Intro to Zoology
... As the layers of tissue form organs and organ systems, some organisms develop a fluid filled space that forms between the digestive tract and the outer wall of the body during development. ...
... As the layers of tissue form organs and organ systems, some organisms develop a fluid filled space that forms between the digestive tract and the outer wall of the body during development. ...
Part I: Levels of Biological Organization
... functions form a structure known as tissue. Tissues are used to construct larger structures within the body known as organs. For example, your brain is an organ that receives, analyzes ...
... functions form a structure known as tissue. Tissues are used to construct larger structures within the body known as organs. For example, your brain is an organ that receives, analyzes ...
2 ONION SKIN (200x) 3 GREEN LEAF (300x) 4 CHEEK CELLS (900x)
... because it is very thin and lies flat against the wall. A-Tiucleus is more clearly seen in the cell at B. C points to a bundle of tubular cells which form a vein. Leaves have many veins. If you look carefully, you can locate others. D shows one of the spaces in which air circulates throughout the le ...
... because it is very thin and lies flat against the wall. A-Tiucleus is more clearly seen in the cell at B. C points to a bundle of tubular cells which form a vein. Leaves have many veins. If you look carefully, you can locate others. D shows one of the spaces in which air circulates throughout the le ...
Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)
... Animal organs are usually composed of more than one cell type. Each organ performs a given function. The stomach is an organ composed of tissues that aid in the digestion of food as part of the digestive system. Most organs have functions in only one organ-system. ...
... Animal organs are usually composed of more than one cell type. Each organ performs a given function. The stomach is an organ composed of tissues that aid in the digestion of food as part of the digestive system. Most organs have functions in only one organ-system. ...
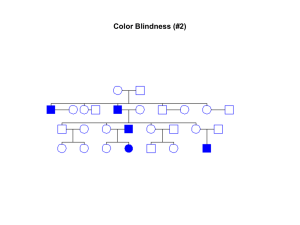
Extra Pedigree Problem - Winona State University
... group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Normal red blood cells are round like doughnuts, and they move through small blood tubes in the body to deliver oxygen. Sickle red blood cells become hard, sticky and shaped like sickles used to cut wheat. When these hard and pointed red cells go through ...
... group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Normal red blood cells are round like doughnuts, and they move through small blood tubes in the body to deliver oxygen. Sickle red blood cells become hard, sticky and shaped like sickles used to cut wheat. When these hard and pointed red cells go through ...
3.2 Powerpoint
... Plate Models • You are now going to make a study tool using paper plates. • Follow along while I show you how to fold the plate, use the directions as a guide. • Pass out plates ...
... Plate Models • You are now going to make a study tool using paper plates. • Follow along while I show you how to fold the plate, use the directions as a guide. • Pass out plates ...
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... Exocytosis and Endocytosis vesicles move substances in and out of cells vesicles can fuse with the cell membrane (where ...
... Exocytosis and Endocytosis vesicles move substances in and out of cells vesicles can fuse with the cell membrane (where ...
Name: Period: _____ Teacher: Science Homework Due: Friday
... analyzes, and sends information, and it is constructed of brain tissue. Brain tissue is a collection of cells, which because of their specialized structure are able to store and transmit information; a muscle cell could not perform the same function as a brain cell because their structures are diffe ...
... analyzes, and sends information, and it is constructed of brain tissue. Brain tissue is a collection of cells, which because of their specialized structure are able to store and transmit information; a muscle cell could not perform the same function as a brain cell because their structures are diffe ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • Tiny structures that carry out specific functions within the cell • Compare to organs in your body… ...
... • Tiny structures that carry out specific functions within the cell • Compare to organs in your body… ...
The History of the Cell Theory
... • He saw small organisms in the water and named them animalcules which means “little animals.” • Leewenhoek was also the first person to discover bacteria by looking at his own teeth scrapings! • Ewwwwwwww! ...
... • He saw small organisms in the water and named them animalcules which means “little animals.” • Leewenhoek was also the first person to discover bacteria by looking at his own teeth scrapings! • Ewwwwwwww! ...
The History of the Cell Theory
... • He saw small organisms in the water and named them animalcules which means “little animals.” • Leewenhoek was also the first person to discover bacteria by looking at his own teeth scrapings! • Ewwwwwwww! ...
... • He saw small organisms in the water and named them animalcules which means “little animals.” • Leewenhoek was also the first person to discover bacteria by looking at his own teeth scrapings! • Ewwwwwwww! ...
Basic Cell Structure
... • Plant cells have a cell wall that is a tough rigid outer covering that protects the plant cell and helps it maintain its shape. It is composed mostly of cellulose. Fungi, algae, and bacteria also have cell walls. • **Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
... • Plant cells have a cell wall that is a tough rigid outer covering that protects the plant cell and helps it maintain its shape. It is composed mostly of cellulose. Fungi, algae, and bacteria also have cell walls. • **Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Select the PLANT CELL tab, and click Sample. Set the Zoom to 2000x. Question: What functions do the organelles in a plant cell perform? 1. Label: Locate each organelle in the plant cell. Label the organelles in the diagram below. ...
... Select the PLANT CELL tab, and click Sample. Set the Zoom to 2000x. Question: What functions do the organelles in a plant cell perform? 1. Label: Locate each organelle in the plant cell. Label the organelles in the diagram below. ...
The Cell - SNC2PSylvia2011
... We and other organisms are made of organs and tissues that are made of cells. Each cell, is made up of smaller parts – called organelles. An organelle is a structure within a cell that carries out specific functions to support the life of the cell. ...
... We and other organisms are made of organs and tissues that are made of cells. Each cell, is made up of smaller parts – called organelles. An organelle is a structure within a cell that carries out specific functions to support the life of the cell. ...
Kingdoms Of Life: Monerans
... They make up more matter than all other living things on earth combined ...
... They make up more matter than all other living things on earth combined ...
Cells - Baldwin Schools Teachers
... cells. There are smaller pieces to cells that include proteins and organelles. There are also larger pieces called tissues and systems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. ...
... cells. There are smaller pieces to cells that include proteins and organelles. There are also larger pieces called tissues and systems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. ...
Mathematical Modeling biological events and cell
... Membrane discs are activated by signals Actin spheres close to activated discs are activated / created Activated spheres grow (polymerize) then divide Global rate of sphere shrinkage (depolymerization) to restore monomer pool ...
... Membrane discs are activated by signals Actin spheres close to activated discs are activated / created Activated spheres grow (polymerize) then divide Global rate of sphere shrinkage (depolymerization) to restore monomer pool ...
Juxtaglomerular cells
... This is different in that blood travels from arteriole to capillary bed back to arteriole. The capsule consists of two layers of epithelium. The visceral layer fits like a glove over the glomerulus. This can not be seen with light microscope. Outer layer the parietal layer can be seen with light mic ...
... This is different in that blood travels from arteriole to capillary bed back to arteriole. The capsule consists of two layers of epithelium. The visceral layer fits like a glove over the glomerulus. This can not be seen with light microscope. Outer layer the parietal layer can be seen with light mic ...
Communication & cell signalling
... Why is it released? In response to high glucose levels What do you think happens when the hormone binds to the receptor? Internal cell response triggered More glucose channels become present in the membrane Cell takes up more glucose Reduces blood glucose levels ...
... Why is it released? In response to high glucose levels What do you think happens when the hormone binds to the receptor? Internal cell response triggered More glucose channels become present in the membrane Cell takes up more glucose Reduces blood glucose levels ...
blood.
... 3. What does specialization of cells mean? They make systems more efficient or better. 4. Why do cells need to be specialized? To do different types of jobs. 5. Cells work together to form ___Tissues (examples: muscle tissue, connective tissue, nervous tissue, blood.) ...
... 3. What does specialization of cells mean? They make systems more efficient or better. 4. Why do cells need to be specialized? To do different types of jobs. 5. Cells work together to form ___Tissues (examples: muscle tissue, connective tissue, nervous tissue, blood.) ...
Cell Organelles
... Surrounded by a double membrane Nucleolus – located within the nucleus, makes ribosomes ...
... Surrounded by a double membrane Nucleolus – located within the nucleus, makes ribosomes ...