
Cancer and the cell cycle
... people can be genetically more likely to develop cancer. Most cells spend a much greater amount of time in interphase and not duplicating. ...
... people can be genetically more likely to develop cancer. Most cells spend a much greater amount of time in interphase and not duplicating. ...
Name: Date: Period: Discovering the Cell Video Worksheet
... 5. Schlieden, Schwann, and Virchow created the cell theory. 6. What was the breakthrough in 1930? 7. Electron microscopes allow you to see tremendous detail, but only in cells that have been killed. 8. The confocal laser scanning microscope provides us with 3D images that enable us to see the shape ...
... 5. Schlieden, Schwann, and Virchow created the cell theory. 6. What was the breakthrough in 1930? 7. Electron microscopes allow you to see tremendous detail, but only in cells that have been killed. 8. The confocal laser scanning microscope provides us with 3D images that enable us to see the shape ...
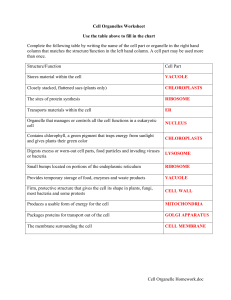
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
Cell Organelles
... physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. ...
... physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found in bacteria as small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. ...
Unit A: Chapter 1: Comparing Living Things Lesson 1: Is It Living or
... Sponges, jellyfish, hydras, and worms are all invertebrates – many-celled animals that lack backbones. Like the sponges, hydras, jellyfish and other relatives have hollow bodies in which they trap and consume in and out of their bodies. Hydras have snakelike tentacles around their mouths that they u ...
... Sponges, jellyfish, hydras, and worms are all invertebrates – many-celled animals that lack backbones. Like the sponges, hydras, jellyfish and other relatives have hollow bodies in which they trap and consume in and out of their bodies. Hydras have snakelike tentacles around their mouths that they u ...
7.2 Cell Structure 196-207
... 21. Nearly all of the mitochondria in your cells were inherited from your mother. 22. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA. ...
... 21. Nearly all of the mitochondria in your cells were inherited from your mother. 22. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA. ...
Formation of Urine
... body would continually lose nutrients, water and salts. RESULT?? Death would quickly follow from dehydration and starvation. CONCLUSION: The fluid must be altered throughout its journey in the remaining tubule. ...
... body would continually lose nutrients, water and salts. RESULT?? Death would quickly follow from dehydration and starvation. CONCLUSION: The fluid must be altered throughout its journey in the remaining tubule. ...
unit 1: the organisation of the human body
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
Transparency – Diffusion Through a Selectively Permeable Membrane
... from areas of high concentration (where it was sprayed) to areas of low concentration (the corner furthest from the origin) by a process called diffusion. Diffusion (and a process called osmosis for water) is the method used in the body to get materials into and out of the cell. The membrane works l ...
... from areas of high concentration (where it was sprayed) to areas of low concentration (the corner furthest from the origin) by a process called diffusion. Diffusion (and a process called osmosis for water) is the method used in the body to get materials into and out of the cell. The membrane works l ...
F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy 4.2.1 The Kidney
... acids by facilitated diffusion As concentration rises, they are able to diffuse out of the opposite side of the cell into the tissue fluid- active transport may also support this process from the tissue fluid, they diffuse into the blood and are ...
... acids by facilitated diffusion As concentration rises, they are able to diffuse out of the opposite side of the cell into the tissue fluid- active transport may also support this process from the tissue fluid, they diffuse into the blood and are ...
Nervous System Class Overview Questions
... 1. How is this potential difference across the cell membrane generated? 2. What characteristics of membranes allow cells to concentrate or exclude ions? 3. What is it about neurons (nerve cells) that make their properties different from those of other cells? In other words, what enables nerve cells ...
... 1. How is this potential difference across the cell membrane generated? 2. What characteristics of membranes allow cells to concentrate or exclude ions? 3. What is it about neurons (nerve cells) that make their properties different from those of other cells? In other words, what enables nerve cells ...
7-2.1 Science Notes
... It is essential for students to know that a cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life functions. Each cell has major structures (organelles) within it that perform these life functions. Many organelles are too small to be seen without the aid of a microscope. Cells in organisms ...
... It is essential for students to know that a cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life functions. Each cell has major structures (organelles) within it that perform these life functions. Many organelles are too small to be seen without the aid of a microscope. Cells in organisms ...
NoB1ch02QUICKcheck-ed
... Classify each of the following as tissue, organ or system. nerve cells in the tip of a finger Nerve cells at a fingertip are similar cells carrying out the same function and so they form a tissue. fleshy part of an apple The fleshy part of an apple is made up of similar cells with the same funct ...
... Classify each of the following as tissue, organ or system. nerve cells in the tip of a finger Nerve cells at a fingertip are similar cells carrying out the same function and so they form a tissue. fleshy part of an apple The fleshy part of an apple is made up of similar cells with the same funct ...
Cell Comic Book Guidelines
... animal cells. This should include all organelles found within the different types of cells. - Students are asked to prepare a comic book in comic book format that tells a story of the differences and similarities between cell types as well as the function of cellular components (organelles). - The c ...
... animal cells. This should include all organelles found within the different types of cells. - Students are asked to prepare a comic book in comic book format that tells a story of the differences and similarities between cell types as well as the function of cellular components (organelles). - The c ...
Cytoplasm!
... • Outer clear glassy layer is ectoplasm, inner layer is endoplasm. • Cytoplasm + nucleus = protoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. • In prokaryotic cells it is basically everything enclosed by the cell membrane (no nucleus). ...
... • Outer clear glassy layer is ectoplasm, inner layer is endoplasm. • Cytoplasm + nucleus = protoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. • In prokaryotic cells it is basically everything enclosed by the cell membrane (no nucleus). ...
Lecture 6
... 1. Hollow cylindrical structures - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
... 1. Hollow cylindrical structures - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
Lecture 6
... 1. Hollow cylindrical structures - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
... 1. Hollow cylindrical structures - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
Stem cells Before we discuss human cloning we need to talk about
... Stem cells Before we discuss human cloning we need to talk about stem cells. These are special cells that can turn into any cell in the body. A stem cell can be made to grow into a skin cell, a heart muscle cell, a white blood cell etc. The most common source of human stem cells used in scientific r ...
... Stem cells Before we discuss human cloning we need to talk about stem cells. These are special cells that can turn into any cell in the body. A stem cell can be made to grow into a skin cell, a heart muscle cell, a white blood cell etc. The most common source of human stem cells used in scientific r ...
Unit 1 and 7 Study Cards You enter the classroom and you see a
... that you do not disrupt the natural setting, would you environment. remove plants from the environment or carefully observe only? Why? Students were asked to observe pond organisms in a Petri dish. At the end of class, how would you clean up after this observation? ...
... that you do not disrupt the natural setting, would you environment. remove plants from the environment or carefully observe only? Why? Students were asked to observe pond organisms in a Petri dish. At the end of class, how would you clean up after this observation? ...
Looking Inside Cells
... ______________________________________________________________________ specialized to perform specific functions Cells are organized into tissues, organs, 1. In many-celled organisms, ______________________________________ and organ systems ___________________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________ specialized to perform specific functions Cells are organized into tissues, organs, 1. In many-celled organisms, ______________________________________ and organ systems ___________________________________________________________ ...
PI determination of cellular DNA content **These protocols are
... dish/flask size, etc. A typical 48h culture in a 6-well plate would use approximately 1-2x105 cells per 6-well plate. Appropriate controls will also be experiment-specific. The cells should be seeded and then synchronized (using serum starvation for 12-72 hours depending on the cell type). Serum sta ...
... dish/flask size, etc. A typical 48h culture in a 6-well plate would use approximately 1-2x105 cells per 6-well plate. Appropriate controls will also be experiment-specific. The cells should be seeded and then synchronized (using serum starvation for 12-72 hours depending on the cell type). Serum sta ...















![Urinary System_student handout[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008293858_1-b77b303d5bfb3ec35a6e80f57f440bef-300x300.png)






