here
... our body that allow tissues to replace dying cells and repair wounds. Using skin as a model, Fuchs explores the unique properties of skin stem cells that allow them to both replenish themselves (selfrenew) and also maintain and regenerate the epidermis and its appendages such as sweat glands and hai ...
... our body that allow tissues to replace dying cells and repair wounds. Using skin as a model, Fuchs explores the unique properties of skin stem cells that allow them to both replenish themselves (selfrenew) and also maintain and regenerate the epidermis and its appendages such as sweat glands and hai ...
Slide ()
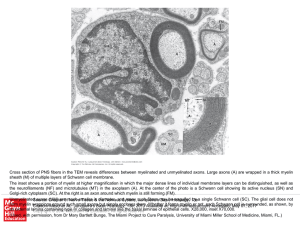
... Golgi-rich cytoplasm (SC). At the right is an axon around which myelin is still forming (FM). UnmyelinatedSource: axons Chapter (UM) are9.much diameter, and many such fibers may engulfed 13e by a single Schwann cell (SC). The glial cell does not Nervesmaller Tissue in & the Nervous System, Junqueira ...
... Golgi-rich cytoplasm (SC). At the right is an axon around which myelin is still forming (FM). UnmyelinatedSource: axons Chapter (UM) are9.much diameter, and many such fibers may engulfed 13e by a single Schwann cell (SC). The glial cell does not Nervesmaller Tissue in & the Nervous System, Junqueira ...
Cells
... In organisms, structure and function are related. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. It includes the shape of a part and the material of which the part is made. Function is the job the part does. For example, the structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. In the lungs, there a ...
... In organisms, structure and function are related. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. It includes the shape of a part and the material of which the part is made. Function is the job the part does. For example, the structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. In the lungs, there a ...
Unit Four - Mr. Distasio`s Wiki
... Summary; Cells are small because: Cells need surface area of their cell membrane large enough to adequately _______________ ___________________with the environment (wastes, gases such as O2 & CO2, and nutrients) Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer ____________ _______ & th ...
... Summary; Cells are small because: Cells need surface area of their cell membrane large enough to adequately _______________ ___________________with the environment (wastes, gases such as O2 & CO2, and nutrients) Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer ____________ _______ & th ...
Cells...smallest unit of an organism capable of life.
... Multicellular organisms composed of many cells, which are specialized and independent. Multicellular organisms can not survive by themselves. Multicellular organisms use a division of labor to survive. Which means different cells preform different functions. For example, the cells that make up your ...
... Multicellular organisms composed of many cells, which are specialized and independent. Multicellular organisms can not survive by themselves. Multicellular organisms use a division of labor to survive. Which means different cells preform different functions. For example, the cells that make up your ...
Test: Cell Structure and Function
... __________ 6. All the living material inside a cell, except the nucleus, makes up the a. cytoplasm. b. membranes. c. vacuole. d. mitochondria. __________ 7. The movement of material from a more crowded area to a less crowded area is called a. osmosis. b. photosynthesis. c. respiration. d. diffusion. ...
... __________ 6. All the living material inside a cell, except the nucleus, makes up the a. cytoplasm. b. membranes. c. vacuole. d. mitochondria. __________ 7. The movement of material from a more crowded area to a less crowded area is called a. osmosis. b. photosynthesis. c. respiration. d. diffusion. ...
Test: Cell Structure and Function
... __________ 6. All the living material inside a cell, except the nucleus, makes up the a. cytoplasm. b. membranes. c. vacuole. d. mitochondria. __________ 7. The movement of material from a more crowded area to a less crowded area is called a. osmosis. b. photosynthesis. c. respiration. d. diffusion. ...
... __________ 6. All the living material inside a cell, except the nucleus, makes up the a. cytoplasm. b. membranes. c. vacuole. d. mitochondria. __________ 7. The movement of material from a more crowded area to a less crowded area is called a. osmosis. b. photosynthesis. c. respiration. d. diffusion. ...
to Study Guide for Test 1-Stephen Grant
... Chloroplasts - contains chlorophyll, the pigment needed for photosynthesis Leucoplasts - starch storage bodies in plants Microfilaments - provide strength and support Lysosomes - suicide bags or sacks; drgest bacteria and "foreign" material Microtubules - used in cells division and cell movement Gol ...
... Chloroplasts - contains chlorophyll, the pigment needed for photosynthesis Leucoplasts - starch storage bodies in plants Microfilaments - provide strength and support Lysosomes - suicide bags or sacks; drgest bacteria and "foreign" material Microtubules - used in cells division and cell movement Gol ...
Test Yourself Questions
... bacteria. They must infect a host cell and commandeer its cellular machinery and energy sources to make more viruses. Like bacteria, viruses cause many common human diseases, including influenza, HIV, herpes, and the common cold. Parasites: These are muticellular eukaryotic organisms such as fungi, ...
... bacteria. They must infect a host cell and commandeer its cellular machinery and energy sources to make more viruses. Like bacteria, viruses cause many common human diseases, including influenza, HIV, herpes, and the common cold. Parasites: These are muticellular eukaryotic organisms such as fungi, ...
lessonuploads/Cells and your school
... assign an organelle for this activity. Pretend you are this organelle for the remaining questions. 2. What is your job? ...
... assign an organelle for this activity. Pretend you are this organelle for the remaining questions. 2. What is your job? ...
cells - Githens Jaguars
... Asexual Reproduction • Requires only one parent • Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent. – In other words, the offspring are exact “clones” of the parent. – Most unicellular organisms reproduce this way. – Mitosis ...
... Asexual Reproduction • Requires only one parent • Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent. – In other words, the offspring are exact “clones” of the parent. – Most unicellular organisms reproduce this way. – Mitosis ...
Stem cells in Hematology
... First clinical trial: Blood made from stem cells will be tested in 2016-17 in UK! 2010: First generation of red blood cells from human ES/iPS (Lapillonne et al., 2010)…. Difficulties in enucleation ...
... First clinical trial: Blood made from stem cells will be tested in 2016-17 in UK! 2010: First generation of red blood cells from human ES/iPS (Lapillonne et al., 2010)…. Difficulties in enucleation ...
Cells - SCHOOLinSITES
... 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells ...
... 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells ...
Paramecium tetraurelia, model organism
... Paramecium are found in stagnant warm freshwater. In their natural habitat these organisms are heavily preyed upon by another ciliate, Didinium. As all Ciliates, Paramecium 's cells possess two nuclei. A germinal nucleus (the micronucleus) is responsible for the transmission of genetic information v ...
... Paramecium are found in stagnant warm freshwater. In their natural habitat these organisms are heavily preyed upon by another ciliate, Didinium. As all Ciliates, Paramecium 's cells possess two nuclei. A germinal nucleus (the micronucleus) is responsible for the transmission of genetic information v ...
Course Guide - Universitat de València
... cell to carry out all functions for survival and reproduction. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are semiautonomous organelles that transform energy by using a chemical (mitochondria) or light (chloroplasts) source. Ribosomes, non-membrane delimited organelles, carry out the genetic instructions contain ...
... cell to carry out all functions for survival and reproduction. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are semiautonomous organelles that transform energy by using a chemical (mitochondria) or light (chloroplasts) source. Ribosomes, non-membrane delimited organelles, carry out the genetic instructions contain ...
BIOL 170 Exploring Biology
... 23. As the eukaryotic body cell prepares to divide, what happens to the chromatin?. 24. In the process of the eukaryotic body cell dividing into two daughter cells, what happens to the chromosomes? 25. How many chromosome pairs are found in the normal human body cell? C. Meiosis (Sexual Reproduction ...
... 23. As the eukaryotic body cell prepares to divide, what happens to the chromatin?. 24. In the process of the eukaryotic body cell dividing into two daughter cells, what happens to the chromosomes? 25. How many chromosome pairs are found in the normal human body cell? C. Meiosis (Sexual Reproduction ...
Cell Signaling
... • These mating factors cause the cells to grow toward one another and bring about other changes. • Inside the cells there are a series of chemical changes, called the signal-transduction pathway, that cause the response. ...
... • These mating factors cause the cells to grow toward one another and bring about other changes. • Inside the cells there are a series of chemical changes, called the signal-transduction pathway, that cause the response. ...
Proposition stage ENS 2017
... immature particles (i.e., non infectious viral particles containing uncleaved prM) is released from DENV infected cells as a consequence of an evolutionary conserved suboptimal cleavage site. The release of immature virions is an important feature observed for the different members of the flavivirus ...
... immature particles (i.e., non infectious viral particles containing uncleaved prM) is released from DENV infected cells as a consequence of an evolutionary conserved suboptimal cleavage site. The release of immature virions is an important feature observed for the different members of the flavivirus ...
Biology Curriculum Guide GPISD 2012
... compare the functions of a cell to the functions of organisms such as waste disposal. ...
... compare the functions of a cell to the functions of organisms such as waste disposal. ...
Supplemental Figure Legends
... were quantified using ImageJ (D). Data are represented as mean ± SD. ...
... were quantified using ImageJ (D). Data are represented as mean ± SD. ...
Chromosomes
... • Consists of two main phases: – Interphase • Period that cells are in when not dividing. • 90% of cell cycle ...
... • Consists of two main phases: – Interphase • Period that cells are in when not dividing. • 90% of cell cycle ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... • Cells are the fundamental units of life. • All organisms are composed of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells. ...
... • Cells are the fundamental units of life. • All organisms are composed of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells. ...