Cellular Transport Notes
... Cell Membrane • Its function is to maintain a balance called homeostasis within the cell. • Remember that the cell membrane is semipermeable or selectively permeable. It controls how, when, and how much stuff enters and leaves the cell. It is picky. ...
... Cell Membrane • Its function is to maintain a balance called homeostasis within the cell. • Remember that the cell membrane is semipermeable or selectively permeable. It controls how, when, and how much stuff enters and leaves the cell. It is picky. ...
Viral Structure - Chapman @ Norquay School
... Why are the structures protruding from the lipid envelope important for bonding to host cells? ...
... Why are the structures protruding from the lipid envelope important for bonding to host cells? ...
Cell Membranes and Disease
... functions, and lead to pleomorphic changes present in neoplasia. The presence of an abnormal structural component in plasma membrane may lead to morphologic changes, appearance of new antigenicity, change in permeability, and alteration in the function of membraneassociated enzymes. T h e interactio ...
... functions, and lead to pleomorphic changes present in neoplasia. The presence of an abnormal structural component in plasma membrane may lead to morphologic changes, appearance of new antigenicity, change in permeability, and alteration in the function of membraneassociated enzymes. T h e interactio ...
Recombinant LONG®R3IGF-1 and rTransferrin
... LONG®R3 IGF‐1 is a human IGF‐1 analog containing a 13 amino acid N‐terminal extension and a mutation at position 3. It activates the Type 1 IGF receptor, which is responsible for growth‐promoting and protein synthesis effects in CHO cells. A common growth factor supplement used in CHO media, insul ...
... LONG®R3 IGF‐1 is a human IGF‐1 analog containing a 13 amino acid N‐terminal extension and a mutation at position 3. It activates the Type 1 IGF receptor, which is responsible for growth‐promoting and protein synthesis effects in CHO cells. A common growth factor supplement used in CHO media, insul ...
Blood 93/6 - Semantic Scholar
... Plasmid construction. For the construction of pCAG-hGM-CSFR ␣-mLIFR and pMKIT-hGM-CSFR c-mLIFR, the cDNA of mouse LIFR was cloned from ES cell line A3.1 by reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).21,39 The PCR products were inserted into pSP72 (Promega, Madison, WI) at the Pvu II si ...
... Plasmid construction. For the construction of pCAG-hGM-CSFR ␣-mLIFR and pMKIT-hGM-CSFR c-mLIFR, the cDNA of mouse LIFR was cloned from ES cell line A3.1 by reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).21,39 The PCR products were inserted into pSP72 (Promega, Madison, WI) at the Pvu II si ...
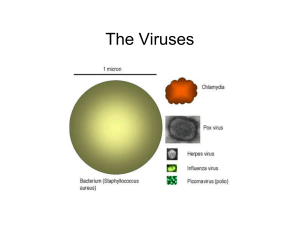
Introduction to Agricultural Biotechnology AGR 0150 Viruses Part 3
... • Most studies have focused on bacterial and animal virus • Some studies on viruses that infect crops • Fungal virus studies are limited, – It is known that they have no extracellular stage ...
... • Most studies have focused on bacterial and animal virus • Some studies on viruses that infect crops • Fungal virus studies are limited, – It is known that they have no extracellular stage ...
File - Mrs. Allen CLMS
... Osmosis: the diffusion of water through the cell membrane. Water goes from where there is a lot of water to ...
... Osmosis: the diffusion of water through the cell membrane. Water goes from where there is a lot of water to ...
Cell Parts Notes - davis.k12.ut.us
... functions properly and gives instructions of what and how to do things. 1. Chromatin/Chromosomes: contain the DNA which contains all the information of what a cell becomes and how it should become what is needed. DNA is sometimes called the blueprint for the cell because it contains the genetic info ...
... functions properly and gives instructions of what and how to do things. 1. Chromatin/Chromosomes: contain the DNA which contains all the information of what a cell becomes and how it should become what is needed. DNA is sometimes called the blueprint for the cell because it contains the genetic info ...
2401-Ch3.pdf
... Cilia – tend to be shorter (10 µm) and occur in large numbers these beat in a power & return stroke and set up a current across the surface of the tissue… e.g. respiratory tract, fallopian tubes ...
... Cilia – tend to be shorter (10 µm) and occur in large numbers these beat in a power & return stroke and set up a current across the surface of the tissue… e.g. respiratory tract, fallopian tubes ...
Protist Presentation (to prepare for mini
... First kingdom of eukaryotes Unicellular Nuclei Organelles Reproduce by mitosis Multiple chromosomes Protists often have a very complicated internal structure: a single cell must do all the functions that we have many different cell types to do. ...
... First kingdom of eukaryotes Unicellular Nuclei Organelles Reproduce by mitosis Multiple chromosomes Protists often have a very complicated internal structure: a single cell must do all the functions that we have many different cell types to do. ...
ppt
... primitive streak is regulated by multiple pathways, including Nodal, Wnt and Bmp • Canonical Wnt signaling is absolutely required for primitive streak formation (Wnt3, LRP5/6) • Wnt signaling can induce expression of at least one primitive streak gene (brachyury) and can antagonize neuronal differen ...
... primitive streak is regulated by multiple pathways, including Nodal, Wnt and Bmp • Canonical Wnt signaling is absolutely required for primitive streak formation (Wnt3, LRP5/6) • Wnt signaling can induce expression of at least one primitive streak gene (brachyury) and can antagonize neuronal differen ...
The Type I Membrane Protein EFF-1 Is Essential for Developmental
... eff-1(hy21) was isolated in a screen for temperaturesensitive vulva defects. One hundred percent of adult eff-1(hy21) worms at 25⬚C are egg-laying defective (n ⫽ 715), 46% have a protruded vulva (142/306), 18% explode in the vulva region (137/751), and 2% have one or two additional pseudovulvae (14/ ...
... eff-1(hy21) was isolated in a screen for temperaturesensitive vulva defects. One hundred percent of adult eff-1(hy21) worms at 25⬚C are egg-laying defective (n ⫽ 715), 46% have a protruded vulva (142/306), 18% explode in the vulva region (137/751), and 2% have one or two additional pseudovulvae (14/ ...
Nucleoids and coated vesicles of “Epulopiscium” spp.
... of these organisms bore one or two daughter cells. Nucleoids of morphotype B As Fig. 1 (A–E) and Fig. 2 (A,B) clearly show, B morphotypes have innumerable, closely-packed, small nucleoids spaced all over their periphery in a shallow layer just beneath their surface. In DAPI preparations, brightly fl ...
... of these organisms bore one or two daughter cells. Nucleoids of morphotype B As Fig. 1 (A–E) and Fig. 2 (A,B) clearly show, B morphotypes have innumerable, closely-packed, small nucleoids spaced all over their periphery in a shallow layer just beneath their surface. In DAPI preparations, brightly fl ...
Research Article Immunohistochemical and
... differentiation [5]. Cambium cells may be activated after mechanical stimulation, such as soft tissue trauma [6], by infection or by some tumors [4]. Under these circumstances, this layer is capable of inducing callus tissue formation and osteogenesis. Ito et al. [7] suggest that the cambium layer s ...
... differentiation [5]. Cambium cells may be activated after mechanical stimulation, such as soft tissue trauma [6], by infection or by some tumors [4]. Under these circumstances, this layer is capable of inducing callus tissue formation and osteogenesis. Ito et al. [7] suggest that the cambium layer s ...
Cell Membranes Practice Test
... Question #8 Which of the following is true of a hypotonic solution? Write in all that apply. a) Occurs when you are dehydrated b) Concentration of salt is higher inside the cell c) Concentration of water is higher inside the cell d) Water moves into the cell e) Cell shrinks ...
... Question #8 Which of the following is true of a hypotonic solution? Write in all that apply. a) Occurs when you are dehydrated b) Concentration of salt is higher inside the cell c) Concentration of water is higher inside the cell d) Water moves into the cell e) Cell shrinks ...
Transport-cell membrane
... • Simple diffusion – substances pass through the membrane with no outside aid – Ex. substances: Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, water and lipid soluble molecules ...
... • Simple diffusion – substances pass through the membrane with no outside aid – Ex. substances: Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, water and lipid soluble molecules ...
Plasma cell - World Health Organization
... Developed by the Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response of the World Health ...
... Developed by the Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response of the World Health ...
Histology
... secretory acini that drain into numerous efferent ducts. These ducts typically merge into a smaller number of main ducts. The parotid salivary glands and the pancreas are examples of this type of gland. h) Compound alveolar glands (Compound acinar ) are compound glands because they have numerous dra ...
... secretory acini that drain into numerous efferent ducts. These ducts typically merge into a smaller number of main ducts. The parotid salivary glands and the pancreas are examples of this type of gland. h) Compound alveolar glands (Compound acinar ) are compound glands because they have numerous dra ...
Homeobox A9 Transcriptionally Regulates the EphB4 Receptor to
... © 2004 American Heart Association, Inc. Circulation Research is available at http://www.circresaha.org ...
... © 2004 American Heart Association, Inc. Circulation Research is available at http://www.circresaha.org ...
Cell Transport
... d. What is the impact of water on life processes? (i.e. osmosis and diffusion) LEQ4: _________________________________________________________________ Structure: Cell/Plasma Membrane Composed of two ___________________ layers (bilayer) There are other molecules embedded in the membrane (_________, ...
... d. What is the impact of water on life processes? (i.e. osmosis and diffusion) LEQ4: _________________________________________________________________ Structure: Cell/Plasma Membrane Composed of two ___________________ layers (bilayer) There are other molecules embedded in the membrane (_________, ...
The Epigenetic Code regulates Chromatin Structure and
... Epigenetic regulation of Cellular Identity Epi- (greek: “over, above”) genetic: heritable changes in gene expression via mechanisms that are separate from the DNA sequence and regulated by environmental signals. Environment Organism level: Nutrition, Behavior, Pollution, Sun light, Toxins, Circadia ...
... Epigenetic regulation of Cellular Identity Epi- (greek: “over, above”) genetic: heritable changes in gene expression via mechanisms that are separate from the DNA sequence and regulated by environmental signals. Environment Organism level: Nutrition, Behavior, Pollution, Sun light, Toxins, Circadia ...