Cell Growth Section 10-1 pgs 241-243
... Before it becomes too large, a growing cell divides, forming two _______________________________ cells. ...
... Before it becomes too large, a growing cell divides, forming two _______________________________ cells. ...
Ubiquitin Found to Mark Pathogen-Containing Vacuoles
... pathogen-containing vacuoles," said Dr. Coers, who along with his colleagues, went on to identify the molecular players responsible both for attaching the ubiquitin tags and for escorting the GBPs to the surface of the vacuole so they can coordinate an attack. The researchers also showed that highly ...
... pathogen-containing vacuoles," said Dr. Coers, who along with his colleagues, went on to identify the molecular players responsible both for attaching the ubiquitin tags and for escorting the GBPs to the surface of the vacuole so they can coordinate an attack. The researchers also showed that highly ...
Endosymbiotic Theory
... of invading organisms. Rather than eliminating competitors, evolution eliminated competition itself on the basis of symboitic relationships. ...
... of invading organisms. Rather than eliminating competitors, evolution eliminated competition itself on the basis of symboitic relationships. ...
Cell Reproduction - Ursuline High School
... amounts of water and oxygen can move into the cell, and wastes can rapidly be eliminated. • When the surface-to-volume ratio is small the cell is unable to exchange enough substances to service the cell. The cell dies. ...
... amounts of water and oxygen can move into the cell, and wastes can rapidly be eliminated. • When the surface-to-volume ratio is small the cell is unable to exchange enough substances to service the cell. The cell dies. ...
Comparing Plant cells and Animal cells Lab Report
... Comparing Plant cells and Animal cells Lab Report Introduction- ...
... Comparing Plant cells and Animal cells Lab Report Introduction- ...
Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water? Molecules Name
... Question 3: Compare and contrast what happens to an animal, a plant, and a Paramecium cell in a hypotonic, an isotonic, and a hypertonic solution. -- The hypotonic solution means the solution with the least amount of solute compared to inside the cell. -- The hypertonic solution means the solution w ...
... Question 3: Compare and contrast what happens to an animal, a plant, and a Paramecium cell in a hypotonic, an isotonic, and a hypertonic solution. -- The hypotonic solution means the solution with the least amount of solute compared to inside the cell. -- The hypertonic solution means the solution w ...
Diffusion and Osmosis - PBSpaces.com Weblogs
... than a cell. Hypo- means “less.” This means the cell has a lower concentration of water than the surrounding fluid. As a result, water diffuses into the cell, and the cell grows larger. Notice how water moves from the area of higher water concentration to the area of lower water concentration in two ...
... than a cell. Hypo- means “less.” This means the cell has a lower concentration of water than the surrounding fluid. As a result, water diffuses into the cell, and the cell grows larger. Notice how water moves from the area of higher water concentration to the area of lower water concentration in two ...
What is a plasmid? - Parkway C-2
... One or more copies per cell, “stringent” vs. “relaxed” : <12 is normal, but can range from ~5 to 700 copies per cell Not all bacteria have plasmids ...
... One or more copies per cell, “stringent” vs. “relaxed” : <12 is normal, but can range from ~5 to 700 copies per cell Not all bacteria have plasmids ...
2. Internal and external cues help regulate the cell cycle
... • The timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance. • The frequency of cell division varies with cell type. • Some human cells divide frequently throughout life (skin cells), others have the ability to divide, ...
... • The timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance. • The frequency of cell division varies with cell type. • Some human cells divide frequently throughout life (skin cells), others have the ability to divide, ...
Anti-Nav1.8 antibody ab63331 Product datasheet 1 References 2 Images
... Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab63331 in the following tested applications. The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab63331 in the following tested applications. The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
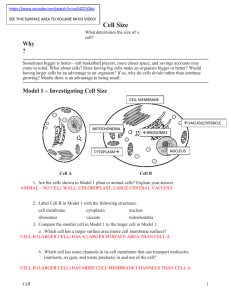
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
Hypersensitivity Reaction
... which increases the life span of the IgE. (Half-life of IgE in serum is days whereas attached to FceR it is increased to months) * Second exposure to the same allergen It bridges between Ig E molecules fixed to mast cells leading to activation and degranulation of mast cells and release of mediators ...
... which increases the life span of the IgE. (Half-life of IgE in serum is days whereas attached to FceR it is increased to months) * Second exposure to the same allergen It bridges between Ig E molecules fixed to mast cells leading to activation and degranulation of mast cells and release of mediators ...
Auxiliary proteins of photosystem II: tuning the enzyme for optimal
... hydrophobic polypeptides that form a ring around the core and a “cap” of 3 or more hydrophilic polypeptides that cover the oxygen-evolving center (OEC). These auxiliary PS II proteins were acquired prior to endosymbiotic uptake of cyanobacteria. The crystal structure of cyanobacterial PS II has reve ...
... hydrophobic polypeptides that form a ring around the core and a “cap” of 3 or more hydrophilic polypeptides that cover the oxygen-evolving center (OEC). These auxiliary PS II proteins were acquired prior to endosymbiotic uptake of cyanobacteria. The crystal structure of cyanobacterial PS II has reve ...
2081 Slc35a2 provides a novel role for glycosylation in glucose
... We found that Lec8 cells exhibit enhanced electrophoretic mobility of Glut1 protein, altered lectin binding, and reduced uptake of 2-NBDG, which was time- and concentration-dependent, and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lect ...
... We found that Lec8 cells exhibit enhanced electrophoretic mobility of Glut1 protein, altered lectin binding, and reduced uptake of 2-NBDG, which was time- and concentration-dependent, and reduced whole cell ATP content. Importantly, we found that enhanced Glut1 electrophoretic mobility, altered lect ...
Biology Semester I Exam Review Sheet 2015
... What happens to resolution when magnification is increased using a compound light microscope? What are the two types of electron microscopes? How are images they produce different? Know common safety procedures used in the lab Review chapter 1 study guide p.30; Complete Chapter One Assessmen ...
... What happens to resolution when magnification is increased using a compound light microscope? What are the two types of electron microscopes? How are images they produce different? Know common safety procedures used in the lab Review chapter 1 study guide p.30; Complete Chapter One Assessmen ...
Chapter 19b Blood, cont`d White Blood Cells WBCs account for less
... show up red.) They have a bi-lobed nucleus that pretty much looks like two nuclei, or an alien face. These cells are phagocytic, but don’t kill their prey by phagocytosis. They use phagocytosis to clear up cellular debris, but for dealing with pathogens they attack it as a group and release their de ...
... show up red.) They have a bi-lobed nucleus that pretty much looks like two nuclei, or an alien face. These cells are phagocytic, but don’t kill their prey by phagocytosis. They use phagocytosis to clear up cellular debris, but for dealing with pathogens they attack it as a group and release their de ...
Erdal, Hamdiye et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 192
... The M65 ELISA measures soluble CK18 released extracellularly from dying cells. It is used to assess overall cell death (apoptosis and necrosis) to determine the relative contribution of apoptosis to the total degree of cell death. ...
... The M65 ELISA measures soluble CK18 released extracellularly from dying cells. It is used to assess overall cell death (apoptosis and necrosis) to determine the relative contribution of apoptosis to the total degree of cell death. ...
Cell junction
... membranes join together forming a virtually impermeable barrier to fluid. A type of junctional complex present only in vertebrates. Consist of linear array of several integral proteins. Junctional proteins occludins and claudins & members of IG suprfamily are transmembrane proteins. ...
... membranes join together forming a virtually impermeable barrier to fluid. A type of junctional complex present only in vertebrates. Consist of linear array of several integral proteins. Junctional proteins occludins and claudins & members of IG suprfamily are transmembrane proteins. ...
Introduction to Course and Cell Cycle - March 21
... – If the cell receives a go-ahead signal, it usually completes the cell cycle and divides. – If it does not receive a go-ahead signal, the cell exits the cycle and switches to a nondividing state, the G0 phase. • Most human cells are in this phase. • Liver cells can be “called back” to the cell cycl ...
... – If the cell receives a go-ahead signal, it usually completes the cell cycle and divides. – If it does not receive a go-ahead signal, the cell exits the cycle and switches to a nondividing state, the G0 phase. • Most human cells are in this phase. • Liver cells can be “called back” to the cell cycl ...
Review Activity Module 2: Cells and Division Laroche
... with a cell in the early stages of G1 that was obtained from a normal culture of slowly dividing cells. No change was observed in the normal cell, but the nucleus from the cancer cell failed to initiate the S phase as predicted, and instead remained in G1. When subjected to further analysis, it was ...
... with a cell in the early stages of G1 that was obtained from a normal culture of slowly dividing cells. No change was observed in the normal cell, but the nucleus from the cancer cell failed to initiate the S phase as predicted, and instead remained in G1. When subjected to further analysis, it was ...
Macromolecules 2016
... What if glucose is needed now? • We make a polymer called glycogen (similar to starch, but only found in animals), which are repeating units, or monomers of glucose with lots of branches. Glycogen curls around and makes a BIG globby molecule. • Globby and branched= sticks out all over the place. • ...
... What if glucose is needed now? • We make a polymer called glycogen (similar to starch, but only found in animals), which are repeating units, or monomers of glucose with lots of branches. Glycogen curls around and makes a BIG globby molecule. • Globby and branched= sticks out all over the place. • ...