Chapter 8 Plate Tectonics With Video
... Throughout the earth’s history, the magnetic field has reversed itself many times. ...
... Throughout the earth’s history, the magnetic field has reversed itself many times. ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary List
... 12. Lithosphere- The rigid outer layer of earth, including the crust and upper mantle. 13. Magnetic time scale- Time scale of the Earth’s Magnetic Field in recent past developed by establishing the magnetic polarity for lava flows of known age. 14. Mantle plume- A mass of hotter –than- normal mantle ...
... 12. Lithosphere- The rigid outer layer of earth, including the crust and upper mantle. 13. Magnetic time scale- Time scale of the Earth’s Magnetic Field in recent past developed by establishing the magnetic polarity for lava flows of known age. 14. Mantle plume- A mass of hotter –than- normal mantle ...
Chapter 4
... 45)How does evidence from molten material support sea floor spreading? 46)How does evidence from magnetic stripes support sea floor spreading? 47)Why do magnetic stripes match on each side of a ridge? 48)How does evidence from drilling samples support sea floor spreading? 49) What are deep-ocean tre ...
... 45)How does evidence from molten material support sea floor spreading? 46)How does evidence from magnetic stripes support sea floor spreading? 47)Why do magnetic stripes match on each side of a ridge? 48)How does evidence from drilling samples support sea floor spreading? 49) What are deep-ocean tre ...
Application cases of the offer Magnetic inversion
... Profile for interpretation has a length of 133 km of azimuth 45°. Bathymetry data correspond to top of sediments and basaltic crust layer. Strike of layers was set equal to infinity in modeling. The value for density layers (in g/cm3), the following: water (1.03), sediment (2.1), the oceanic crust ( ...
... Profile for interpretation has a length of 133 km of azimuth 45°. Bathymetry data correspond to top of sediments and basaltic crust layer. Strike of layers was set equal to infinity in modeling. The value for density layers (in g/cm3), the following: water (1.03), sediment (2.1), the oceanic crust ( ...
What happens at tectonic plate boundaries?
... Almost perfectly symmetrical with respect to the crest of the md-ocean ridge Are evidence that Earth’s magnetic field does not remain constant Magnetic reversals occur, flipping the orientation of the North and South pole When iron rich lavas cool, they become slightly but permanently magnet ...
... Almost perfectly symmetrical with respect to the crest of the md-ocean ridge Are evidence that Earth’s magnetic field does not remain constant Magnetic reversals occur, flipping the orientation of the North and South pole When iron rich lavas cool, they become slightly but permanently magnet ...
Review sheet for Exam 1, Locations and Maps
... 10. Be able to calculate how fast a plate is moving based on distance and time data 11. Be able to look at a map of the major topographic features of the Earth and say something about the tectonic setting (i.e., say we point out a ridge on the ocean floor- you should be able to identify whether this ...
... 10. Be able to calculate how fast a plate is moving based on distance and time data 11. Be able to look at a map of the major topographic features of the Earth and say something about the tectonic setting (i.e., say we point out a ridge on the ocean floor- you should be able to identify whether this ...
8.2 Continental Drift Theory and Sea-Floor Spreading
... is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 micro Tesla (0.25 to 0.65 Gauss). It is approximately the field of a magnetic dipole tilted a ...
... is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 micro Tesla (0.25 to 0.65 Gauss). It is approximately the field of a magnetic dipole tilted a ...
8.3: Plates move apart
... the new rock line up with the Earth’s magnetic field The material hardens and those minerals are permanently fixed in the directions pointing north and south Date the rocks, and can have further evidence of plate movement Most recent reversal: 760,000 years ago ...
... the new rock line up with the Earth’s magnetic field The material hardens and those minerals are permanently fixed in the directions pointing north and south Date the rocks, and can have further evidence of plate movement Most recent reversal: 760,000 years ago ...
Seafloor Spreading - Paramus Public Schools
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
Earthlike planets
... 16. The greenhouse effect keeps Venus hot because a. the atmosphere contains free oxygen. b. the atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide. c. the surface converts infrared into visible radiation. d. the surface is free of sulfur compounds. e. the magnetic field traps a large number of particles from the ...
... 16. The greenhouse effect keeps Venus hot because a. the atmosphere contains free oxygen. b. the atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide. c. the surface converts infrared into visible radiation. d. the surface is free of sulfur compounds. e. the magnetic field traps a large number of particles from the ...
Plate Tectonics Exercises
... During WWII, naval ships accompanying supply convoys crossing the Atlantic Ocean towed sensitive magnetometers behind. These magnetometers were looking for submarines (a large metal body capable of deflecting the Earth’s magnetic field locally). The operators of the magnetometers found strange pa ...
... During WWII, naval ships accompanying supply convoys crossing the Atlantic Ocean towed sensitive magnetometers behind. These magnetometers were looking for submarines (a large metal body capable of deflecting the Earth’s magnetic field locally). The operators of the magnetometers found strange pa ...
Conversations with the Earth
... • Single number to quantify the amount of seismic energy released by an earthquake. Amplitude of largest displacement • Under 6.0 - At most slight damage to well-designed buildings. Can cause major damage to poorly constructed buildings. • 6.1-6.9 - Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilome ...
... • Single number to quantify the amount of seismic energy released by an earthquake. Amplitude of largest displacement • Under 6.0 - At most slight damage to well-designed buildings. Can cause major damage to poorly constructed buildings. • 6.1-6.9 - Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilome ...
File
... _______________________________(a volcanic rock rich in iron) with alternating magnetic lines. As rock rose from inside the Earth, the iron in the molten rock would align itself in the Earth’s magnetic field before the rock__________________________. The study of the magnetic record is called ______ ...
... _______________________________(a volcanic rock rich in iron) with alternating magnetic lines. As rock rose from inside the Earth, the iron in the molten rock would align itself in the Earth’s magnetic field before the rock__________________________. The study of the magnetic record is called ______ ...
The plate tectonic story: a scientific jigsaw
... explanation was that the two halves of the ocean floor were moving apart and new rock was forming in the gap. And when the scientists looked at the magnetic rocks on the ocean floor they found they were magnetised in opposite directions. Each time the Earth’s magnetic field had reversed direction, t ...
... explanation was that the two halves of the ocean floor were moving apart and new rock was forming in the gap. And when the scientists looked at the magnetic rocks on the ocean floor they found they were magnetised in opposite directions. Each time the Earth’s magnetic field had reversed direction, t ...
plate tectonics - Trupia
... Magnetic Bands Reversals – Lava comes up along ridge lines (mostly underwater) as plates separate. – In 76 million years there’ve been 171 reversals of the earth’s magnetic field. – Lava contains iron. – Cooling lava locks in the prevailing magnetism. – The ocean floor near the ridges has the prevai ...
... Magnetic Bands Reversals – Lava comes up along ridge lines (mostly underwater) as plates separate. – In 76 million years there’ve been 171 reversals of the earth’s magnetic field. – Lava contains iron. – Cooling lava locks in the prevailing magnetism. – The ocean floor near the ridges has the prevai ...
Science 10 - TheScienceWoman
... fastening or fixing of any hazards in your home; an escape plan from your home; an emergency preparedness kit. I will put resources on our class website to develop this plan. You will provide evidence in the form of written plans and photographs. A criteria for this will be available on our website ...
... fastening or fixing of any hazards in your home; an escape plan from your home; an emergency preparedness kit. I will put resources on our class website to develop this plan. You will provide evidence in the form of written plans and photographs. A criteria for this will be available on our website ...
Plates move apart.
... Scientists found that each magnetic reversal is recorded in the sea-floor rock. These records are especially clear at some mid-ocean ridges. As the molten material rises and cools, some magnetic minerals line up with the Earth’s magnetic field. When the material hardens, these minerals are permanent ...
... Scientists found that each magnetic reversal is recorded in the sea-floor rock. These records are especially clear at some mid-ocean ridges. As the molten material rises and cools, some magnetic minerals line up with the Earth’s magnetic field. When the material hardens, these minerals are permanent ...
Plates move apart.
... Scientists found that each magnetic reversal is recorded in the sea-floor rock. These records are especially clear at some mid-ocean ridges. As the molten material rises and cools, some magnetic minerals line up with the Earth’s magnetic field. When the material hardens, these minerals are permanent ...
... Scientists found that each magnetic reversal is recorded in the sea-floor rock. These records are especially clear at some mid-ocean ridges. As the molten material rises and cools, some magnetic minerals line up with the Earth’s magnetic field. When the material hardens, these minerals are permanent ...
File
... Earth’s magnetic field will go away for good may have resulted in the planet’s lack when its iron core cools, just as Mars’ did. of a life-sustaining atmosphere. Scientists have calculated the amount of material in the iron core and the rate of cooling. Based on these calculations, Earth should sust ...
... Earth’s magnetic field will go away for good may have resulted in the planet’s lack when its iron core cools, just as Mars’ did. of a life-sustaining atmosphere. Scientists have calculated the amount of material in the iron core and the rate of cooling. Based on these calculations, Earth should sust ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... fractured plate pieces travel in the same direction as the original plate was traveling -away from the ocean ridge. During the early 1900's, a theory of a 'super-continent' was developed by Alfred Wegener. He was ridiculed for his ideas that continental drift produced the present positions of the c ...
... fractured plate pieces travel in the same direction as the original plate was traveling -away from the ocean ridge. During the early 1900's, a theory of a 'super-continent' was developed by Alfred Wegener. He was ridiculed for his ideas that continental drift produced the present positions of the c ...
Study Guide Key-Layers of the Earth Continental Drift
... 4. __Alfred Wegener_______ was the scientist responsible for the theory of Continental Drift. 5. List and explain 5 pieces of evidence that Alfred Wegener used to explain his theory of Continental Drift: a) Fit- Africa and South America fit together like a puzzle piece b) Fossil Evidence-similar pl ...
... 4. __Alfred Wegener_______ was the scientist responsible for the theory of Continental Drift. 5. List and explain 5 pieces of evidence that Alfred Wegener used to explain his theory of Continental Drift: a) Fit- Africa and South America fit together like a puzzle piece b) Fossil Evidence-similar pl ...
Why won`t my compass work the other side of the equator
... vertically downward at the poles, horizontal at the Equator and dipping at various angles, depending upon latitude, between the Equator and the poles. The ‘Magnetic Earth: modelling the magnetic field of the Earth’ and the ‘Frozen magnetism: preserving evidence of a past magnetic field in wax’ Earth ...
... vertically downward at the poles, horizontal at the Equator and dipping at various angles, depending upon latitude, between the Equator and the poles. The ‘Magnetic Earth: modelling the magnetic field of the Earth’ and the ‘Frozen magnetism: preserving evidence of a past magnetic field in wax’ Earth ...
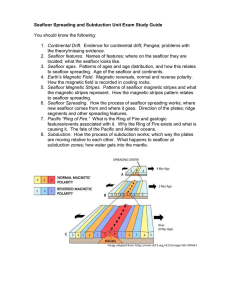
Seafloor Spreading and Subduction Unit Exam Study Guide You
... 1. Pangea – The Supercontinent that existed when all of the continents were one piece of land. 2. Continental Drift – The idea that continents moved and changed positions. 3. Bathymetry – The shape of the seafloor. 4. Trench – The deepest feature in the oceans that forms when one plate subducts bene ...
... 1. Pangea – The Supercontinent that existed when all of the continents were one piece of land. 2. Continental Drift – The idea that continents moved and changed positions. 3. Bathymetry – The shape of the seafloor. 4. Trench – The deepest feature in the oceans that forms when one plate subducts bene ...
Geomagnetic reversal
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged. The Earth's field has alternated between periods of normal polarity, in which the direction of the field was the same as the present direction, and reverse polarity, in which the field was the opposite. These periods are called chrons. The time spans of chrons are randomly distributed with most being between 0.1 and 1 million years with an average of 450,000 years. Most reversals are estimated to take between 1,000 and 10,000 years.The latest one, the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, occurred 780,000 years ago;and may have happened very quickly, within a human lifetime. A brief complete reversal, known as the Laschamp event, occurred only 41,000 years ago during the last glacial period. That reversal lasted only about 440 years with the actual change of polarity lasting around 250 years. During this change the strength of the magnetic field dropped to 5% of its present strength. Brief disruptions that do not result in reversal are called geomagnetic excursions.