Unit 1 – Life on Earth
... engineering is the process of ARTIFICIALLY altering the genome (Genetic make-up) of a cell. • Scientists use genetic engineering to alter a bacterial plasmid to produce useful substances QUICKLY. • 2 substances which are produced in this manner are : ...
... engineering is the process of ARTIFICIALLY altering the genome (Genetic make-up) of a cell. • Scientists use genetic engineering to alter a bacterial plasmid to produce useful substances QUICKLY. • 2 substances which are produced in this manner are : ...
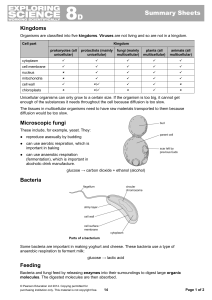
8D Unicellular Organisms
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... change enables us to compare different starting masses in (ii). This is a common practice in many experiments and the examiners were disappointed that many candidates did not understand its purpose. However, in (c), almost all were able to explain why the potato cubes gained mass. Most could also c ...
... change enables us to compare different starting masses in (ii). This is a common practice in many experiments and the examiners were disappointed that many candidates did not understand its purpose. However, in (c), almost all were able to explain why the potato cubes gained mass. Most could also c ...
cell-junctions - WordPress.com
... together when pressed tightly against one another, to the point that nothing will pass through the tight seal. And so, this is why tight junctions prevent virtually any and all fluid from leaking across a layer of epithelial cells, like those of the skin. Unsurprisingly, such tight junctions are fou ...
... together when pressed tightly against one another, to the point that nothing will pass through the tight seal. And so, this is why tight junctions prevent virtually any and all fluid from leaking across a layer of epithelial cells, like those of the skin. Unsurprisingly, such tight junctions are fou ...
Defining the inner membrane proteome of E coli
... • The work presented here is an important framework for many future studies of membrane proteins • Incorporation of experimental topology information improves the topology models • These papers have been a nice cooperation between experimentalists and bioinformaticians, where both have ...
... • The work presented here is an important framework for many future studies of membrane proteins • Incorporation of experimental topology information improves the topology models • These papers have been a nice cooperation between experimentalists and bioinformaticians, where both have ...
Cell Structure and Organisation
... available, yeast can carry out anaerobic respiration (fermentation). In this respect, we can use yeast for the production of bread and alcohol. ...
... available, yeast can carry out anaerobic respiration (fermentation). In this respect, we can use yeast for the production of bread and alcohol. ...
How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and
... 13 Distinguish among amyloplasts, chromoplasts, and chloroplasts. ...
... 13 Distinguish among amyloplasts, chromoplasts, and chloroplasts. ...
• What is a cell? The smallest unit of a living thing. A cell is
... g) controls the activities of the cell = genetic material (DNA and/or RNA), the nucleus h) carries out photosynthesis = chloroplasts (containing chlorophyll) i) carries out [cellular] respiration = mitochond ...
... g) controls the activities of the cell = genetic material (DNA and/or RNA), the nucleus h) carries out photosynthesis = chloroplasts (containing chlorophyll) i) carries out [cellular] respiration = mitochond ...
Topic #2 - OCHS Biology
... 5) Can prokaryotes be autotrophic? Yes 6) What does “autotrophic” mean? an organism can make its own food (like through the process of photosynthesis); it does not have to consume other organisms as a food source 7) Can prokaryotes be heterotrophic? Yes 8) What does “heterotrophic” mean? an organism ...
... 5) Can prokaryotes be autotrophic? Yes 6) What does “autotrophic” mean? an organism can make its own food (like through the process of photosynthesis); it does not have to consume other organisms as a food source 7) Can prokaryotes be heterotrophic? Yes 8) What does “heterotrophic” mean? an organism ...
cells - CBSD.org
... too long to diffuse into the center of the cell. • DNA prevents the growth of larger cells because it has to control cellular functions but can only do so from the nuclei. – The largest cells are often multi-nucleated. ...
... too long to diffuse into the center of the cell. • DNA prevents the growth of larger cells because it has to control cellular functions but can only do so from the nuclei. – The largest cells are often multi-nucleated. ...
combindedAronsMyxoNoSim
... Preliminary data suggests that cells stall during division. (Yellow arrow highlight additional time between frames during division. Red arrow point to septum forming) Questions: How does polarity of mother cell relate to daughter cells? Does phase of reversal period get passed to daughter cells? ...
... Preliminary data suggests that cells stall during division. (Yellow arrow highlight additional time between frames during division. Red arrow point to septum forming) Questions: How does polarity of mother cell relate to daughter cells? Does phase of reversal period get passed to daughter cells? ...
Chapter 2 Mitosis and Meiosis
... • Kinetochore is the joining of the spindle fiber to the centromere. Improper connection can result in devastating results for the resulting cell. ...
... • Kinetochore is the joining of the spindle fiber to the centromere. Improper connection can result in devastating results for the resulting cell. ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 2-9: The ankyrin-spectrin lattice. (A) Structural model of a spectrin repeat unit based on the crystal structure of a dimer of the 14th repeat unit of Drosophila spectrin (Adapted from (Yan et al., 1993), with permission). (B) Cartoon of the domain structure of a spectrin dimer. Many of the ...
... FIGURE 2-9: The ankyrin-spectrin lattice. (A) Structural model of a spectrin repeat unit based on the crystal structure of a dimer of the 14th repeat unit of Drosophila spectrin (Adapted from (Yan et al., 1993), with permission). (B) Cartoon of the domain structure of a spectrin dimer. Many of the ...
Vacuole Biogenesis in Living Soybean Root Tip
... high voltage EM of thick sections stained en bloc with ZIO, Marty and coworkers have shown that a complex array of provacuole tubules forms a cage around cytoplasm in root tip meristem cells [2]. These tubules fuse together to form an autophagic vacuole that digests the enclosed cytoplasm. According ...
... high voltage EM of thick sections stained en bloc with ZIO, Marty and coworkers have shown that a complex array of provacuole tubules forms a cage around cytoplasm in root tip meristem cells [2]. These tubules fuse together to form an autophagic vacuole that digests the enclosed cytoplasm. According ...
What is a membrane potential?
... Why are patch clamps useful for studying Vm? What are the properties of voltage-gated channels? What is “self-propagation” and why is this property important with regards to a cellular membrane potential? What is saltatory conduction and why is it so fast? How do gap junctions create an electric syn ...
... Why are patch clamps useful for studying Vm? What are the properties of voltage-gated channels? What is “self-propagation” and why is this property important with regards to a cellular membrane potential? What is saltatory conduction and why is it so fast? How do gap junctions create an electric syn ...
SEMESTER I EXAM - Hudson City Schools / Homepage
... • SER: synthesise lipids, detoxify drugs and alcohol, store Ca ions • RER: assemble proteins, make membrane proteins ...
... • SER: synthesise lipids, detoxify drugs and alcohol, store Ca ions • RER: assemble proteins, make membrane proteins ...
Chapter 3
... Bacterial chromosome or nucleoid—Composed of condensed DNA molecules. DNA directs all genetics and heredity of the cell and codes for all proteins. ...
... Bacterial chromosome or nucleoid—Composed of condensed DNA molecules. DNA directs all genetics and heredity of the cell and codes for all proteins. ...
Lecture 05 - Intro to Eukaryotes - Cal State LA
... supply of carbon compounds from its host cell - eukaryote got a more efficient form of metabolism ...
... supply of carbon compounds from its host cell - eukaryote got a more efficient form of metabolism ...
Unit 1 PPT 7 (2ciii-iv Channels and transporters)
... There are two classes of binding sites, one for Na+ and the other for glucose. Binding of either molecule enhances the binding of the other. As this system is driven by the Na+ gradient generated by the Na+/K+ ATPase it is described as secondary active transport. When all binding sites are filled a ...
... There are two classes of binding sites, one for Na+ and the other for glucose. Binding of either molecule enhances the binding of the other. As this system is driven by the Na+ gradient generated by the Na+/K+ ATPase it is described as secondary active transport. When all binding sites are filled a ...
Chapter 5 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 1. Cells that are expose to an Isotonic External environment Usually have no difficulty keeping the movement of water across the cell membrane in balance. 2. This is the case with the cells of vertebrate animals on land and most other organisms living in the sea. 3. Many cells function in a Hypoton ...
... 1. Cells that are expose to an Isotonic External environment Usually have no difficulty keeping the movement of water across the cell membrane in balance. 2. This is the case with the cells of vertebrate animals on land and most other organisms living in the sea. 3. Many cells function in a Hypoton ...
MEMBRANES
... Boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid Arranged in a bilayer ...
... Boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid Arranged in a bilayer ...
Biology Midterm Study Guide
... Calculate the total magnification of a microscope. Label organelles if given a diagram of a cell. Identify the type of cell (plant, animal, or prokaryote) if given a diagram. Provide examples of plants, animals, and prokaryotes. Explain that prokaryotes evolved before eukaryotes. Describe the differ ...
... Calculate the total magnification of a microscope. Label organelles if given a diagram of a cell. Identify the type of cell (plant, animal, or prokaryote) if given a diagram. Provide examples of plants, animals, and prokaryotes. Explain that prokaryotes evolved before eukaryotes. Describe the differ ...