Specific learning outcomes for bio 2.8 File
... Media, Ministry of Education, 2007, Level 7. By the end of this topic you should be able to: ...
... Media, Ministry of Education, 2007, Level 7. By the end of this topic you should be able to: ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... The body’s main airways are supported and kept open by rings of CARTILAGE. Their lining secretes MUCUS to trap dirt and this is swept up and away from the lungs by CILIA. ...
... The body’s main airways are supported and kept open by rings of CARTILAGE. Their lining secretes MUCUS to trap dirt and this is swept up and away from the lungs by CILIA. ...
1 - The main principle of cell theory are 2
... Agricultural Biotechnology Program Course : Cell biology ( AB 0802 Selective ) ...
... Agricultural Biotechnology Program Course : Cell biology ( AB 0802 Selective ) ...
Human Body Systems
... Nervous: controls body activities; carries and interprets messages Endocrine: regulates body activities with hormones Digestive: breaks down food into a usable form Circulatory: transports needed materials to cells and carries away wastes Respiratory: exchanges gases with the environment Excretory: ...
... Nervous: controls body activities; carries and interprets messages Endocrine: regulates body activities with hormones Digestive: breaks down food into a usable form Circulatory: transports needed materials to cells and carries away wastes Respiratory: exchanges gases with the environment Excretory: ...
Document
... The advantages of membranous organelles (compartments) include: 1) metabolic processes in the cell that require different specific chemical conditions may occur simultaneous and 2) an increase in the cell's total surface area. ...
... The advantages of membranous organelles (compartments) include: 1) metabolic processes in the cell that require different specific chemical conditions may occur simultaneous and 2) an increase in the cell's total surface area. ...
Cells: the building block of all living things
... b) Some float free; others are attached to (rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum. 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum: a system of fluid-filled tubules that coil and twist through the cytoplasm. a) ½ of total cell’s membranes b) Network is to carry substances, primarily proteins from one part of the cell to another. c ...
... b) Some float free; others are attached to (rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum. 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum: a system of fluid-filled tubules that coil and twist through the cytoplasm. a) ½ of total cell’s membranes b) Network is to carry substances, primarily proteins from one part of the cell to another. c ...
Circulatory System Notes - Manhasset Public Schools
... your heart pumps 5 liters of blood per minute _________________: lungs (5 27 4) _________________: body (6 8 1 3) _________________: heart _________________: filters foreign substances like bacteria from transport fluid i. lymph vessels: tubes that branch through all the tissues ii. _________ ...
... your heart pumps 5 liters of blood per minute _________________: lungs (5 27 4) _________________: body (6 8 1 3) _________________: heart _________________: filters foreign substances like bacteria from transport fluid i. lymph vessels: tubes that branch through all the tissues ii. _________ ...
cells - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... chemical energy from sunlight. Sunlight + CO2 Carbohydrates • A plastid (not part of endomembrane system). • Have their own DNA, RNA, Proteins, and Ribosomes (70-S). • Grow and reproduce independently. • Plants, Protists. ...
... chemical energy from sunlight. Sunlight + CO2 Carbohydrates • A plastid (not part of endomembrane system). • Have their own DNA, RNA, Proteins, and Ribosomes (70-S). • Grow and reproduce independently. • Plants, Protists. ...
Chapter16/18 Drugs_Alcohol
... • No more 3drinks/occasion • No more than 2/wk • Drink on full stomach • Metabolize 1 drink/hour ...
... • No more 3drinks/occasion • No more than 2/wk • Drink on full stomach • Metabolize 1 drink/hour ...
ORGANELLE MATCHING
... 7. a double membrane that protects the nucleus 8. synthesizes proteins to be released from the cell 9. plants are enclosed in this rigid structure ...
... 7. a double membrane that protects the nucleus 8. synthesizes proteins to be released from the cell 9. plants are enclosed in this rigid structure ...
Cell Biology
... • Pseudopodia (amoeboid movement) found in amoebae and phagocytes (white blood cells). • Cleavage furrow formation. • Maintenance and changes in cell shape. ...
... • Pseudopodia (amoeboid movement) found in amoebae and phagocytes (white blood cells). • Cleavage furrow formation. • Maintenance and changes in cell shape. ...
Cells: form fits function - Science-Hinz
... more than one nucleus. Given the shape of this cell, explain why having more than one nucleus is necessary. ...
... more than one nucleus. Given the shape of this cell, explain why having more than one nucleus is necessary. ...
Step 1: The History of the Cell Theory
... b) This became the basis of the theory of _______________, even though the mechanisms of nuclear division were not understood. 9. The cell was also seen as the basic element of the ____________________. ...
... b) This became the basis of the theory of _______________, even though the mechanisms of nuclear division were not understood. 9. The cell was also seen as the basic element of the ____________________. ...
The Blood Line
... Their demands seemed pretty reasonable to me, but I’ll let you decide how you feel about all this. This ambitious group of broken bits of cells is simply asking that they receive greater recognition from all political parties of Bloodstream City. The head of the union, John Cell, pointed out to me t ...
... Their demands seemed pretty reasonable to me, but I’ll let you decide how you feel about all this. This ambitious group of broken bits of cells is simply asking that they receive greater recognition from all political parties of Bloodstream City. The head of the union, John Cell, pointed out to me t ...
• Individual chromosomes are made up of 2 identical strands of
... into two daughter cells. The cytoplasm and organelles are divided equally between the 2 new daughter cells. ...
... into two daughter cells. The cytoplasm and organelles are divided equally between the 2 new daughter cells. ...
01. Reproduction of Cells
... The hereditary material , also called the genetic blueprint is organized into 46 parts known as chromosomes (DNA molecules are found in chromosomes). Every time a cell reproduces, or divides, each chromosome must be copied and distributed so that each new cell gets a complete and accurate set of inf ...
... The hereditary material , also called the genetic blueprint is organized into 46 parts known as chromosomes (DNA molecules are found in chromosomes). Every time a cell reproduces, or divides, each chromosome must be copied and distributed so that each new cell gets a complete and accurate set of inf ...
End of Chapter 23 Questions
... compressed by surrounding tissues. It also serves as protection from being jarred by the mother’s body movements. 18. Describe the formation of the umbilical cord. As the amnion encloses the embryo and subsequently surrounds it with amniotic fluid, it envelops the tissues on the underside of the emb ...
... compressed by surrounding tissues. It also serves as protection from being jarred by the mother’s body movements. 18. Describe the formation of the umbilical cord. As the amnion encloses the embryo and subsequently surrounds it with amniotic fluid, it envelops the tissues on the underside of the emb ...
Levels of Organization Student Handout
... 3. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) – Delivers food/oxygen to body cells; carries carbon dioxide away from cells. (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries) 4. Muscular – Allows for movement. (muscles, tendons) Examples of muscles: tricep, bicep, quadricep, hamstring 5. Digestive – Food is broken down into s ...
... 3. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) – Delivers food/oxygen to body cells; carries carbon dioxide away from cells. (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries) 4. Muscular – Allows for movement. (muscles, tendons) Examples of muscles: tricep, bicep, quadricep, hamstring 5. Digestive – Food is broken down into s ...
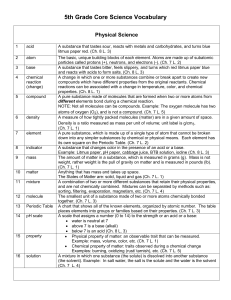
5th Grade - IUSD.org
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
Apple Cells
... In comparison to onion cells and elodea cells, apple cells more time to induce visible plasmolysis. One hypothesis to account for this is that the cell wall of apple peel cells has a higher resistance to water movement perhaps due to impregnation with a waxy or other hydrophobic component. ...
... In comparison to onion cells and elodea cells, apple cells more time to induce visible plasmolysis. One hypothesis to account for this is that the cell wall of apple peel cells has a higher resistance to water movement perhaps due to impregnation with a waxy or other hydrophobic component. ...
4.1 Answer packet for quiz
... The exchange of materials between a cell and its environment takes place across cell cell membrane. Water is the substance used during osmosis. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. Water molecules do not need energy to enter the cell. Large particles (protein) have a hard time entering th ...
... The exchange of materials between a cell and its environment takes place across cell cell membrane. Water is the substance used during osmosis. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. Water molecules do not need energy to enter the cell. Large particles (protein) have a hard time entering th ...
HyStem Hydrogels for Stem Cell Research
... In addition to being fully-defined and consisting of components that mimic a native ECM, a further advantage of HyStem hydrogels over other matrices, is that they are easily customizable. Generally, stem cells depend on specific ECM components to grow and differentiate. To affect specific cell perfo ...
... In addition to being fully-defined and consisting of components that mimic a native ECM, a further advantage of HyStem hydrogels over other matrices, is that they are easily customizable. Generally, stem cells depend on specific ECM components to grow and differentiate. To affect specific cell perfo ...
Cell Structure & Function - Woodcliff Lake Public Schools
... • Both cells have organelles in them. • Each organelle has a special job to do to help the cell function. • We will only be learning about some of the organelles. ...
... • Both cells have organelles in them. • Each organelle has a special job to do to help the cell function. • We will only be learning about some of the organelles. ...
What the Cell? - Effingham County Schools
... These fellahs, despite their simplicity, carryout activities like any other living creature; in fact, they grow, reproduce, respond to their environment and can move. They are older and smaller than Eukaryotes. ...
... These fellahs, despite their simplicity, carryout activities like any other living creature; in fact, they grow, reproduce, respond to their environment and can move. They are older and smaller than Eukaryotes. ...