File - Team 6
... This energy is stored in molecules called _____________________. ATP provides a cell with energy to perform many functions, such as: Chloroplasts: Plants and many other autotrophs have ______________________ and ___________________. ______________________ capture light and convert it into __________ ...
... This energy is stored in molecules called _____________________. ATP provides a cell with energy to perform many functions, such as: Chloroplasts: Plants and many other autotrophs have ______________________ and ___________________. ______________________ capture light and convert it into __________ ...
Slide 1
... 2 K+ ions then bind the pump and causes the release of the P group another shape change by the pump - releases the K+ into the cell ...
... 2 K+ ions then bind the pump and causes the release of the P group another shape change by the pump - releases the K+ into the cell ...
Cell Analogy - Calmeca Academy
... This text will then need to be made in to a poster illustrating the kingdom with a castle, a queen, and artisans. What does a quality analogy look like? To get full credit for each analogy, think about this: Does the analogy for this structure/process make sense? Are the two things truly comparabl ...
... This text will then need to be made in to a poster illustrating the kingdom with a castle, a queen, and artisans. What does a quality analogy look like? To get full credit for each analogy, think about this: Does the analogy for this structure/process make sense? Are the two things truly comparabl ...
Biology 410 - KSU Web Home
... What effect would you see in mutant cells in which the activity of the component was completely lost? You must specifically state what effects or changes would be observed in the mutant cells as compared to the wild type. “The cell dies,” “It won’t work anymore,” or other such statements are not acc ...
... What effect would you see in mutant cells in which the activity of the component was completely lost? You must specifically state what effects or changes would be observed in the mutant cells as compared to the wild type. “The cell dies,” “It won’t work anymore,” or other such statements are not acc ...
A significant similarity is the fact that both prokaryotes and
... membrane bound organelle, known as the nucleus, and is easily seen using a microscope. On the other hand, prokaryotes lack this distinct nucleus and nucleur membrane but instead have a nucleoid, which is an irregularly shaped region within the cell where the genetic information is localised in the f ...
... membrane bound organelle, known as the nucleus, and is easily seen using a microscope. On the other hand, prokaryotes lack this distinct nucleus and nucleur membrane but instead have a nucleoid, which is an irregularly shaped region within the cell where the genetic information is localised in the f ...
cell = TRANSPORT
... The movement of materials from lower to higher concentration requiring energy in the form of ATP is called 1. movement 2. diffusion 3. active transport 4. cell division ...
... The movement of materials from lower to higher concentration requiring energy in the form of ATP is called 1. movement 2. diffusion 3. active transport 4. cell division ...
What are the Effects of Osmosis?
... – a cell in salt water – example: shellfish – problem: lose water • shrinking cell – solution: take up water ...
... – a cell in salt water – example: shellfish – problem: lose water • shrinking cell – solution: take up water ...
Growth and multiplication in bacteria
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
Key concepts: Apoptosis Animal cells can activate an intracellular
... In most cases, these deaths occur by apoptosis: the cells shrink, condense, and frequently fragment, and neighboring cells or macrophages rapidly phagocytose the cells or fragments before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, whic ...
... In most cases, these deaths occur by apoptosis: the cells shrink, condense, and frequently fragment, and neighboring cells or macrophages rapidly phagocytose the cells or fragments before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, whic ...
Exam #1 Review
... 1. Proteins are composed of 20 standard amino acids. Be familiar with the general structure of an amino acid (central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom and an R-group.) *Be able to recognize the names and abbreviations (both 3- and 1-letter) of these amino acids. I will provide the ...
... 1. Proteins are composed of 20 standard amino acids. Be familiar with the general structure of an amino acid (central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom and an R-group.) *Be able to recognize the names and abbreviations (both 3- and 1-letter) of these amino acids. I will provide the ...
2.4 cell membrane transport
... Vesicle-mediated transport Vesicles and vacuoles that fuse with the cell membrane may be utilized to release or transport chemicals out of the cell or to allow them to enter a cell. Exocytosis is the term applied when transport is out of the cell. ...
... Vesicle-mediated transport Vesicles and vacuoles that fuse with the cell membrane may be utilized to release or transport chemicals out of the cell or to allow them to enter a cell. Exocytosis is the term applied when transport is out of the cell. ...
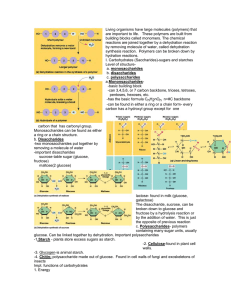
Living organisms have large molecules (polymers) that are
... of two fatty acids, glycerol and a charged phosphate group. They are an integral part of all cell membrane. Phospholipids have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic part to their structure. ...
... of two fatty acids, glycerol and a charged phosphate group. They are an integral part of all cell membrane. Phospholipids have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic part to their structure. ...
Cell Transport Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... Ions such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and chloride (Cl-) are important for cell functions Since they are not soluble in lipids they will not pass through the cell membrane on their own ...
... Ions such as sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), and chloride (Cl-) are important for cell functions Since they are not soluble in lipids they will not pass through the cell membrane on their own ...
Study Guide 2 for Macro to Micro Organisms
... 6. List positive and negative effects of fungi on our environment (class discussion / notes / D of LT ch. 2) 7. Explain in detail the process of photosynthesis and how various wavelengths of light affect it. 8. Explain what a seed needs to grow (class exp. / notes / lab manual) 9. Review the plant ...
... 6. List positive and negative effects of fungi on our environment (class discussion / notes / D of LT ch. 2) 7. Explain in detail the process of photosynthesis and how various wavelengths of light affect it. 8. Explain what a seed needs to grow (class exp. / notes / lab manual) 9. Review the plant ...
Cells
... you’ll have energy. You already know that you breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide, and you already know that you sweat and urinate water out of your body. The chemical formula for this process just looks at this in a little more detail. For instance, most of the food you eat gets broken ...
... you’ll have energy. You already know that you breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide, and you already know that you sweat and urinate water out of your body. The chemical formula for this process just looks at this in a little more detail. For instance, most of the food you eat gets broken ...
cell wall
... Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells but not animal cells. Most plants do not eat food like animals, and they must generate their own food using photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts use two inorganic compounds, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), plus sunlight to build t ...
... Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells but not animal cells. Most plants do not eat food like animals, and they must generate their own food using photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts use two inorganic compounds, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), plus sunlight to build t ...
Elements Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and
... nails, horns and hoofs are all proteins. contraction of muscle tissues transporting oxygen in the bloodstream providing immunity regulating other proteins carrying out chemical reactions (enzymes) ...
... nails, horns and hoofs are all proteins. contraction of muscle tissues transporting oxygen in the bloodstream providing immunity regulating other proteins carrying out chemical reactions (enzymes) ...
Cell Structures – Part 3 - Glasgow Independent Schools
... E. All cells are considered Open Systems in their natural settings because there are materials coming into the cell from the surrounding environment; as well as, materials leaving the cell and going into the surrounding environment. The cell is open to interaction with the environment. ...
... E. All cells are considered Open Systems in their natural settings because there are materials coming into the cell from the surrounding environment; as well as, materials leaving the cell and going into the surrounding environment. The cell is open to interaction with the environment. ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
... barrier known as the cell membrane. The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support. The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membra ...
... barrier known as the cell membrane. The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support. The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membra ...
Grade: 5 Description: This lesson set covers cells. It goes along with
... Review the parts of the cell. *The students need to be able to distinguish between mitochondria and vacuole. ...
... Review the parts of the cell. *The students need to be able to distinguish between mitochondria and vacuole. ...
Cell Organelles and Organization
... Cilia and Flagella Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (plants and animals) Function: Hair-like structures for movement ...
... Cilia and Flagella Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (plants and animals) Function: Hair-like structures for movement ...
Previous work on CVD
... leading to an electric field enhancement that can then be coupled to the photoactive absorption region. It has been extensively studied that surface plasmons can be tuned by changing the size, shape, particle material, substrates and overcoating of the metal particles ...
... leading to an electric field enhancement that can then be coupled to the photoactive absorption region. It has been extensively studied that surface plasmons can be tuned by changing the size, shape, particle material, substrates and overcoating of the metal particles ...
The Cell
... What Are the Parts of Cells Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have some things in common. nuclear cell membrane ribosomes cytoplasm material ...
... What Are the Parts of Cells Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have some things in common. nuclear cell membrane ribosomes cytoplasm material ...
Lineage specification, commitment and self
... We have shown that Oct4 can inhibit commitment in multiple lineages, allowing ES cells to progress in and out of immediate early states of differentiation, but always remaining uncommitted. The means by which Oct4 does this is not the suppression of differentiation down specific lineages, but by mai ...
... We have shown that Oct4 can inhibit commitment in multiple lineages, allowing ES cells to progress in and out of immediate early states of differentiation, but always remaining uncommitted. The means by which Oct4 does this is not the suppression of differentiation down specific lineages, but by mai ...