for the enzymatic activi ...
... 66. A cell membrane exists to form an inside and an outside of a cell. The presence of an inside and an outside allows the establishment of different environments. In addition, membranes hold integral proteins with a variety of chemical properties and activities. This allows for the enzymatic activi ...
WHAT IS A CELL - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The invention of the microscope made many important discoveries possible. One of these discoveries was made by Robert Hooke in 1665. Hooke, an English scientist, discovered that living things are made up of tiny living parts. He called these parts cells. Living things that can be seen only with a mi ...
... The invention of the microscope made many important discoveries possible. One of these discoveries was made by Robert Hooke in 1665. Hooke, an English scientist, discovered that living things are made up of tiny living parts. He called these parts cells. Living things that can be seen only with a mi ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.