Syllabus, BIOSC 2105: Cell Signaling Spring Term, 2014 Instructor
... 10. Explain how cells sense changes in nutrient availability to activate growth or autophagy. Hint: Discuss bidirectional transport of amino acids across cell membrane and how it depends on nutrient availability (i.e. presence and absence of nutrients). Also, explain if this mechanism changes in ...
... 10. Explain how cells sense changes in nutrient availability to activate growth or autophagy. Hint: Discuss bidirectional transport of amino acids across cell membrane and how it depends on nutrient availability (i.e. presence and absence of nutrients). Also, explain if this mechanism changes in ...
Tissue Fluid and Lymph
... • This tissue fluid is very similar to plasma but does not have large plasma protein molecules in it • This fluid bathes every cell in the body supplying them with glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen ...
... • This tissue fluid is very similar to plasma but does not have large plasma protein molecules in it • This fluid bathes every cell in the body supplying them with glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen ...
Protein Secretion in Plants: from the trans
... clathrin coats to membranes but also play a role in the control of membrane lipid composition, actin remodeling and related events (18). Structurally related ARF-like proteins (ARLs) are members of the same subgroup of the ras superfamily, but have different functions. For example, Arabidopsis ARL2 ...
... clathrin coats to membranes but also play a role in the control of membrane lipid composition, actin remodeling and related events (18). Structurally related ARF-like proteins (ARLs) are members of the same subgroup of the ras superfamily, but have different functions. For example, Arabidopsis ARL2 ...
Text Structure and Functions of the Cell Membrane The cell
... permeable i.e. they permit the passage of certain ions and molecules while excluding others. Membranes are relatively permeable to water, some simple sugars, amino acids and lipidsoluble materials but are relatively impermeable to very large ...
... permeable i.e. they permit the passage of certain ions and molecules while excluding others. Membranes are relatively permeable to water, some simple sugars, amino acids and lipidsoluble materials but are relatively impermeable to very large ...
renal replacement therapy in acute kidney failure
... dialysate through the dialysate compartment in an opposite direction at a rate of300 -900 ml/min. in this process the excess of fluid and water moves out of the blood stream . This process called ultrafiltration.second process is called diffusion, here the waste products in the blood moves through t ...
... dialysate through the dialysate compartment in an opposite direction at a rate of300 -900 ml/min. in this process the excess of fluid and water moves out of the blood stream . This process called ultrafiltration.second process is called diffusion, here the waste products in the blood moves through t ...
Blood Gas Homeostasis Ventilation Diffusion Transport Regulation
... the Z membrane has low solubility for X molecule and high solubility for Y molecule if all other factors are the same for two solutes, one with higher solubility coefficient will achieve equilibrium sooner Solubility coefficient due to molecular nature and molecular weight CO2 has a highe ...
... the Z membrane has low solubility for X molecule and high solubility for Y molecule if all other factors are the same for two solutes, one with higher solubility coefficient will achieve equilibrium sooner Solubility coefficient due to molecular nature and molecular weight CO2 has a highe ...
Unit 23.2: The Respiratory System
... the lungs. The lungs are the organs in which gas exchange takes place between blood and air. • Air enters the respiratory system through the nose. As the air passes through the nasal cavity, mucus and hairs trap any particles in the air. The air is also warmed and moistened so it won’t harm delicate ...
... the lungs. The lungs are the organs in which gas exchange takes place between blood and air. • Air enters the respiratory system through the nose. As the air passes through the nasal cavity, mucus and hairs trap any particles in the air. The air is also warmed and moistened so it won’t harm delicate ...
Multiscale Systems Analysis of Root Growth and
... within pathways that often function in a nonlinear fashion, integrating negative and positive feedback loops (Middleton et al., 2012). Computational and mathematical modeling approaches are set to become much more important as our knowledge of pathways becomes increasingly detailed and their network ...
... within pathways that often function in a nonlinear fashion, integrating negative and positive feedback loops (Middleton et al., 2012). Computational and mathematical modeling approaches are set to become much more important as our knowledge of pathways becomes increasingly detailed and their network ...
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... – Below is abdominal hemocoel, blood flows posteriorly there. ...
... – Below is abdominal hemocoel, blood flows posteriorly there. ...
Chapter One Part Two - Appoquinimink High School
... body; some of these are sensitive to levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide, some to chemicals, and some to blood pressure itself. ...
... body; some of these are sensitive to levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide, some to chemicals, and some to blood pressure itself. ...
The Insect Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... – Below is abdominal hemocoel, blood flows posteriorly there. ...
... – Below is abdominal hemocoel, blood flows posteriorly there. ...
Turgor / Torpor - Uludağ Üniversitesi
... giving a sense of “thorough, complete, or intense” to the pouring action. As with diffuse and infuse, perfuse has a particular medical usage. It is used to describe the action of artificially supplying an organ, a tissue, or the body with a fluid by circulating that fluid through blood vessels or ot ...
... giving a sense of “thorough, complete, or intense” to the pouring action. As with diffuse and infuse, perfuse has a particular medical usage. It is used to describe the action of artificially supplying an organ, a tissue, or the body with a fluid by circulating that fluid through blood vessels or ot ...
Thermal inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes
... been considered to 'be only a minor fraction of total enthalpy (Lepock et al., 1988). Peak area is a function of protein concentration and the specific calorimetric enthalpy of the protein (Privalov & Knechninashvili, 1974). Hence, large peaks in thermograms of whole cells will either be due to prot ...
... been considered to 'be only a minor fraction of total enthalpy (Lepock et al., 1988). Peak area is a function of protein concentration and the specific calorimetric enthalpy of the protein (Privalov & Knechninashvili, 1974). Hence, large peaks in thermograms of whole cells will either be due to prot ...
Module syllabus: Advanced light microscope techniques
... The main objective of this module is to teach the basic knowledge of the advanced light microscopy techniques that are used in studies of plant cells. The basic concepts of light microscopy, construction and principles of microscopy operation and the proper techniques of light microscopy to analyse ...
... The main objective of this module is to teach the basic knowledge of the advanced light microscopy techniques that are used in studies of plant cells. The basic concepts of light microscopy, construction and principles of microscopy operation and the proper techniques of light microscopy to analyse ...
The FRA1 kinesin contributes to cortical microtubule
... polysaccharides are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus and secreted. The trafficking of vesicles containing cell wall components is thought to depend on actin-myosin. Here, we implicate microtubules in this process through studies of the kinesin-4 family member, FRA1. In a fra1-5 knockout mutant, th ...
... polysaccharides are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus and secreted. The trafficking of vesicles containing cell wall components is thought to depend on actin-myosin. Here, we implicate microtubules in this process through studies of the kinesin-4 family member, FRA1. In a fra1-5 knockout mutant, th ...
Migration Cues Induce Chromatin Alterations
... Directed cell migration is a fundamental property of both simple and complex organisms, which is necessary for the proper execution of various biological processes including foraging, embryonic development, immunity, tissue repair and homeostasis. Improper cell migration is an underlying cause of nu ...
... Directed cell migration is a fundamental property of both simple and complex organisms, which is necessary for the proper execution of various biological processes including foraging, embryonic development, immunity, tissue repair and homeostasis. Improper cell migration is an underlying cause of nu ...
Connective Tissue
... • Fibroblasts within the granulation tissue produce growth factors, collagen fibers & contractile proteins to pull edges of wound together • Epithelium begins to regenerate • Debris is phagocytized by macrophages and undelying fibrous patch becomes scar tissue resistant to infection ...
... • Fibroblasts within the granulation tissue produce growth factors, collagen fibers & contractile proteins to pull edges of wound together • Epithelium begins to regenerate • Debris is phagocytized by macrophages and undelying fibrous patch becomes scar tissue resistant to infection ...
High sensitivity of embryonic stem cells to
... analysis. As previously reported, the ubiquitin proteasome system is involved in the regulation of self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation of ES cells (14). Oct4 is one of the major regulation factors in ES cells. It is known that Oct4 is transcriptionally regulated in ES cells. In addition ...
... analysis. As previously reported, the ubiquitin proteasome system is involved in the regulation of self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation of ES cells (14). Oct4 is one of the major regulation factors in ES cells. It is known that Oct4 is transcriptionally regulated in ES cells. In addition ...
Bio 2175 Developmental Biology Lecture 17: Organogenesis The
... a. Discussion Thursday with written prep due b. Suggested statistical tests for your zebrafish data i. Fisher’s exact test (categorical data) 1. R.A. Fisher’s wager with Muriel Bristol-Roach, Ph.D: the lady tasting tea 2. e.g. Is observing 8 normal and 0 cyclopic fish sig. diff. from 4 of each? 3. G ...
... a. Discussion Thursday with written prep due b. Suggested statistical tests for your zebrafish data i. Fisher’s exact test (categorical data) 1. R.A. Fisher’s wager with Muriel Bristol-Roach, Ph.D: the lady tasting tea 2. e.g. Is observing 8 normal and 0 cyclopic fish sig. diff. from 4 of each? 3. G ...
Myeloma Terms and Definitions
... the bloodstream. (See Hypercalcemia.) Cancer: A term for diseases in which malignant cells divide without control. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body. Carcinogen: Any substance or agent that produces or stimulates ...
... the bloodstream. (See Hypercalcemia.) Cancer: A term for diseases in which malignant cells divide without control. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body. Carcinogen: Any substance or agent that produces or stimulates ...
Magnetoglobus, Magnetic Aggregates in Anaerobic Environments
... fusion. All cells face the outer environment, too, from which they take up nutrients. Magnetoglobus sp. cells are polarized. The cells that form such aggregates are very close to one another, and the four membranes of two adjacent cells are parallel. The regions of contact between two adjacent cells ...
... fusion. All cells face the outer environment, too, from which they take up nutrients. Magnetoglobus sp. cells are polarized. The cells that form such aggregates are very close to one another, and the four membranes of two adjacent cells are parallel. The regions of contact between two adjacent cells ...
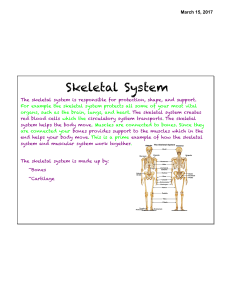
Skeletal System
... system helps the body move. Muscles are connected to bones. Since they are connected your bones provides support to the muscles which in the end helps your body move. This is a prime example of how the skeletal system and muscular system work together. ...
... system helps the body move. Muscles are connected to bones. Since they are connected your bones provides support to the muscles which in the end helps your body move. This is a prime example of how the skeletal system and muscular system work together. ...