Dave Cooke Mitosis
... coiling & folding to make a smaller package from DNA molecule to chromatin to highly condensed mitotic chromosome mitotic chromosome ...
... coiling & folding to make a smaller package from DNA molecule to chromatin to highly condensed mitotic chromosome mitotic chromosome ...
CHAPTER 4 FREE ENERGY AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA
... To attain equilibrium, some of the NaCl will move. It will move from the outer solution through the membrane into the bag with the protein in it. In effect, the added salt reduces and at high enough salt concentration, eliminates the Donnan effect. ...
... To attain equilibrium, some of the NaCl will move. It will move from the outer solution through the membrane into the bag with the protein in it. In effect, the added salt reduces and at high enough salt concentration, eliminates the Donnan effect. ...
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES
... properties and physical shape during the individual’s lifetime. • This may be one of the major mechanisms of learning. – Experiences at one time in life produce long-term changes in synapses, so that future experiences are processed by the nervous system in altered ways. ...
... properties and physical shape during the individual’s lifetime. • This may be one of the major mechanisms of learning. – Experiences at one time in life produce long-term changes in synapses, so that future experiences are processed by the nervous system in altered ways. ...
Wet Mounts – Onion Skin Cells
... 1. Why do we stain specimens? Support your answer using the observations made when examining the onion cells with and without the iodine stain. Be specific by referring to the substances and organelles affected by the stain(s). (4 marks) 2. Stains increase contrast because certain structures absorb ...
... 1. Why do we stain specimens? Support your answer using the observations made when examining the onion cells with and without the iodine stain. Be specific by referring to the substances and organelles affected by the stain(s). (4 marks) 2. Stains increase contrast because certain structures absorb ...
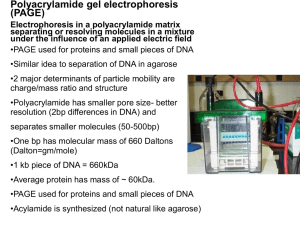
Polyacrylamide gels
... The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
... The copolymerization of acrylamide with methylenebisacrylamide produces a mesh-like network in three dimensions, consisting of acrylamide chains with interconnections formed from the methylenebisacrylamide ...
Lipid transfer and metabolism across the endolysosomal
... overview of lysosomal and mitochondrial functions, with particular attention to their roles in metabolic homeostasis. Moreover, we have included four explanatory Boxes, dedicated to LTP families operating at MCSs discussed in this review, containing conserved ORD (Box 1), START (Box 2A), START-like/ ...
... overview of lysosomal and mitochondrial functions, with particular attention to their roles in metabolic homeostasis. Moreover, we have included four explanatory Boxes, dedicated to LTP families operating at MCSs discussed in this review, containing conserved ORD (Box 1), START (Box 2A), START-like/ ...
Apoptosis Apoptosis is a process of cell death that is carried out by
... through a series of steps, and for this reason apoptosis is also referred to as programmed cell death. There are numerous reasons why apoptosis occurs, including normal development of fingers and toes in the fetus, shedding of uterine lining cells at menstruation, and synapse formation. Apoptosis is ...
... through a series of steps, and for this reason apoptosis is also referred to as programmed cell death. There are numerous reasons why apoptosis occurs, including normal development of fingers and toes in the fetus, shedding of uterine lining cells at menstruation, and synapse formation. Apoptosis is ...
Unit: Cell Biology | PDF 98.6 KB - Edexcel
... Unit abstract Understanding the cell, and the role and function of the cell in the multicellular organism, are of fundamental importance in understanding biology and related ...
... Unit abstract Understanding the cell, and the role and function of the cell in the multicellular organism, are of fundamental importance in understanding biology and related ...
New astrocyte cell surface markers
... Institute of Molecular Sytems Biology, NCCR Neuro Center for Proteomics, ETH Zurich, Switzerland ...
... Institute of Molecular Sytems Biology, NCCR Neuro Center for Proteomics, ETH Zurich, Switzerland ...
Biology LP 9.19-9.30
... Summarize a brief description of the characteristics of water that make it essential for life. - Using the text book, read pages 51-60 and describe the major characteristics of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. -(2d) Note taking on the structure, properties, and principle functions of carbohydrat ...
... Summarize a brief description of the characteristics of water that make it essential for life. - Using the text book, read pages 51-60 and describe the major characteristics of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. -(2d) Note taking on the structure, properties, and principle functions of carbohydrat ...
10.1 Cell Biology.indd NS NEW.indd
... resembling eukaryote scaffold-protein genes probing the insides of bacteria has practical found nothing, scientists assumed that these applications, and bacterial cell biologists recproteins evolved after bacteria split from ognize the need to remind funding agencies eukaryotes, some 1.5 billion to ...
... resembling eukaryote scaffold-protein genes probing the insides of bacteria has practical found nothing, scientists assumed that these applications, and bacterial cell biologists recproteins evolved after bacteria split from ognize the need to remind funding agencies eukaryotes, some 1.5 billion to ...
Chapter 7: A View of the Cell
... Your cells need nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids to function. It is the job of the plasma membrane, the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment, to allow a steady supply of these nutrients to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. However, too ...
... Your cells need nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids to function. It is the job of the plasma membrane, the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment, to allow a steady supply of these nutrients to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. However, too ...
A major glycoprotein of the nuclear pore complex is a membrane
... proteins of the pore complex have been identified in higher eucaryotes by imunocytochemistry (for review, see Gerace and Burke, 1988). The first of these was a glycoprotein called gpl90 that was identified in rat liver nuclear envelopes with polyclonal antibodies (Gerace et al., 1982). This protein ...
... proteins of the pore complex have been identified in higher eucaryotes by imunocytochemistry (for review, see Gerace and Burke, 1988). The first of these was a glycoprotein called gpl90 that was identified in rat liver nuclear envelopes with polyclonal antibodies (Gerace et al., 1982). This protein ...
Remember what qualifies as *alive*?
... membrane –controls/regulates the flow of nutrients in/out of the cell. cytoplasm (watery goo in ALL cells that support all the organelles of the cell) vacuoles store water & nutrients for balance in complex cells. chloroplasts in producer cells perform photosynthesis that make sugar food nutrients f ...
... membrane –controls/regulates the flow of nutrients in/out of the cell. cytoplasm (watery goo in ALL cells that support all the organelles of the cell) vacuoles store water & nutrients for balance in complex cells. chloroplasts in producer cells perform photosynthesis that make sugar food nutrients f ...
A View of the Cell
... Your cells need nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids to function. It is the job of the plasma membrane, the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment, to allow a steady supply of these nutrients to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. However, too ...
... Your cells need nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, and lipids to function. It is the job of the plasma membrane, the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment, to allow a steady supply of these nutrients to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. However, too ...
Transport Across Membranes
... • Active Transport allows cells to uptake necessary ions and molecules and remove waste products • These Mechanisms often referred to as Pumps • Most common is Sodium Pump ...
... • Active Transport allows cells to uptake necessary ions and molecules and remove waste products • These Mechanisms often referred to as Pumps • Most common is Sodium Pump ...
Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields
... In cellular aggregates that form tissues of higher animals, cells are separated by narrow fluid channels that take on special importance in signaling from cell to cell. These channels act as windows on the electrochemical world surrounding each cell. Hormones, antibodies, neurotransmitters and chemi ...
... In cellular aggregates that form tissues of higher animals, cells are separated by narrow fluid channels that take on special importance in signaling from cell to cell. These channels act as windows on the electrochemical world surrounding each cell. Hormones, antibodies, neurotransmitters and chemi ...