Cell Signaling - Scott County Schools
... phospholipid bilayer– these play a major role in cell signaling ...
... phospholipid bilayer– these play a major role in cell signaling ...
Science 10
... The Cell as an Open System 3. Plant cells have one large central vacuole that stores water; animal cells have several small vacuoles that store water, nutrients or wastes 4. Animal cells have centrioles, plant cells do not ...
... The Cell as an Open System 3. Plant cells have one large central vacuole that stores water; animal cells have several small vacuoles that store water, nutrients or wastes 4. Animal cells have centrioles, plant cells do not ...
44401 Molecular biology of the cell
... 4.Structure and function of the nucleus. Structure of the nuclear envelope and lamina, link between cytosol cytoskeleton and chromatin through transmembrane proteins of nuclear membrane and nuclear matrix, mechanisms of nuclear envelope breakdown and reconstitution during mitosis, laminopathies, tra ...
... 4.Structure and function of the nucleus. Structure of the nuclear envelope and lamina, link between cytosol cytoskeleton and chromatin through transmembrane proteins of nuclear membrane and nuclear matrix, mechanisms of nuclear envelope breakdown and reconstitution during mitosis, laminopathies, tra ...
notes - QuarkPhysics.ca
... as they separate. An “untwister” enzyme (topo-isomerase) systematically cuts and repairs resulting strands to prevent tangling as each DNA strand is formed. Other enzymes copy the flat, untwisted sections of DNA, which are then connected together via DNA ligases into one continuous strand. There are ...
... as they separate. An “untwister” enzyme (topo-isomerase) systematically cuts and repairs resulting strands to prevent tangling as each DNA strand is formed. Other enzymes copy the flat, untwisted sections of DNA, which are then connected together via DNA ligases into one continuous strand. There are ...
Role of tumor suppressor WOX1 in breast cancer cell migration
... acts as a proapoptotic protein and tumor suppressor. Loss of heterozygosity and chromosomal rearrangement of the WOX1 gene is associated with ovarian, breast, hepatocellular, and prostate carcinomas. In addition, loss of WOX1 expression results in tumorigenesis. WOX1 is also associated with malignan ...
... acts as a proapoptotic protein and tumor suppressor. Loss of heterozygosity and chromosomal rearrangement of the WOX1 gene is associated with ovarian, breast, hepatocellular, and prostate carcinomas. In addition, loss of WOX1 expression results in tumorigenesis. WOX1 is also associated with malignan ...
Biobowl
... 33. The amount of ATP used in glycolysis per molecule of glucose is 34. The net amount of ATP produced in glycolysis is 35. The majority of NADH is produced during __________________ 36. The majority of ATP made during aerobic oxidation of glucose is made during which process? 37. An example of a mo ...
... 33. The amount of ATP used in glycolysis per molecule of glucose is 34. The net amount of ATP produced in glycolysis is 35. The majority of NADH is produced during __________________ 36. The majority of ATP made during aerobic oxidation of glucose is made during which process? 37. An example of a mo ...
Lesson 4 Organisms Made of Cells
... Background: Onion tissue provides excellent cells to study under the microscope. The main cell structures are easy to see when viewed with the microscope at medium power. For example, you will observe a large circular nucleus in each cell, which contains the genetic material for the cell. In each nu ...
... Background: Onion tissue provides excellent cells to study under the microscope. The main cell structures are easy to see when viewed with the microscope at medium power. For example, you will observe a large circular nucleus in each cell, which contains the genetic material for the cell. In each nu ...
comparison of cheek and onion cells
... By the end of this exercise, you should be able to... explain how the cell is the basic unit for all living things. relate characteristics of living things to cell structure. diagram prepared slides of prokaryotic cells (bacteria) and label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Identify the s ...
... By the end of this exercise, you should be able to... explain how the cell is the basic unit for all living things. relate characteristics of living things to cell structure. diagram prepared slides of prokaryotic cells (bacteria) and label the cell wall, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Identify the s ...
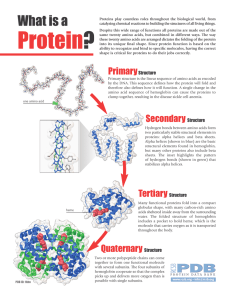
Protein?
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
Prokaryotic Cell Division
... Due to the relative simplicity of the prokaryotes, the cell division process, called binary ssion, is a less complicated and much more rapid process than cell division in eukaryotes. The single, circular DNA chromosome of bacteria is not enclosed in a nucleus, but instead occupies a speci c locatio ...
... Due to the relative simplicity of the prokaryotes, the cell division process, called binary ssion, is a less complicated and much more rapid process than cell division in eukaryotes. The single, circular DNA chromosome of bacteria is not enclosed in a nucleus, but instead occupies a speci c locatio ...
A. Movement of substances across the cell membrane
... a) Carrier proteins bind a specific type of and carry the solute to the other side of the membrane. The carrier then discharges the solute and reorients in the membrane to its original state. Typically, a given carrier will transport only a small group of related molecules b) Ion Channels do not bin ...
... a) Carrier proteins bind a specific type of and carry the solute to the other side of the membrane. The carrier then discharges the solute and reorients in the membrane to its original state. Typically, a given carrier will transport only a small group of related molecules b) Ion Channels do not bin ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... to cellular energy. The extensive surface area of the folded inner membranes allows both organelles to produce much more energy than would otherwise be possible. 80) The structure and function of the cytoplasmic membrane are explained in the fluid mosaic model. The cytoplasmic membranes of bacterial ...
... to cellular energy. The extensive surface area of the folded inner membranes allows both organelles to produce much more energy than would otherwise be possible. 80) The structure and function of the cytoplasmic membrane are explained in the fluid mosaic model. The cytoplasmic membranes of bacterial ...
"pdf" copy of Topic 6, The Plant Cell
... barely visible or invisible with the light microscope can be viewed with startling detail. Other structures such as ribosomes may be viewed only with the electron microscope. Below is an EM of a young plant cell: For Figure E-3 (below), note the nucleus (N) surrounded by a double unit membrane; the ...
... barely visible or invisible with the light microscope can be viewed with startling detail. Other structures such as ribosomes may be viewed only with the electron microscope. Below is an EM of a young plant cell: For Figure E-3 (below), note the nucleus (N) surrounded by a double unit membrane; the ...
Document
... Useful for measuring number of cells in aquatic samples Sample passed through filter with small pore size Filters placed on agar plates to allow growth of colonies ...
... Useful for measuring number of cells in aquatic samples Sample passed through filter with small pore size Filters placed on agar plates to allow growth of colonies ...
Reproduction PPT - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Plant cells have a fibrous cell wall that provides structure and support for the cell. Plants need this cell wall to provide with support. Example and sunflower. Plant cells contain chloroplasts. They are organelles that enable the plant to make their own food through the process of ...
... Plant cells have a fibrous cell wall that provides structure and support for the cell. Plants need this cell wall to provide with support. Example and sunflower. Plant cells contain chloroplasts. They are organelles that enable the plant to make their own food through the process of ...
Mitosis - KS Blogs
... Eukaryotes (cells with a nucleus) go through 2 stages of division Mitosis – division of the nucleus Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm ...
... Eukaryotes (cells with a nucleus) go through 2 stages of division Mitosis – division of the nucleus Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm ...
Hypertonic, Hypotonic, and Isotonic Solutions Impact on Cells
... Osmosis is a form of passive transport of water into or out of a cell based on environmental solute concentrations. Since every organism exists in conjunction with its environment, it has to adapt to changes that arise. Most cells exist in conditions that have either higher or lower numbers of disso ...
... Osmosis is a form of passive transport of water into or out of a cell based on environmental solute concentrations. Since every organism exists in conjunction with its environment, it has to adapt to changes that arise. Most cells exist in conditions that have either higher or lower numbers of disso ...
Centrosome - English at the Shore Spot
... http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/bio%20101/Bio%201 01%20Lectures/Mitosis/mitosis.htm ...
... http://faculty.clintoncc.suny.edu/faculty/michael.gregory/files/bio%20101/Bio%201 01%20Lectures/Mitosis/mitosis.htm ...
Genus species
... Ribosomes for making proteins) Unicellular; Most are autotrophs (Chemosynthesis) Habitat: Extreme environments Methanogens, thermoacidophiles, halophiles Reproduction: binary fission(asexual), conjugation(sexual) Eubacteria ...
... Ribosomes for making proteins) Unicellular; Most are autotrophs (Chemosynthesis) Habitat: Extreme environments Methanogens, thermoacidophiles, halophiles Reproduction: binary fission(asexual), conjugation(sexual) Eubacteria ...







![Best_SOL_review[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282052_1-bb0b88ec2a2d778a830fa1c37d632272-300x300.png)