A plant that bends toward to the light is
... ____ 18. The difference between plant and animal cells is a. plants have cell walls b. plants have chloroplasts c. all of the above d. none of the above _____ 19. The control center or BRAIN of the cell is the a. Nucleus b. Vacuole c. Cytoplasm d. Chloroplast _____ 20. Passive transport is defined a ...
... ____ 18. The difference between plant and animal cells is a. plants have cell walls b. plants have chloroplasts c. all of the above d. none of the above _____ 19. The control center or BRAIN of the cell is the a. Nucleus b. Vacuole c. Cytoplasm d. Chloroplast _____ 20. Passive transport is defined a ...
The Cell - Acpsd.net
... B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and all presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells). B-2.3 Compare the structures and organelles of prokar ...
... B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and all presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells). B-2.3 Compare the structures and organelles of prokar ...
The Cell
... B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and all presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells). B-2.3 Compare the structures and organelles of prokar ...
... B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; and all presently existing cells arose from previously existing cells). B-2.3 Compare the structures and organelles of prokar ...
Antibody-induced nonapoptotic cell death in human lymphoma and
... Monocolonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized the treatment of B-cell malignancies. In particular, mAbs direct to malignant B cell-surface antigens CD20 have proven the most clinically effective. Although Fc-FcγR mechanisms are thought to account for much of mAb-induced tumor clearance, certain ...
... Monocolonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized the treatment of B-cell malignancies. In particular, mAbs direct to malignant B cell-surface antigens CD20 have proven the most clinically effective. Although Fc-FcγR mechanisms are thought to account for much of mAb-induced tumor clearance, certain ...
January 11, 2017 Class Presentation
... The observations of Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow formed the Cell Theory which states: 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. ...
... The observations of Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow formed the Cell Theory which states: 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. ...
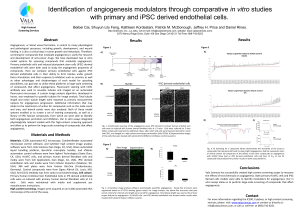
Abstract Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Contact Results
... Angiogenesis, or blood vessel formation, is central to many physiological and pathological processes, including growth, development, and wound healing. It is also a critical step in tumor growth and metastasis. Therefore, screening for compounds that modulate angiogenesis is useful for research and ...
... Angiogenesis, or blood vessel formation, is central to many physiological and pathological processes, including growth, development, and wound healing. It is also a critical step in tumor growth and metastasis. Therefore, screening for compounds that modulate angiogenesis is useful for research and ...
Mitosis Notes - Madeira City Schools
... D. Type of molecules that make up the cell cycle control system 1. Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases a. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (Cdks) – proteins that activate or inactivate other proteins by phosphorylating them. b. They are “cyclin-dependent” because they are only active when attached to a cy ...
... D. Type of molecules that make up the cell cycle control system 1. Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases a. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (Cdks) – proteins that activate or inactivate other proteins by phosphorylating them. b. They are “cyclin-dependent” because they are only active when attached to a cy ...
Similarities and Differences Among Living Things
... gradients ▪ Leads to an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane that is important for nerve impulses and resulting movement ...
... gradients ▪ Leads to an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane that is important for nerve impulses and resulting movement ...
This organelle looks like a stack of pancakes
... Prokaryotes- no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles; DNA in 1 circular chromosome Eukaryotes- nucleus; membrane bound organelles, ...
... Prokaryotes- no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles; DNA in 1 circular chromosome Eukaryotes- nucleus; membrane bound organelles, ...
Similarities and Differences Among Living Things
... gradients ▪ Leads to an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane that is important for nerve impulses and resulting movement ...
... gradients ▪ Leads to an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane that is important for nerve impulses and resulting movement ...
Protomorphogen Information Sheet
... most basic level, the attached nucleoprotein moiety is simply attracted and bound due to this chemical affinity of the mineral skeleton. It follows then that the individual genetic pattern is actively formed over this basic framework. While in the cell determinant state, there appears to be an affin ...
... most basic level, the attached nucleoprotein moiety is simply attracted and bound due to this chemical affinity of the mineral skeleton. It follows then that the individual genetic pattern is actively formed over this basic framework. While in the cell determinant state, there appears to be an affin ...
Cell Organelles
... by two membranes and that is the site of cellular respiration the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms; usually consists of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a membrane ...
... by two membranes and that is the site of cellular respiration the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms; usually consists of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a membrane ...
Viewing Cells Microscopes are used to magnify cells. The number of
... tiny glass bead for a lens. With it, he reported seeing things in pond water that no one had ever imagined. His microscope could magnify up the image of an object 270 times larger than its actual size. Today you would say his lens has a power of 270x. Early compound microscopes were crude by today’s ...
... tiny glass bead for a lens. With it, he reported seeing things in pond water that no one had ever imagined. His microscope could magnify up the image of an object 270 times larger than its actual size. Today you would say his lens has a power of 270x. Early compound microscopes were crude by today’s ...
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
... Leukocytes are the only formed elements that are complete cells, with nuclei and the usual organelles. Accounting for less than 1% of total blood volume, leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells. On average, there are 4800–10,800 WBCs/μl of blood. Leukocytes are crucial to our defense a ...
... Leukocytes are the only formed elements that are complete cells, with nuclei and the usual organelles. Accounting for less than 1% of total blood volume, leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells. On average, there are 4800–10,800 WBCs/μl of blood. Leukocytes are crucial to our defense a ...
Running rescues defective adult neurogenesis by
... Institute of Cell Biology and Neurobiology, National Research Council, Fondazione Santa Lucia, Rome, Italy. ...
... Institute of Cell Biology and Neurobiology, National Research Council, Fondazione Santa Lucia, Rome, Italy. ...
September 26 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... Do Now (Quiz) 3. The chemical reactions involved in respiration are virtually identical between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, ATP is synthesized primarily on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Where are the corresponding reactions likely to occur in prokaryotic respi ...
... Do Now (Quiz) 3. The chemical reactions involved in respiration are virtually identical between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, ATP is synthesized primarily on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Where are the corresponding reactions likely to occur in prokaryotic respi ...
UNIT 1: Matter and Energy For Life
... As these packets move to the end of the Golgi Apparatus, part of the membrane surrounds the protein and pinches off forming another vesicle. The packet can then be transported to another organelle or moved to the cell membrane. Once there, it fuses with the plasma membrane and dumps its contents out ...
... As these packets move to the end of the Golgi Apparatus, part of the membrane surrounds the protein and pinches off forming another vesicle. The packet can then be transported to another organelle or moved to the cell membrane. Once there, it fuses with the plasma membrane and dumps its contents out ...
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells make up the
... What exactly are cells? Cells are sacs of fluid surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float chemicals and organelles. An organism contains parts that are smaller than a cell, but the cell is the smallest part of the organism that retains characteristics of the entire organism. For example, a cel ...
... What exactly are cells? Cells are sacs of fluid surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float chemicals and organelles. An organism contains parts that are smaller than a cell, but the cell is the smallest part of the organism that retains characteristics of the entire organism. For example, a cel ...
Cell Wall - WordPress.com
... Cells don’t increase in size when living organisms grow. Instead they divide the cells in their body and produce more cells. That happens because of the cell’s function. For example if the cell was larger in size it would take longer to transport all the materials / substances to other organelles th ...
... Cells don’t increase in size when living organisms grow. Instead they divide the cells in their body and produce more cells. That happens because of the cell’s function. For example if the cell was larger in size it would take longer to transport all the materials / substances to other organelles th ...
Cells - Tuckahoe Common School District
... • Gonads = specialized sex organs where gametes are created by meiosis (male = testes, female = ovaries) • Fertilization = the fusion of gametes that results in the formation of a new organism, or offspring. ...
... • Gonads = specialized sex organs where gametes are created by meiosis (male = testes, female = ovaries) • Fertilization = the fusion of gametes that results in the formation of a new organism, or offspring. ...
8.2 Cell Transport
... • the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • Allows cells to maintain balance as their environment changes. ...
... • the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • Allows cells to maintain balance as their environment changes. ...
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is
... 20. Hairlike projections from the plasma membrane that aid in ...
... 20. Hairlike projections from the plasma membrane that aid in ...
Bacteria PPT
... Plasmid = extra chromosome that can replicate separately from the main chromosome ...
... Plasmid = extra chromosome that can replicate separately from the main chromosome ...
File eoct review with answers
... Bacteria, Archae, and Eukarya (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia). 78. How are organisms named? According to their physical characteristics. 79. What are the levels of classification of organisms? Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species ( kings play chess on fine gold setting) 80. Whi ...
... Bacteria, Archae, and Eukarya (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia). 78. How are organisms named? According to their physical characteristics. 79. What are the levels of classification of organisms? Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species ( kings play chess on fine gold setting) 80. Whi ...
2. ______ Active Transport uses the energy
... d. Carrier releases ____ to outside of membrane, then binds extracellular K+ e. Pi dissociates from carrier, and carrier releases ____ inside cell f. Carrier returns to original ____________ 2. ___________ Active Transport uses the energy provided by ___________ active transport to move substances a ...
... d. Carrier releases ____ to outside of membrane, then binds extracellular K+ e. Pi dissociates from carrier, and carrier releases ____ inside cell f. Carrier returns to original ____________ 2. ___________ Active Transport uses the energy provided by ___________ active transport to move substances a ...