Chloroplasts discovered
... • In most tissue, no cell is ever more than three or four cells away from a blood vessel. • Yet the vessels and blood take up no more than about 5% of the body’s volume. • The total length of an adult’s blood vessels is ...
... • In most tissue, no cell is ever more than three or four cells away from a blood vessel. • Yet the vessels and blood take up no more than about 5% of the body’s volume. • The total length of an adult’s blood vessels is ...
Cell division and the process to therapeutic vs reproductive cloning
... Placenta and Amniotic Membrane ...
... Placenta and Amniotic Membrane ...
File
... • In most tissue, no cell is ever more than three or four cells away from a blood vessel. • Yet the vessels and blood take up no more than about 5% of the body’s volume. • The total length of an adult’s blood vessels is ...
... • In most tissue, no cell is ever more than three or four cells away from a blood vessel. • Yet the vessels and blood take up no more than about 5% of the body’s volume. • The total length of an adult’s blood vessels is ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... membrane. Within the membrane is a semi-fluid substance, cytoplasm, in which organelles are found. All cells contain chromosomes, carrying genes in the form of DNA. In addition, all cells have ribosomes, tiny organelles that make proteins according to instructions from the genes. 2 Types of Cells __ ...
... membrane. Within the membrane is a semi-fluid substance, cytoplasm, in which organelles are found. All cells contain chromosomes, carrying genes in the form of DNA. In addition, all cells have ribosomes, tiny organelles that make proteins according to instructions from the genes. 2 Types of Cells __ ...
First Six Weeks Test Corrections The cell membrane controls what
... 1. The cell membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell. 2. The mitochondria releases chemical energy for the cell’s activities. 3. Plant cells are usually rectangular in shape. 4. The thick-jelly like substance that holds organelles in place inside a cell is the cytoplasm. 5. Central vacuole ...
... 1. The cell membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell. 2. The mitochondria releases chemical energy for the cell’s activities. 3. Plant cells are usually rectangular in shape. 4. The thick-jelly like substance that holds organelles in place inside a cell is the cytoplasm. 5. Central vacuole ...
Chapter 7 Test Review Guide
... 9. Know the name, location, and function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, nucleolus, vacuole, vesicle, lysosome, cytoskeleton, centriole, cilia, flagella, ribosome, RER, SER, Golgi apparatus, chloroplast, mitochondria, and cell wall. 10. ...
... 9. Know the name, location, and function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, nucleolus, vacuole, vesicle, lysosome, cytoskeleton, centriole, cilia, flagella, ribosome, RER, SER, Golgi apparatus, chloroplast, mitochondria, and cell wall. 10. ...
CHAPTER 4 Notes
... F. ___________ _____________ : processes and packages substances produced by the cell G. ___________: digests molecules, old organelles, and foreign substances H. ___________: short hair-like structures on the outside of the cell present in large numbers that assist in movement. Example: in respirat ...
... F. ___________ _____________ : processes and packages substances produced by the cell G. ___________: digests molecules, old organelles, and foreign substances H. ___________: short hair-like structures on the outside of the cell present in large numbers that assist in movement. Example: in respirat ...
7th Grade Chapter 13 Study Guide Vocabulary: Section One Cell
... 1. Identify and describe how the scientists (Hooke, Leeuwenhook) have helped contribute to our understanding of the cell. 2. Compare the levels of organization among eukaryotes with the types of organization found among prokaryotes. 3. Explain why cells in an embryo will grow no larger than a certai ...
... 1. Identify and describe how the scientists (Hooke, Leeuwenhook) have helped contribute to our understanding of the cell. 2. Compare the levels of organization among eukaryotes with the types of organization found among prokaryotes. 3. Explain why cells in an embryo will grow no larger than a certai ...
Learning Outcomes
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
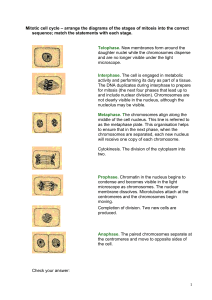
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
Candidates should be able to: (a) state the resolution and
... microscope and be able to recognise the following structures: nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, lysosomes, chloroplasts, plasma (cell surface) membrane, centrioles, flagella and cilia; (f) outline the function ...
... microscope and be able to recognise the following structures: nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, lysosomes, chloroplasts, plasma (cell surface) membrane, centrioles, flagella and cilia; (f) outline the function ...
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
... • Observed that cells had a dark structure within plant cells • Brown observed the nucleus ...
... • Observed that cells had a dark structure within plant cells • Brown observed the nucleus ...
daughter DNA interphase volume binary fission G1 nucleus cell
... During interphase, there are three stages. During the __________ phase, the cell grows. During the ___________ phase, the genetic material (DNA) of the cell is copied. During the ____________ phase, the cell prepares for division. ...
... During interphase, there are three stages. During the __________ phase, the cell grows. During the ___________ phase, the genetic material (DNA) of the cell is copied. During the ____________ phase, the cell prepares for division. ...
Cell Cycle & Cancer
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
... The Cell Cycle • Interphase Cell Growth and Preparation for Division • Mitosis Division of the Nucleus and its DNA • Cytokinesis Division of the Cytoplasm ...
Cell Theory
... What are the 3 tenets of the cell theory? What is the lowest level of structure capable of life? What are unicellular organisms? Multicellular organisms? What are the two types of cells? What are the 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 9. Give me an example of a prokaryotic cell. ...
... What are the 3 tenets of the cell theory? What is the lowest level of structure capable of life? What are unicellular organisms? Multicellular organisms? What are the two types of cells? What are the 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 9. Give me an example of a prokaryotic cell. ...
Biology B: Genetics Unit
... You might need to complete these on notebook paper or a word document. You can put answers on this page if you feel you have enough room. Please use complete sentences unless it specifically say “list”. ...
... You might need to complete these on notebook paper or a word document. You can put answers on this page if you feel you have enough room. Please use complete sentences unless it specifically say “list”. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
Introduction_to_Mitosis
... Cells that contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms ...
... Cells that contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms ...
Is efficiency of organic solar cells limited by their size?
... Serious progress has been achieved in improvement of the photovoltaic (PV) performance of fullerene/polymer solar cells with bulk heterojunction (BHJ) over the last decade: certified efficiencies beyond 8 % have been reported. Efficient charge generation in BHJ requires that the donor and acceptor m ...
... Serious progress has been achieved in improvement of the photovoltaic (PV) performance of fullerene/polymer solar cells with bulk heterojunction (BHJ) over the last decade: certified efficiencies beyond 8 % have been reported. Efficient charge generation in BHJ requires that the donor and acceptor m ...
File
... organisms. • Describe how an organism displays each of the seven characteristics of life and how it must overcome challenges of life. • Describe how chemical functions of organisms start and are carried out within a cell and how material moves in and out of the cell. • Draw and label the parts of di ...
... organisms. • Describe how an organism displays each of the seven characteristics of life and how it must overcome challenges of life. • Describe how chemical functions of organisms start and are carried out within a cell and how material moves in and out of the cell. • Draw and label the parts of di ...