Cell Organelles
... • Questions about life – from ecology to behavior, from evolution to reproduction – must be partly answered at the level of the cell because cells are the basic units of life. ...
... • Questions about life – from ecology to behavior, from evolution to reproduction – must be partly answered at the level of the cell because cells are the basic units of life. ...
Slide 1
... transmitted disease, trachoma, an eye infection that is a frequent cause of blindness and other human diseases. – C. psittaci- causes psittacosis in humans and infects many other mammals as well. – C. pneumoniae - a causative agent of human pneumonia ...
... transmitted disease, trachoma, an eye infection that is a frequent cause of blindness and other human diseases. – C. psittaci- causes psittacosis in humans and infects many other mammals as well. – C. pneumoniae - a causative agent of human pneumonia ...
cell structure and tissue
... membrane separates the material outside the cell, extracellular, from the material inside the cell, intracellular. It maintains the integrity of a cell and controls passage of materials into and out of the cell. All materials within a cell must have access to the cell membrane (the cell's boundary) ...
... membrane separates the material outside the cell, extracellular, from the material inside the cell, intracellular. It maintains the integrity of a cell and controls passage of materials into and out of the cell. All materials within a cell must have access to the cell membrane (the cell's boundary) ...
Slide 1
... DNA carries the genetic information of a cell Consists of thousands of genes It specifies everything that is needed for the maintenance, function, and replication of the cell It is made up of 4 different bases: (A) adenine ...
... DNA carries the genetic information of a cell Consists of thousands of genes It specifies everything that is needed for the maintenance, function, and replication of the cell It is made up of 4 different bases: (A) adenine ...
GENES AND DEVELOPMENT Lecture 11/7. Regulating protein
... Explain the mechanism by which an inducer molecule can increase the rate of synthesis of a specific protein or group of proteins; predict what happens to the rate of synthesis if any given element of the mechanism is lost. Explain the mechanism by which a molecule can repress (turn off) the rate of ...
... Explain the mechanism by which an inducer molecule can increase the rate of synthesis of a specific protein or group of proteins; predict what happens to the rate of synthesis if any given element of the mechanism is lost. Explain the mechanism by which a molecule can repress (turn off) the rate of ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function.notebook
... helps move cellular materials around the cell reactions occur in the cytoplasm cell expands and growscell division protects organelles from damage due to movement break down macromolecules so it is easily available for other organelles Nucleus an area inside the cell Functions controls most cell pr ...
... helps move cellular materials around the cell reactions occur in the cytoplasm cell expands and growscell division protects organelles from damage due to movement break down macromolecules so it is easily available for other organelles Nucleus an area inside the cell Functions controls most cell pr ...
Micr-22 Exam 1 Study Guide Revised Fall 2016 Test Preparation
... 18. Explain how bacterial identification makes use of unique features within certain groups (ex: flagella, cell wall types, cell shape, cell arrangement, inclusions). 19. Distinguish among active and passive transport methods, including simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and group tra ...
... 18. Explain how bacterial identification makes use of unique features within certain groups (ex: flagella, cell wall types, cell shape, cell arrangement, inclusions). 19. Distinguish among active and passive transport methods, including simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and group tra ...
4.1 Answer packet for quiz
... The exchange of materials between a cell and its environment takes place across cell cell membrane. Water is the substance used during osmosis. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. Water molecules do not need energy to enter the cell. Large particles (protein) have a hard time entering th ...
... The exchange of materials between a cell and its environment takes place across cell cell membrane. Water is the substance used during osmosis. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. Water molecules do not need energy to enter the cell. Large particles (protein) have a hard time entering th ...
2401_ch3.pdf
... many of the organelles in place. Made up of: Actin (microfilaments) – 8nm diameter fibrils which form bundles, networks and layers inside the cell. These adjust cell shape and are responsible for cell movements Tubulin – hollow tubes about 25nm in diameter. These form internal scaffolding within the ...
... many of the organelles in place. Made up of: Actin (microfilaments) – 8nm diameter fibrils which form bundles, networks and layers inside the cell. These adjust cell shape and are responsible for cell movements Tubulin – hollow tubes about 25nm in diameter. These form internal scaffolding within the ...
2401_ch3.ppt
... many of the organelles in place. Made up of: Actin (microfilaments) – 8nm diameter fibrils which form bundles, networks and layers inside the cell. These adjust cell shape and are responsible for cell movements Tubulin – hollow tubes about 25nm in diameter. These form internal scaffolding within the ...
... many of the organelles in place. Made up of: Actin (microfilaments) – 8nm diameter fibrils which form bundles, networks and layers inside the cell. These adjust cell shape and are responsible for cell movements Tubulin – hollow tubes about 25nm in diameter. These form internal scaffolding within the ...
cell_analogy_collage_HONORS_2014
... _____ The analogy should be written to show the similarity between the cell part and the everyday object. _____ It must explain the reasoning behind the correlation. (e.g., “the nucleus is like a brain because it controls and coordinates the activities of the whole cell in the same way the brain con ...
... _____ The analogy should be written to show the similarity between the cell part and the everyday object. _____ It must explain the reasoning behind the correlation. (e.g., “the nucleus is like a brain because it controls and coordinates the activities of the whole cell in the same way the brain con ...
File
... different from those of the original organ the body will reject it as a foreign invader. ...
... different from those of the original organ the body will reject it as a foreign invader. ...
cell-transport-questions-2012
... Why do the phospholipid molecules arrange themselves in that pattern when they are poured into the beaker of water? ...
... Why do the phospholipid molecules arrange themselves in that pattern when they are poured into the beaker of water? ...
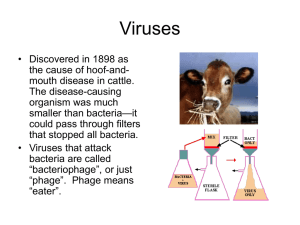
Viruses - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... • Some plants are infected by small circular RNA molecules that have no protein coat. These are called viroids. • Viroids resemble the introns that are spliced out of most eukaryotic genes. ...
... • Some plants are infected by small circular RNA molecules that have no protein coat. These are called viroids. • Viroids resemble the introns that are spliced out of most eukaryotic genes. ...
Cell Catalog - Mission Hills High School
... living things and cells reproduce other cells. Each cell has many organelles (parts) which carry out the physical and chemical functions for it. ...
... living things and cells reproduce other cells. Each cell has many organelles (parts) which carry out the physical and chemical functions for it. ...
التركيب الدقيق للخلية البكتيرية Structure of bacterial cell
... • Consists of – an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (LPS) – thin shell of peptidoglycan – periplasmic space – inner membrane ...
... • Consists of – an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (LPS) – thin shell of peptidoglycan – periplasmic space – inner membrane ...
Print › Biology Honors NC EOC Review | Quizlet
... A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. ...
... A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. ...
How substances get in and out of cells - questions
... 5 (a) Which one of the following is the best definition of osmosis? (i) The movement of water from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially permeable membrane. . (ii) The movement of a dissolved substance from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially per ...
... 5 (a) Which one of the following is the best definition of osmosis? (i) The movement of water from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially permeable membrane. . (ii) The movement of a dissolved substance from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially per ...
Chapter 3, Section 1 - Rock Hill High School
... – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
Cell Analogy Project
... between the cell’s structure and its function. You will be creating analogies for each of the organelles within the cell. You will also design and construct a cereal box display. This will illustrate the organelles of a typical animal and plant cell and it will include a brief summary of a current r ...
... between the cell’s structure and its function. You will be creating analogies for each of the organelles within the cell. You will also design and construct a cereal box display. This will illustrate the organelles of a typical animal and plant cell and it will include a brief summary of a current r ...
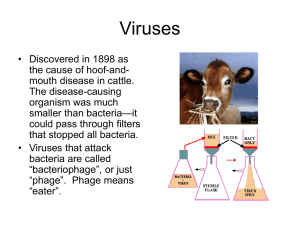
Viruses
... • Some plants are infected by small circular RNA molecules that have no protein coat. These are called viroids. • Viroids resemble the introns that are spliced out of most eukaryotic genes. ...
... • Some plants are infected by small circular RNA molecules that have no protein coat. These are called viroids. • Viroids resemble the introns that are spliced out of most eukaryotic genes. ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.