The medicinal leech as a model organism for establishing the
... How is sensory information processed? It was shown in [6] that a skin stimulation activates a large number of cells. Among others, the pressure sensitive P-Cell and a cell of unknown function, the AP-Cell, were active. ...
... How is sensory information processed? It was shown in [6] that a skin stimulation activates a large number of cells. Among others, the pressure sensitive P-Cell and a cell of unknown function, the AP-Cell, were active. ...
“Virtual Cell” Activity
... “Virtual Cell” Activity Go to www.virtualcell.com, then CLICK on “The Virtual Textbook”, then CLICK on “Cell Biology” to begin. The virtual cell will allow you to get a close-up view of several organelles in 3-D! You will be able to choose certain organelles within the cell and manipulate them by zo ...
... “Virtual Cell” Activity Go to www.virtualcell.com, then CLICK on “The Virtual Textbook”, then CLICK on “Cell Biology” to begin. The virtual cell will allow you to get a close-up view of several organelles in 3-D! You will be able to choose certain organelles within the cell and manipulate them by zo ...
Multiple Expression of Ly-6C and Accumulation of a Ly-6C Pre-mRNA... Activated Macrophages Involved in Rejection of an Allografted Tumor
... by immunoblot data obtained with antiserum against Ly-6C (Fig. 3). Furthermore, when the expression of Ly-6C on these cells was examined by FCM using an AL-21 mAb specific for Ly-6C (24), more than 90% of the AIMs (Fig. 1F) or BCG-elicited Møs (Fig. 1G) and about 50% of the bone marrow cells (Fig. 1 ...
... by immunoblot data obtained with antiserum against Ly-6C (Fig. 3). Furthermore, when the expression of Ly-6C on these cells was examined by FCM using an AL-21 mAb specific for Ly-6C (24), more than 90% of the AIMs (Fig. 1F) or BCG-elicited Møs (Fig. 1G) and about 50% of the bone marrow cells (Fig. 1 ...
Epithelial and Connective Tissues
... collagen network) that supports epithelium-really associated connective tissue • Connective tissue support • Nutrients from capillaries in underlying connective tissue • Nerves pass through • Easily regenerates • E.g. skin, lining of gut, mucous membranes Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. ...
... collagen network) that supports epithelium-really associated connective tissue • Connective tissue support • Nutrients from capillaries in underlying connective tissue • Nerves pass through • Easily regenerates • E.g. skin, lining of gut, mucous membranes Human Anatomy, Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. ...
title: green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its cancer cells
... cancer cell lines. The synthesis of nanoparticles was confirmed by UV- Visible ...
... cancer cell lines. The synthesis of nanoparticles was confirmed by UV- Visible ...
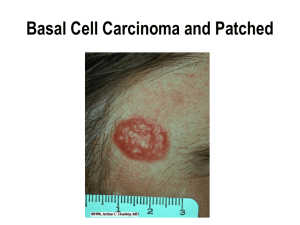
The Sonic Hedgehog
... •Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common skin cancer, and possibly the most common cancer of all ...
... •Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common skin cancer, and possibly the most common cancer of all ...
Protista
... Structure of Amoeba Contractile Vacuole: maintains salt and water balance within cell (Osmoregulation): - collects water entering cell by osmosis. - swells, touches cell membrane. ...
... Structure of Amoeba Contractile Vacuole: maintains salt and water balance within cell (Osmoregulation): - collects water entering cell by osmosis. - swells, touches cell membrane. ...
The basic structural and functional unit of an organism
... Chromosomes are condensed form of the fine thread like structure called chromatin material (thread) which are seen only cell undergoing cell division. The chromatin thread are made up of DNA which organize into gene. Chromosomes are called hereditary vehicle This is because they contain gene which ...
... Chromosomes are condensed form of the fine thread like structure called chromatin material (thread) which are seen only cell undergoing cell division. The chromatin thread are made up of DNA which organize into gene. Chromosomes are called hereditary vehicle This is because they contain gene which ...
Hormones in action
... Agonists act like the "normal" hormone, although perhaps more or less potently. Natural hormones are themselves agonists and, in many cases, more than one distinct hormone binds to the same receptor. For a given receptor, different agonists can have dramatically different potencies. Antagonists ...
... Agonists act like the "normal" hormone, although perhaps more or less potently. Natural hormones are themselves agonists and, in many cases, more than one distinct hormone binds to the same receptor. For a given receptor, different agonists can have dramatically different potencies. Antagonists ...
Summary for the non-biologist Developmental biology
... same time that they relay the signal (or pass on the message). This is how multicellular development is triggered and its dependence on extracellular cAMP is a unique feature of Dictyostelium development. The proteins or enzymes that produce cAMP are called adenylyl cyclases and we find three in Dic ...
... same time that they relay the signal (or pass on the message). This is how multicellular development is triggered and its dependence on extracellular cAMP is a unique feature of Dictyostelium development. The proteins or enzymes that produce cAMP are called adenylyl cyclases and we find three in Dic ...
osmosis - School
... The contents of the cell cytoplasm are a complex mixture of dissolved solutes, giving a certain water potential. If the cell is placed in a solution of equal concentration then as much water will diffuse in as out and the two solutions are ...
... The contents of the cell cytoplasm are a complex mixture of dissolved solutes, giving a certain water potential. If the cell is placed in a solution of equal concentration then as much water will diffuse in as out and the two solutions are ...
Cel l and Tissue Injury
... • Pathology is "Scientific study of disease“ Study of structural and functional changes in disease. • Diseases is an expression of "discomfort" due to structural or functional abnormality. • "Pathology deals with knowledge of what causes disease, how disease starts, progresses & it explains the rea ...
... • Pathology is "Scientific study of disease“ Study of structural and functional changes in disease. • Diseases is an expression of "discomfort" due to structural or functional abnormality. • "Pathology deals with knowledge of what causes disease, how disease starts, progresses & it explains the rea ...
chapter3_Cells - Moore Middle School
... • A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system. Each organ system has a specific job in the body. • Examples of organ systems are the digestive system, the respiratory system, and the cardiovascular system. • Examples of plant organ systems are leaf s ...
... • A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system. Each organ system has a specific job in the body. • Examples of organ systems are the digestive system, the respiratory system, and the cardiovascular system. • Examples of plant organ systems are leaf s ...
Midterm_Review
... vacuole, centriole, chloroplast, chromatin, chromosome, cilia, crista, (plural, cristae), cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, electron microscope (EM), endomembrane system, endoplasmic reticulum (ER),, endosymbiosis, eukaryotic cell, extracellular ...
... vacuole, centriole, chloroplast, chromatin, chromosome, cilia, crista, (plural, cristae), cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, electron microscope (EM), endomembrane system, endoplasmic reticulum (ER),, endosymbiosis, eukaryotic cell, extracellular ...
Chapter 3
... • A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system. Each organ system has a specific job in the body. • Examples of organ systems are the digestive system, the respiratory system, and the cardiovascular system. • Examples of plant organ systems are leaf s ...
... • A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system. Each organ system has a specific job in the body. • Examples of organ systems are the digestive system, the respiratory system, and the cardiovascular system. • Examples of plant organ systems are leaf s ...
Chapter 3 - Cobb Learning
... • As a cell’s volume increases, its surface area grows. But volume increases faster than the surface area. • The area of a cell’s surface–compared with the cell’s volume–limits the cell’s size. • The ratio of the cell’s outer surface to the cell’s volume is called the surface area-to-volume ratio: ...
... • As a cell’s volume increases, its surface area grows. But volume increases faster than the surface area. • The area of a cell’s surface–compared with the cell’s volume–limits the cell’s size. • The ratio of the cell’s outer surface to the cell’s volume is called the surface area-to-volume ratio: ...
Chapter 5
... Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Endocytosis Brings macromolecules, large particles, small molecules, and even other cells into the eukaryotic cell. • Exocytosis Process by which materials packaged in vesicles are secreted from the cell. ...
... Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Endocytosis Brings macromolecules, large particles, small molecules, and even other cells into the eukaryotic cell. • Exocytosis Process by which materials packaged in vesicles are secreted from the cell. ...
Maintaining a Dynamic Equilibrium The Need for Homeostasis
... as its external environment changes. This ability of all living things to detect deviations and to maintain a constant internal environment is known as homeostasis. An obvious change that has occurred in the course of evolution is the development of larger multicellular organisms from microscopic, s ...
... as its external environment changes. This ability of all living things to detect deviations and to maintain a constant internal environment is known as homeostasis. An obvious change that has occurred in the course of evolution is the development of larger multicellular organisms from microscopic, s ...
Cells
... Hypertonic to the cell – Concentration of solute is greater outside cell → water moves in until equilibrium is reached. Cell may shrivel. Hypotonic to the cell – Concentration of solute is lower outside cell → water moves into cell until equilibrium is reached. Cell may swell to bursting point. ...
... Hypertonic to the cell – Concentration of solute is greater outside cell → water moves in until equilibrium is reached. Cell may shrivel. Hypotonic to the cell – Concentration of solute is lower outside cell → water moves into cell until equilibrium is reached. Cell may swell to bursting point. ...
Introduction to Cell Biology
... unit of all living organisms, conserving the features of the organism, having the ability of self-control, self-regulation, and ...
... unit of all living organisms, conserving the features of the organism, having the ability of self-control, self-regulation, and ...
4150 Lecture 8
... What happens when telomeres get too short? • Cell detects short telomere ends and become senescent or undergo apoptosis • Biological clock for regulating the number of cell divisions for a cell • Genes located near telomeres may be regulated by length – age-regulated gene expression ...
... What happens when telomeres get too short? • Cell detects short telomere ends and become senescent or undergo apoptosis • Biological clock for regulating the number of cell divisions for a cell • Genes located near telomeres may be regulated by length – age-regulated gene expression ...
GENETICS
... The history of chemotherapy starts with Paul Ehrlich • Development of salvarsan to treat syphilis ...
... The history of chemotherapy starts with Paul Ehrlich • Development of salvarsan to treat syphilis ...
Polycationic Polypeptides: a Possible Model for the
... phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.2 (PBS) (Dulbecco & Vogt, 1954)at room temperature, and collected by low-speed centrifugation at 1OOOg. JM cells were kindly provided by Dr H. W. Kreth, Institut fur Virologie, Universitat Wiirzburg. The JM cell line is a human lymphoblastoid cell line with T cell char ...
... phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.2 (PBS) (Dulbecco & Vogt, 1954)at room temperature, and collected by low-speed centrifugation at 1OOOg. JM cells were kindly provided by Dr H. W. Kreth, Institut fur Virologie, Universitat Wiirzburg. The JM cell line is a human lymphoblastoid cell line with T cell char ...
Undergraduate student projects in the Department of Molecular
... Irx3 and Irx5 target genes in adipocyte differentiation Our laboratory has recently identified Irx3 and Irx5 as major regulators of energy homeostasis in both the hypothalamus and adipose tissue. Knockout of Irx3 or Irx5 leads to profound defects in adipocyte differentiation. This summer project wil ...
... Irx3 and Irx5 target genes in adipocyte differentiation Our laboratory has recently identified Irx3 and Irx5 as major regulators of energy homeostasis in both the hypothalamus and adipose tissue. Knockout of Irx3 or Irx5 leads to profound defects in adipocyte differentiation. This summer project wil ...