174 kb
... Living things are similar to each other yet different from nonliving things. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of living things (cell theory). For all living things, life activities are accomplished at the cellular level. Human beings are an interactive organization of cells, tiss ...
... Living things are similar to each other yet different from nonliving things. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of living things (cell theory). For all living things, life activities are accomplished at the cellular level. Human beings are an interactive organization of cells, tiss ...
Transport in Vascular Plants
... – suberin prevents H20 etc. from passing through ____________ of adjacent cells – forces H20 and dissolved minerals to follow ____________________ – ________________ allows plant to select what substances pass into stele and ...
... – suberin prevents H20 etc. from passing through ____________ of adjacent cells – forces H20 and dissolved minerals to follow ____________________ – ________________ allows plant to select what substances pass into stele and ...
Lymphatic System / Immunity
... A. Two Semi-Independent Parts B. Lymphatic Vessels: transport fluids escaped from the vascular system back to the blood C. Lymphoid Tissues and Organs: house phagocytic cells, lymphocytes (roles in body defense, disease resistance) II. Lymphatic Vessels A. Special system of drainage vessels which we ...
... A. Two Semi-Independent Parts B. Lymphatic Vessels: transport fluids escaped from the vascular system back to the blood C. Lymphoid Tissues and Organs: house phagocytic cells, lymphocytes (roles in body defense, disease resistance) II. Lymphatic Vessels A. Special system of drainage vessels which we ...
C) Cells and Transport Practice Qs
... c. Excess Na+ ions will leave the cell via osmosis. d. More Na+ ions will be transported in through membrane protein channels. ____ 22. What type of transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. active transport c. osmosis ...
... c. Excess Na+ ions will leave the cell via osmosis. d. More Na+ ions will be transported in through membrane protein channels. ____ 22. What type of transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. active transport c. osmosis ...
5th Grade Chapter 3 Notes Continued
... - rid the body of wastes that are in Urinary system the blood. • ______________ are a pair of organs that remove wastes kidneys from your blood. They are on either side of your ____________, just under your lowest ribs. backbone • When wastes are filtered out of the blood, many other materials also ...
... - rid the body of wastes that are in Urinary system the blood. • ______________ are a pair of organs that remove wastes kidneys from your blood. They are on either side of your ____________, just under your lowest ribs. backbone • When wastes are filtered out of the blood, many other materials also ...
renal disease - CAITLIN MCFARLAND
... functioning of the kidney • Leading causes are diabetes, high blood pressure, inherited disease, and infection. • Symptoms of disease include; nausea, vomiting, decreased or increased urination, swelling of ankles, puffiness around the eyes, fetid breathe, fatigue, shortness of breathe, loss of appe ...
... functioning of the kidney • Leading causes are diabetes, high blood pressure, inherited disease, and infection. • Symptoms of disease include; nausea, vomiting, decreased or increased urination, swelling of ankles, puffiness around the eyes, fetid breathe, fatigue, shortness of breathe, loss of appe ...
The Effect of Bisphenol A of the Growth of Brest Cancer Cell
... After using calculations to figure out theoretical number of cells in the cell solution, make a solution of 20ml of medium and cell solution so that each well in a 96 well plate will have 5000 cells (50,000 cells/plate). Vortex 20ml solution for thirty seconds and then pipette the solution into well ...
... After using calculations to figure out theoretical number of cells in the cell solution, make a solution of 20ml of medium and cell solution so that each well in a 96 well plate will have 5000 cells (50,000 cells/plate). Vortex 20ml solution for thirty seconds and then pipette the solution into well ...
The digestive system
... striated muscles. In other parts of the tube contains smooth muscle fibers forming two layers: an inner circular and outer longitudinal ...
... striated muscles. In other parts of the tube contains smooth muscle fibers forming two layers: an inner circular and outer longitudinal ...
File
... Alveoli: airway end in clusters of tiny sacs called alveoli that form the respiratory membrane. Each cluster is surrounded by a network of capillaries. Each alveolus is tiny measuring (0.1 to 0.2 micrometers in diameter). There are approximately 150million in each lung •If the entire surface area of ...
... Alveoli: airway end in clusters of tiny sacs called alveoli that form the respiratory membrane. Each cluster is surrounded by a network of capillaries. Each alveolus is tiny measuring (0.1 to 0.2 micrometers in diameter). There are approximately 150million in each lung •If the entire surface area of ...
WilliamsPJAS2008
... After using calculations to figure out theoretical number of cells in the cell solution, make a solution of 20ml of medium and cell solution so that each well in a 96 well plate will have 5000 cells (50,000 cells/plate). Vortex 20ml solution for thirty seconds and then pipette the solution into well ...
... After using calculations to figure out theoretical number of cells in the cell solution, make a solution of 20ml of medium and cell solution so that each well in a 96 well plate will have 5000 cells (50,000 cells/plate). Vortex 20ml solution for thirty seconds and then pipette the solution into well ...
4. White blood cells are necessary for pregnancy.
... Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is colorless, odorless, tasteless and toxic. It is not only produced by fuel burning devices, but is also produced as a by-product of cellular processes. If carbon monoxide is produced naturally during normal cell functions, why aren't organisms poisoned by it? Because CO is ...
... Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is colorless, odorless, tasteless and toxic. It is not only produced by fuel burning devices, but is also produced as a by-product of cellular processes. If carbon monoxide is produced naturally during normal cell functions, why aren't organisms poisoned by it? Because CO is ...
Chapter 1: Cell Structure
... molecules provides support for the cell and the plant as a whole. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the plant cell in which chemical reactions take place ...
... molecules provides support for the cell and the plant as a whole. To the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane that controls entry and exit of substances and is composed of proteins and phospholipids. The cytoplasm is the “factory” part of the plant cell in which chemical reactions take place ...
Protists
... once light is detected it moves towards it for photosynthesis. The long whip-like structure is a flagellum that quickly moves back and forth the propel the Euglena through water. Amoeba: An amoeba is a unicellular protist. They are animal-like because they are capable of movement and feed on o ...
... once light is detected it moves towards it for photosynthesis. The long whip-like structure is a flagellum that quickly moves back and forth the propel the Euglena through water. Amoeba: An amoeba is a unicellular protist. They are animal-like because they are capable of movement and feed on o ...
INTRODUCTION OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... Last 7 generations of airways 17-19 generation respiratory bronchioles 20-22 generation alveolar ducts 23 alveolar sac This region is only approximately 5 mm long Alveoli start budding off from 17 gen (~ 300 million) All airways of a single terminal bronchiole (resp. bronchioles, alveolar ducts ‘n’ ...
... Last 7 generations of airways 17-19 generation respiratory bronchioles 20-22 generation alveolar ducts 23 alveolar sac This region is only approximately 5 mm long Alveoli start budding off from 17 gen (~ 300 million) All airways of a single terminal bronchiole (resp. bronchioles, alveolar ducts ‘n’ ...
Skeletal Muscle Function
... Muscle cells have numerous mitochondria, more than other types of cells. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a variation of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. It is able to store many ions in solution that the cell will need at a later time. When a cell needs to do something immediately, it doesn’t ma ...
... Muscle cells have numerous mitochondria, more than other types of cells. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a variation of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. It is able to store many ions in solution that the cell will need at a later time. When a cell needs to do something immediately, it doesn’t ma ...
questions-2 - WordPress.com
... nutrition 8) What do fungi and arthropods have in common? A) Both groups are commonly coenocytic. B) The haploid state is dominant in both groups. C) Both groups are predominantly heterotrophs that ingest their food. D) The protective coats of both groups are made of chitin. E) Both groups have cell ...
... nutrition 8) What do fungi and arthropods have in common? A) Both groups are commonly coenocytic. B) The haploid state is dominant in both groups. C) Both groups are predominantly heterotrophs that ingest their food. D) The protective coats of both groups are made of chitin. E) Both groups have cell ...
Powerpoint
... • Neurons send messages to other neurons – this is what keeps every part of our body in communication with every other part. • Neurons “fire” – send an impulse (message) down their length ...
... • Neurons send messages to other neurons – this is what keeps every part of our body in communication with every other part. • Neurons “fire” – send an impulse (message) down their length ...
6 Kingdoms Notes
... Key concepts include: • how their structures and functions vary between and within the kingdoms; • comparison of their metabolic activities; • analyses of their responses to the environment; • maintenance of homeostasis; • human health issues, human anatomy, body systems, and life functions; and • ...
... Key concepts include: • how their structures and functions vary between and within the kingdoms; • comparison of their metabolic activities; • analyses of their responses to the environment; • maintenance of homeostasis; • human health issues, human anatomy, body systems, and life functions; and • ...
2013-2014 LIFE SCIENCE (Weekly Pacing Guide) Week Dates SOL
... population. Key concepts include a) competition, cooperation, social hierarchy, territorial imperative; and b) influence of behavior on a population. LS 8 The student will investigate and understand interactions among populations in a biological community. Key concepts include a) the relationships a ...
... population. Key concepts include a) competition, cooperation, social hierarchy, territorial imperative; and b) influence of behavior on a population. LS 8 The student will investigate and understand interactions among populations in a biological community. Key concepts include a) the relationships a ...
Development
... By 24 hours, pockets of blood cells and developing blood vessels, called blood islands, begin to appear on the surface of the yolk along the outer edges of the area opaca. These are called the vitelline vessels. At the same time, the heart and vessels within the chick embryo have begun to develop. ...
... By 24 hours, pockets of blood cells and developing blood vessels, called blood islands, begin to appear on the surface of the yolk along the outer edges of the area opaca. These are called the vitelline vessels. At the same time, the heart and vessels within the chick embryo have begun to develop. ...
Hematopathology
... differentiated normal cells. This is partly because it is difficult to obtain meaningful results from such experiments. The small amount of cytoplasm in differentiated cells renders their nuclei susceptible to damage through exposure to the saline medium, and this makes it difficult to assess the si ...
... differentiated normal cells. This is partly because it is difficult to obtain meaningful results from such experiments. The small amount of cytoplasm in differentiated cells renders their nuclei susceptible to damage through exposure to the saline medium, and this makes it difficult to assess the si ...
The Body`s Acid / Alkaline Balance
... part of strong acids (sulfuric, phosphoric and nitric acids). Alkaline bicarbonates of sodium, potassium, calcium or magnesium are used to buffer these acids (The kidneys try to increase the pH by the exchange of hydrogen ions for sodium ions. When acid and alkaline molecules combine they form neutr ...
... part of strong acids (sulfuric, phosphoric and nitric acids). Alkaline bicarbonates of sodium, potassium, calcium or magnesium are used to buffer these acids (The kidneys try to increase the pH by the exchange of hydrogen ions for sodium ions. When acid and alkaline molecules combine they form neutr ...
Slide ()
... The axons of lateral motor column neurons are guided into the limb by ephrin class tyrosine kinase receptors. Motor neurons in the medial and lateral divisions of the lateral motor column (LMC) project axons into the ventral and dorsal halves of the limb mesenchyme, respectively. The profile of expr ...
... The axons of lateral motor column neurons are guided into the limb by ephrin class tyrosine kinase receptors. Motor neurons in the medial and lateral divisions of the lateral motor column (LMC) project axons into the ventral and dorsal halves of the limb mesenchyme, respectively. The profile of expr ...
Team Publications
... carried out on a cohort of 130 breast cancer samples. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) was found to be significantly overexpressed in TNBC compared with the other breast cancer subtypes. High PLK1 expression was confirmed by reverse phase protein and tissue microarrays. In triple-negative cell lines, RNAi-me ...
... carried out on a cohort of 130 breast cancer samples. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) was found to be significantly overexpressed in TNBC compared with the other breast cancer subtypes. High PLK1 expression was confirmed by reverse phase protein and tissue microarrays. In triple-negative cell lines, RNAi-me ...
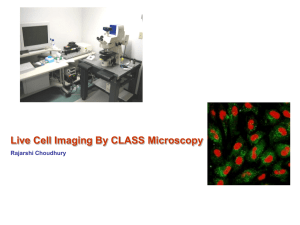
Slide 1
... Like a conventional optical microscope, the resolution of a confocal microscope is limited by diffraction of light. The image of an ideal point viewed through a circular aperture is blurred, and the diffracted image is known as an Airy disc. The size of the Airy disc depends on the wavelength of the ...
... Like a conventional optical microscope, the resolution of a confocal microscope is limited by diffraction of light. The image of an ideal point viewed through a circular aperture is blurred, and the diffracted image is known as an Airy disc. The size of the Airy disc depends on the wavelength of the ...