GLY 150 Exam #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Explain the geologic, paleontologic, and paleoclimatic evidence that supports the Theory of Continental Drift. In 1962 Harry Hess proposed the hypothesis of sea-floor spreading. What new data did he take into account to derive this hypothesis? Briefly describe the hypothesis of sea floor spreading. ...
... Explain the geologic, paleontologic, and paleoclimatic evidence that supports the Theory of Continental Drift. In 1962 Harry Hess proposed the hypothesis of sea-floor spreading. What new data did he take into account to derive this hypothesis? Briefly describe the hypothesis of sea floor spreading. ...
The Earth An Intimate History R.Fortey August 18
... reference to Euler and the sphere, but wherein that actually consists is left as a mystery. Rigid motions along a sphere is mathematics, and the understanding of which is essential to the appreciation of tectonic movement. So what does the author present instead of mathematics? Diversions. Historic ...
... reference to Euler and the sphere, but wherein that actually consists is left as a mystery. Rigid motions along a sphere is mathematics, and the understanding of which is essential to the appreciation of tectonic movement. So what does the author present instead of mathematics? Diversions. Historic ...
Key topics today: How do we know about the Earth`s interior structure?
... thinner near ridges • Crust should cool and shrink as it moves away from ridges, deepening ocean • Specific ideas about where certain kinds of EQ and volcanoes should be found ...
... thinner near ridges • Crust should cool and shrink as it moves away from ridges, deepening ocean • Specific ideas about where certain kinds of EQ and volcanoes should be found ...
ch07 - earthjay science
... Which of the following is paleoclimatological evidence for continental drift? a. Magnetic reversals b. Lack of annual tree rings in fossilized trees c. Orientation of mountain ranges d. The fit of the continental margins e. Apparent polar wandering ...
... Which of the following is paleoclimatological evidence for continental drift? a. Magnetic reversals b. Lack of annual tree rings in fossilized trees c. Orientation of mountain ranges d. The fit of the continental margins e. Apparent polar wandering ...
Supplement to Activity 9: A Soda Bottle Magnetometer
... Abstract: The magnetosphere is, at once, one of the most familiar and the least understood elements to the earth's environment for grades 7-12 in the typical Earth and physical science curriculum. Students learn that it resembles a bar magnet, but what they seldom encounter is the concept of the geo ...
... Abstract: The magnetosphere is, at once, one of the most familiar and the least understood elements to the earth's environment for grades 7-12 in the typical Earth and physical science curriculum. Students learn that it resembles a bar magnet, but what they seldom encounter is the concept of the geo ...
The Restless Earth Unit Study Guide 1. What is the outermost layer
... 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?____________________________________________________ 2. The layer made of solid rock that slowly flows.______________________________________________________ 3. Most geologists think that the movement of Earth’s plates is caused by _________________ ...
... 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?____________________________________________________ 2. The layer made of solid rock that slowly flows.______________________________________________________ 3. Most geologists think that the movement of Earth’s plates is caused by _________________ ...
Marine Geology Final Exam Information and Review
... basin, joint, normal fault, reverse fault, thrust fault, strike slip fault. ...
... basin, joint, normal fault, reverse fault, thrust fault, strike slip fault. ...
Chapter One: Plate Tectonics
... make and shape planet Earth. • study the chemical and physical characteristics of rock. • map where different types of rocks are found on and beneath the surface. • describe landforms, features that form in rock by water, wind, and waves. ...
... make and shape planet Earth. • study the chemical and physical characteristics of rock. • map where different types of rocks are found on and beneath the surface. • describe landforms, features that form in rock by water, wind, and waves. ...
Doug - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Seafloor Spreading Development of a New Theory • Continental drift hypothesis was reexamined in 1960’s with new information. • Seafloor Spreading • Evidence supporting seafloor spreading… – Paleomagnetism – Age of Seafloor ...
... Seafloor Spreading Development of a New Theory • Continental drift hypothesis was reexamined in 1960’s with new information. • Seafloor Spreading • Evidence supporting seafloor spreading… – Paleomagnetism – Age of Seafloor ...
Review Topics for Test I
... Evidence: fit of the continents, fossils glossopteris and mesosaurus, glacial evidence (till and striations), rock type and age (Appalachian, Atlas, Caledonian mountain ranges similar), paleomagnetism recorded in continental rocks points to the poles and documents the changing strength of magnetic f ...
... Evidence: fit of the continents, fossils glossopteris and mesosaurus, glacial evidence (till and striations), rock type and age (Appalachian, Atlas, Caledonian mountain ranges similar), paleomagnetism recorded in continental rocks points to the poles and documents the changing strength of magnetic f ...
KEY
... hemisphere after the breakup of the original supercontinent is A. Pangaea B. Laurasia C. Gondwanaland D. Micronesia 38. Iceland is an example of a(n) A. above sea-level expression of a divergent boundary. B. stalled convergent boundary. C. intraplate hot spot. D. extinct volcano. 39. The best possib ...
... hemisphere after the breakup of the original supercontinent is A. Pangaea B. Laurasia C. Gondwanaland D. Micronesia 38. Iceland is an example of a(n) A. above sea-level expression of a divergent boundary. B. stalled convergent boundary. C. intraplate hot spot. D. extinct volcano. 39. The best possib ...
Glossopteris flora continental drift Pangaea magnetism
... The area in which magnetic substances are affected by lines of magnetic force emanating from Earth. ...
... The area in which magnetic substances are affected by lines of magnetic force emanating from Earth. ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... Tethys Sea cut into Pangaea and the ocean that surrounded it was later called Panthalassa. Break up of Pangaea _____________________during the Mesozoic Era, Pangaea broke up into 2 continents, Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Laurasia drifted northward and rotated and then split into North America and Eur ...
... Tethys Sea cut into Pangaea and the ocean that surrounded it was later called Panthalassa. Break up of Pangaea _____________________during the Mesozoic Era, Pangaea broke up into 2 continents, Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Laurasia drifted northward and rotated and then split into North America and Eur ...
Name:______________________________ o ___________________ Samples
... o Plates: a section of the lithosphere that slowly ___________________ over the Asthenosphere ___________________ pieces of the continental and oceanic crust Combined continental drift and sea floor spreading into a ___________________ theory o Scientific Theory: well ___________________ concept t ...
... o Plates: a section of the lithosphere that slowly ___________________ over the Asthenosphere ___________________ pieces of the continental and oceanic crust Combined continental drift and sea floor spreading into a ___________________ theory o Scientific Theory: well ___________________ concept t ...
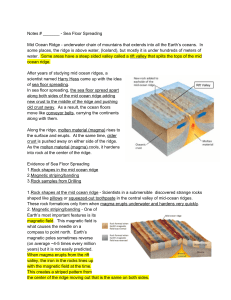
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... Magnetic striping/banding One of Earth’s most important features is its magnetic field . This magnetic field is what causes the needle on a compass to point north. Earth’s magnetic poles sometimes reverse (on average ~45 times every million years) but it is not easily predicted. When ...
... Magnetic striping/banding One of Earth’s most important features is its magnetic field . This magnetic field is what causes the needle on a compass to point north. Earth’s magnetic poles sometimes reverse (on average ~45 times every million years) but it is not easily predicted. When ...
Discuss on Sea Floor Evidence Submitted by WWW
... and creates a higher magnetic measurement at that location. Rocks are negatively polarized when the earth's field is reversed, which reduces the earth's net field strength. Since the ages of these anomalies are known from dating the paleomagnetic reversals on land, the rate of movement of the ocean ...
... and creates a higher magnetic measurement at that location. Rocks are negatively polarized when the earth's field is reversed, which reduces the earth's net field strength. Since the ages of these anomalies are known from dating the paleomagnetic reversals on land, the rate of movement of the ocean ...
study guide – unit 9 – plate tectonics
... Continental “fit” : coastlines match up Rocks, minerals and fossils: similar age and composition ...
... Continental “fit” : coastlines match up Rocks, minerals and fossils: similar age and composition ...
The Sea Floor
... The sea floor records magnetic polarity reversals in the geologic past. As new crust is created on the ocean floor (such as at the Mid-Atlantic ridge) it solidifies with its iron oxide acting like miniature compass needles. Presently the iron points to magnetic north. White bands in the figure above ...
... The sea floor records magnetic polarity reversals in the geologic past. As new crust is created on the ocean floor (such as at the Mid-Atlantic ridge) it solidifies with its iron oxide acting like miniature compass needles. Presently the iron points to magnetic north. White bands in the figure above ...
Chapter 10: Section 1 Continental Drift
... • Over time, all of the continents collide to form a supercontinent. • Then, heat from Earth’s interior builds up under the supercontinent, and rifts form in the supercontinent. The supercontinent breaks apart, and plates carrying separate continents move around the globe. Formation of Pangaea • The ...
... • Over time, all of the continents collide to form a supercontinent. • Then, heat from Earth’s interior builds up under the supercontinent, and rifts form in the supercontinent. The supercontinent breaks apart, and plates carrying separate continents move around the globe. Formation of Pangaea • The ...
Earth`sInterior
... Planet Earth is a rocky planet. It is made up of rocks and minerals. This sphere is called the “geosphere”. The Earth is made up of a number of elements. The interior of the Earth is quite different than the exterior (continental crust). ...
... Planet Earth is a rocky planet. It is made up of rocks and minerals. This sphere is called the “geosphere”. The Earth is made up of a number of elements. The interior of the Earth is quite different than the exterior (continental crust). ...
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
... Which statement represents the most logical conclusion to draw from this evidence? A) Mesosaurus migrated across the ocean from location X to location Y. B) Mesosaurus came into existence on several widely separated continents at different times. C) The continents of South America and Africa were jo ...
... Which statement represents the most logical conclusion to draw from this evidence? A) Mesosaurus migrated across the ocean from location X to location Y. B) Mesosaurus came into existence on several widely separated continents at different times. C) The continents of South America and Africa were jo ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Virtual Lab http://earthguide
... Click forward to 0.05 mybp. What is the main difference you see on the map from 0.05 mybp to present day? __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is plate tectonics? The concept that describes and explains how the major features of the Earth _______ ...
... Click forward to 0.05 mybp. What is the main difference you see on the map from 0.05 mybp to present day? __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is plate tectonics? The concept that describes and explains how the major features of the Earth _______ ...
Study Guide for the Movie The Core
... heard while the shuttle is flying at a low altitude, because the atmosphere is too thick at low altitudes for the shuttle to move faster than sound. An object must be moving faster than the speed of sound to make a sonic boom (‘break the sound barrier’). Cosmic waves are deflected by earth’s magneti ...
... heard while the shuttle is flying at a low altitude, because the atmosphere is too thick at low altitudes for the shuttle to move faster than sound. An object must be moving faster than the speed of sound to make a sonic boom (‘break the sound barrier’). Cosmic waves are deflected by earth’s magneti ...
Geomagnetic reversal
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged. The Earth's field has alternated between periods of normal polarity, in which the direction of the field was the same as the present direction, and reverse polarity, in which the field was the opposite. These periods are called chrons. The time spans of chrons are randomly distributed with most being between 0.1 and 1 million years with an average of 450,000 years. Most reversals are estimated to take between 1,000 and 10,000 years.The latest one, the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, occurred 780,000 years ago;and may have happened very quickly, within a human lifetime. A brief complete reversal, known as the Laschamp event, occurred only 41,000 years ago during the last glacial period. That reversal lasted only about 440 years with the actual change of polarity lasting around 250 years. During this change the strength of the magnetic field dropped to 5% of its present strength. Brief disruptions that do not result in reversal are called geomagnetic excursions.