7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... oRibosomes produce proteins by following _______ _______________ that come from the ___________. ...
... oRibosomes produce proteins by following _______ _______________ that come from the ___________. ...
Morphological changes induced in bacteria as evaluated by electron
... µm and cell width of 0.41 µm. This Gram-negative rod (Fig. 1d) exhibit extra-cellular filamentous materials detectable as smoothly curved filaments (Fig. 1a). Figure 1e shows the thin section TEM micrograph of P. aeruginosa control with a typical cell wall, outer and cytoplasmic membrane, periplasmi ...
... µm and cell width of 0.41 µm. This Gram-negative rod (Fig. 1d) exhibit extra-cellular filamentous materials detectable as smoothly curved filaments (Fig. 1a). Figure 1e shows the thin section TEM micrograph of P. aeruginosa control with a typical cell wall, outer and cytoplasmic membrane, periplasmi ...
Full details. - CCP-EM
... The structural and molecular microbiology lab focuses on the structure and function of bacterial cell surfaces and their roles in host-‐pathogen interactions. In this project you will work on the biogenesis ...
... The structural and molecular microbiology lab focuses on the structure and function of bacterial cell surfaces and their roles in host-‐pathogen interactions. In this project you will work on the biogenesis ...
Chapter 10 Roche Bio
... ◦ The more demands it places on its DNA ◦ It becomes more difficult to move enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane ◦ If there is more space between the cell’s membrane and the center of the cell, it takes longer to move materials in and out ...
... ◦ The more demands it places on its DNA ◦ It becomes more difficult to move enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane ◦ If there is more space between the cell’s membrane and the center of the cell, it takes longer to move materials in and out ...
Sec14p-like proteins regulate phosphoinositide homoeostasis and
... Sfh5p-mediated control of plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 and efficient Sec9p t-SNARE (target membrane soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor) function Stt4p and Mss4p reside in the yeast plasma membrane [22]. This raises the possibility that SFH proteins modulate ...
... Sfh5p-mediated control of plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 and efficient Sec9p t-SNARE (target membrane soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor) function Stt4p and Mss4p reside in the yeast plasma membrane [22]. This raises the possibility that SFH proteins modulate ...
Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... coacervates (microscopic spheres formed from lipids in water). 17. There was no oxygen on Earth 4 billion years ago; therefore, early forms of life on Earth were anaerobic cells like bacteria. 18. About 3.5 billion years ago, certain bacteria developed the capacity to photosynthesize (make their own ...
... coacervates (microscopic spheres formed from lipids in water). 17. There was no oxygen on Earth 4 billion years ago; therefore, early forms of life on Earth were anaerobic cells like bacteria. 18. About 3.5 billion years ago, certain bacteria developed the capacity to photosynthesize (make their own ...
Different subcellular locations of secretome components of
... throughout the membrane. Possible mechanisms for maintaining the localization of these secretion machineries involve their interaction with proteins of the cytoskeleton or components of the cell wall synthesis machinery, or the presence of lipid subdomains surrounding the transport systems. ...
... throughout the membrane. Possible mechanisms for maintaining the localization of these secretion machineries involve their interaction with proteins of the cytoskeleton or components of the cell wall synthesis machinery, or the presence of lipid subdomains surrounding the transport systems. ...
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the
... Dividing cell duplicates DNA separates each copy to opposite ends of cell splits into 2 daughter cells ...
... Dividing cell duplicates DNA separates each copy to opposite ends of cell splits into 2 daughter cells ...
Ch12mitosis - Environmental
... Dividing cell duplicates DNA separates each copy to opposite ends of cell splits into 2 daughter cells ...
... Dividing cell duplicates DNA separates each copy to opposite ends of cell splits into 2 daughter cells ...
Pre-Bio LP 9.19-9.30
... Summarize a brief description of the characteristics of water that make it essential for life. - Using the text book, read pages 51-60 and describe the major characteristics of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. -(2d) Note taking on the structure, properties, and principle functions of carbohydrat ...
... Summarize a brief description of the characteristics of water that make it essential for life. - Using the text book, read pages 51-60 and describe the major characteristics of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. -(2d) Note taking on the structure, properties, and principle functions of carbohydrat ...
Anatomical and functional recovery of the goldfish saccule following
... Mammalian and avian auditory hair cells display tonotopic mapping of frequency along the length of the cochlea and basilar papilla. It is not known whether the auditory hair cells of fish possess a similar tonotopic organization in the saccule, the primary auditory receptor in many teleosts. To inve ...
... Mammalian and avian auditory hair cells display tonotopic mapping of frequency along the length of the cochlea and basilar papilla. It is not known whether the auditory hair cells of fish possess a similar tonotopic organization in the saccule, the primary auditory receptor in many teleosts. To inve ...
No Slide Title
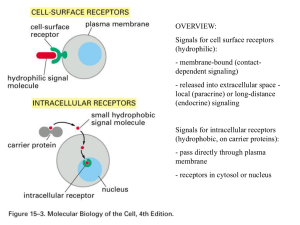
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
Why don`t Cells Grow Indefinitely Lab
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely, until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows large? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
... Many cells grow until they reach a certain size and then divide. Why don’t cells grow indefinitely, until they become the size of basketballs? What problems arise when a cell grows large? Why does a cell divide into two smaller cells when it reaches a certain size? These are all questions that scien ...
My Course - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... All of the following are found in the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria except a) b) c) d) ...
... All of the following are found in the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria except a) b) c) d) ...
Insights from studies of premature aging
... replenish themselves and this gives rise to the Werner’s syndrome phenotype. ...
... replenish themselves and this gives rise to the Werner’s syndrome phenotype. ...
Document
... Potassium has several critical roles in plant growth and yield formation including cell elongation, maintenance of turgor pressure and photosynthesis, stomatal closure, protein synthesis and photoassimilate transport. Potassium transporter proteins play critical role in K uptake and translocation (c ...
... Potassium has several critical roles in plant growth and yield formation including cell elongation, maintenance of turgor pressure and photosynthesis, stomatal closure, protein synthesis and photoassimilate transport. Potassium transporter proteins play critical role in K uptake and translocation (c ...
+K - IPNI
... Potassium has several critical roles in plant growth and yield formation including cell elongation, maintenance of turgor pressure and photosynthesis, stomatal closure, protein synthesis and photoassimilate transport. Potassium transporter proteins play critical role in K uptake and translocation (c ...
... Potassium has several critical roles in plant growth and yield formation including cell elongation, maintenance of turgor pressure and photosynthesis, stomatal closure, protein synthesis and photoassimilate transport. Potassium transporter proteins play critical role in K uptake and translocation (c ...
Week 11
... Activity: Complete parts D, E and the activity on eukaryotic cells. structures: mitochondria and conclusion questions on the cell lab. chloroplast. Assessment: Student participation Assessment: Student participation Assessment: Correct answers. and correct answers Homework: Cell Factory WS Objective ...
... Activity: Complete parts D, E and the activity on eukaryotic cells. structures: mitochondria and conclusion questions on the cell lab. chloroplast. Assessment: Student participation Assessment: Student participation Assessment: Correct answers. and correct answers Homework: Cell Factory WS Objective ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
Decomposition
... • Lysosomes are spherical organelles that contain enzymes (acid hydrolases). They break up food so it is easier to digest. They are found in animal cells, while in yeast and plants the same roles are performed by lytic vacuoles. • Some important enzymes found within lysosomes include: • Lipase diges ...
... • Lysosomes are spherical organelles that contain enzymes (acid hydrolases). They break up food so it is easier to digest. They are found in animal cells, while in yeast and plants the same roles are performed by lytic vacuoles. • Some important enzymes found within lysosomes include: • Lipase diges ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
Section 2
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported from the cell. Slide 17 of 49 Copyrigh ...
CHAPTER 4 FREE ENERGY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA
... To attain equilibrium, some of the NaCl will move. It will move from the outer solution through the membrane into the bag with the protein in it. In effect, the added salt reduces and at high enough salt concentration, eliminates the Donnan effect. ...
... To attain equilibrium, some of the NaCl will move. It will move from the outer solution through the membrane into the bag with the protein in it. In effect, the added salt reduces and at high enough salt concentration, eliminates the Donnan effect. ...