Structure of skin
... /membrane-coated /characteristic racket-shape /15-30 nm long, 4 nm in D ---function: • antigen presenting cell in skin • involve in immune reaction ...
... /membrane-coated /characteristic racket-shape /15-30 nm long, 4 nm in D ---function: • antigen presenting cell in skin • involve in immune reaction ...
Active transport - PrelimBio
... Simple Diffusion Lipid soluble molecules and small simple molecules diffuse across cell membranes. Living organisms rely on diffusion to function in a large number of instances. Oxygen diffuses from air into cells in the lungs Oxygen diffuses from the cells of the lungs into the blood capillari ...
... Simple Diffusion Lipid soluble molecules and small simple molecules diffuse across cell membranes. Living organisms rely on diffusion to function in a large number of instances. Oxygen diffuses from air into cells in the lungs Oxygen diffuses from the cells of the lungs into the blood capillari ...
Chapter 1-7 Specification notes File
... Diffusion: Movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It is passive – it does not need energy from respiration as it depends on the movement energy of the particles themselves (their kinetic energy) Osmosis: net movement of water molecules from an ...
... Diffusion: Movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It is passive – it does not need energy from respiration as it depends on the movement energy of the particles themselves (their kinetic energy) Osmosis: net movement of water molecules from an ...
Embryo
... Stages having 2 and then 3 layers of cells develop A hollow ball, made of a single layer of cells, develop The 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 cell stages develop The fertilized egg divides into 2 cells ...
... Stages having 2 and then 3 layers of cells develop A hollow ball, made of a single layer of cells, develop The 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 cell stages develop The fertilized egg divides into 2 cells ...
How do you think materials move in and out of the cell?
... sodium from urine in kidneys) Maintain internal conditions different from the environment Regulate the volume of cells by controlling osmotic potential Control cellular pH Re-establish concentration gradients to run facilitated diffusion. (Ex. Sodium-Potassium pump and Proton pumps) ...
... sodium from urine in kidneys) Maintain internal conditions different from the environment Regulate the volume of cells by controlling osmotic potential Control cellular pH Re-establish concentration gradients to run facilitated diffusion. (Ex. Sodium-Potassium pump and Proton pumps) ...
The DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor camptothecin blocks postmitotic
... conditions. Daughter cells had entered interphase within 2 h as judged by the decondensed state of their chromatin and the presence of distinct nucleoli (Fig. 1; see also [2]). Daughter cells derived from an injected mother cell could be clearly identified by the presence of mouse IgGs in the cytopl ...
... conditions. Daughter cells had entered interphase within 2 h as judged by the decondensed state of their chromatin and the presence of distinct nucleoli (Fig. 1; see also [2]). Daughter cells derived from an injected mother cell could be clearly identified by the presence of mouse IgGs in the cytopl ...
Biology HSA Review Packet
... 25. genetics study was conducted that crossed two red-flowered plants. The next generation was a mixture of red-flowered and white-flowered offspring. Which of these represents those of the parent generation? A) rr and rr B) Rr and Rr C) RR and rr D) RR and RR ...
... 25. genetics study was conducted that crossed two red-flowered plants. The next generation was a mixture of red-flowered and white-flowered offspring. Which of these represents those of the parent generation? A) rr and rr B) Rr and Rr C) RR and rr D) RR and RR ...
Cell Transport Worksheet
... D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the A. B. C. D. ...
... D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the A. B. C. D. ...
A. diffuser
... D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the A. B. C. D. ...
... D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration When the A. B. C. D. ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... o These stabilize the membrane by forming hydrogen bonds between water molecules. o These can act as receptor sites where drugs, hormones and antibodies can bind. o They can acts as receptors for cell signaling o They are also antigens – cell surface molecules involved in the immune ...
... o These stabilize the membrane by forming hydrogen bonds between water molecules. o These can act as receptor sites where drugs, hormones and antibodies can bind. o They can acts as receptors for cell signaling o They are also antigens – cell surface molecules involved in the immune ...
Chapter 10: Classification of Microorganisms
... u Viruses are not considered living organisms by most biologists, because they lack cells and their own anabolic machinery. ...
... u Viruses are not considered living organisms by most biologists, because they lack cells and their own anabolic machinery. ...
Chapter 1: The Microbial World and You
... Bacterial species: Population of cells with similar ...
... Bacterial species: Population of cells with similar ...
Limits to Cell Size
... can’t cells ever become larger than that? Why don’t we regularly find one-celled organisms the size of small multicellular animals, like frogs or even flies? In other words, why can’t there ever be an organism which is visible to the naked eye and that is one giant cell? In order for cells to surviv ...
... can’t cells ever become larger than that? Why don’t we regularly find one-celled organisms the size of small multicellular animals, like frogs or even flies? In other words, why can’t there ever be an organism which is visible to the naked eye and that is one giant cell? In order for cells to surviv ...
Human Reproduction
... develop properly at the normal body temperature of 37°C. They must be kept about two degrees cooler in order to develop properly. Once sperm are produced in the testes, they travel through one of two muscular tubes inside the body called the vas deferens (VASS-deaf-uh-RENS). As sperm travel through ...
... develop properly at the normal body temperature of 37°C. They must be kept about two degrees cooler in order to develop properly. Once sperm are produced in the testes, they travel through one of two muscular tubes inside the body called the vas deferens (VASS-deaf-uh-RENS). As sperm travel through ...
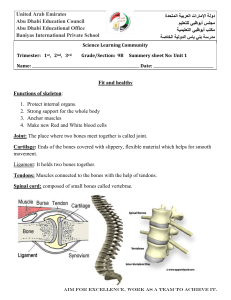
Abu Dhabi Education Council - baniyas international private school
... Strong support for the whole body Anchor muscles Make new Red and White blood cells ...
... Strong support for the whole body Anchor muscles Make new Red and White blood cells ...
Chapter 1: The Microbial World and You
... Bacterial species: Population of cells with similar ...
... Bacterial species: Population of cells with similar ...
Macromolecule?
... summarize his years of work? He stated that new cells could be produced only from the division of existing cells. ...
... summarize his years of work? He stated that new cells could be produced only from the division of existing cells. ...
Lab 6
... allow water to pass freely through the membrane but exclude most other molecules from doing so. Plant cell membranes are elastic and inflate or deflate depending on the amount of water in them. The structure of a plant cell is defined by a plant cell’s wall. Plant cell walls provide a rigid enclosur ...
... allow water to pass freely through the membrane but exclude most other molecules from doing so. Plant cell membranes are elastic and inflate or deflate depending on the amount of water in them. The structure of a plant cell is defined by a plant cell’s wall. Plant cell walls provide a rigid enclosur ...
Chapter 3
... Damage to Cell Walls • Protoplast: a gram-positive or plant cell treated (e.g. lysozyme) to remove the cell wall. • Spheroplast: a gram-negative bacterium treated (e.g. lysozyme) to damage the cell wall. • L forms are wall-less cells that swell into irregular shapes. e.g. some members of Proteus • ...
... Damage to Cell Walls • Protoplast: a gram-positive or plant cell treated (e.g. lysozyme) to remove the cell wall. • Spheroplast: a gram-negative bacterium treated (e.g. lysozyme) to damage the cell wall. • L forms are wall-less cells that swell into irregular shapes. e.g. some members of Proteus • ...
Where is the HIGH oxygen concentration?
... 2) Across which part of the cell does diffusion mostly occur? 3) Which molecule of energy is not required during passive transport? 4) True or False: More solutes creates less concentrated water. 5) Which chemical is involved in osmosis? 6) Examine the picture. If the dots are solutes, where is the ...
... 2) Across which part of the cell does diffusion mostly occur? 3) Which molecule of energy is not required during passive transport? 4) True or False: More solutes creates less concentrated water. 5) Which chemical is involved in osmosis? 6) Examine the picture. If the dots are solutes, where is the ...
RELEASED North Carolina READY End-of-Course Assessment
... A freshwater plant is placed in a container of saltwater. What will most likely happen to the cells of the plant? They will swell because water will move into them. ...
... A freshwater plant is placed in a container of saltwater. What will most likely happen to the cells of the plant? They will swell because water will move into them. ...
Lesson Smoking Fact File
... Carbon monoxide – this reduces the oxygen in the body. If carbon monoxide passes from the lungs into the blood it is dangerous. Haemoglobin in the blood helps carry oxygen because oxygen links to ...
... Carbon monoxide – this reduces the oxygen in the body. If carbon monoxide passes from the lungs into the blood it is dangerous. Haemoglobin in the blood helps carry oxygen because oxygen links to ...