The Civil War - Davis School District
... The tide of the war began to shift in the Union’s favor in 1863. After victory at Vicksburg, Union General Ulysses S. Grant achieved the Union goal of splitting the Confederacy in two. Next, the Union faced a Confederate invasion at the Battle of Gettysburg and defeated Lee’s troops there. The batt ...
... The tide of the war began to shift in the Union’s favor in 1863. After victory at Vicksburg, Union General Ulysses S. Grant achieved the Union goal of splitting the Confederacy in two. Next, the Union faced a Confederate invasion at the Battle of Gettysburg and defeated Lee’s troops there. The batt ...
H A R F O R D C E C I L K E N T Q U E E N A N N E`S
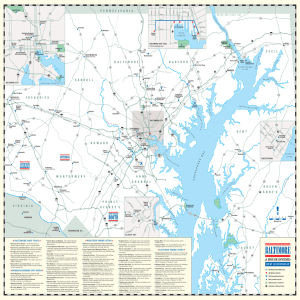
... Fort McHenry, aimed their guns at the city, and ensured Federal control for the remainder of the war. In June 1861, an officer wrote, “The loss of Baltimore would have been the loss of Maryland; the loss of Maryland would have been the loss of the national capital, and perhaps, if not probably, the ...
... Fort McHenry, aimed their guns at the city, and ensured Federal control for the remainder of the war. In June 1861, an officer wrote, “The loss of Baltimore would have been the loss of Maryland; the loss of Maryland would have been the loss of the national capital, and perhaps, if not probably, the ...
Slide 1
... deaths were from disease, including about 8,000 12,000 who died while prisoners of war. The number of Revolutionaries seriously wounded or disabled by the war has been estimated from ...
... deaths were from disease, including about 8,000 12,000 who died while prisoners of war. The number of Revolutionaries seriously wounded or disabled by the war has been estimated from ...
13-1 Civil War Intro
... 1. Blockade the South to keep out needed supplies. 2. Gain control of the Mississippi River to cut off supplies and cut the South in half. 3. Capture confederate capital, Richmond, VA. ...
... 1. Blockade the South to keep out needed supplies. 2. Gain control of the Mississippi River to cut off supplies and cut the South in half. 3. Capture confederate capital, Richmond, VA. ...
Chapter 20 Focus Questions: Essay question: Assess the validity of
... President Lincoln’s decision on what to do about the situation at Fort Sumter can best described how? Why did the Confederates fire on Fort Sumter? What impact did the firing on Fort Sumter have on northern opinion concerning waging war to preserve the Union? How did Lincoln respond to the threat th ...
... President Lincoln’s decision on what to do about the situation at Fort Sumter can best described how? Why did the Confederates fire on Fort Sumter? What impact did the firing on Fort Sumter have on northern opinion concerning waging war to preserve the Union? How did Lincoln respond to the threat th ...
matt barber epq
... the bread riots in Richmond, while in the North the drac riots in 1863 clearly show a lack of support for the war. The bread riots simply were about not having enough food. Furthermore if we look at le#ers from Confederate soldiers wriEng back home we see them far more commi#ed to the war than expec ...
... the bread riots in Richmond, while in the North the drac riots in 1863 clearly show a lack of support for the war. The bread riots simply were about not having enough food. Furthermore if we look at le#ers from Confederate soldiers wriEng back home we see them far more commi#ed to the war than expec ...
civil war arkansas - Arkansas Press Association
... stampede into the Confederate camp when President Lincoln raises an army to invade the seceding states. In Maywith only one opposing votethe state convention votes to secede. This chapter relates how from this point on, the state’s loyal Unionist become very guarded in voicing support for the Unio ...
... stampede into the Confederate camp when President Lincoln raises an army to invade the seceding states. In Maywith only one opposing votethe state convention votes to secede. This chapter relates how from this point on, the state’s loyal Unionist become very guarded in voicing support for the Unio ...
Welcome! We hope you enjoy our presentation! Jackie Brown Paul
... •Disposes of Southern cotton •Destruction of over 100 millions dollars •Cripples Southern Economy •Southern demoralization •General Sherman is ridiculed for his use of ...
... •Disposes of Southern cotton •Destruction of over 100 millions dollars •Cripples Southern Economy •Southern demoralization •General Sherman is ridiculed for his use of ...
D:\TEACHING\CIVWAR\ONLINE\week2_304_guide.NB Job 1
... the Trans-Mississippi West in 1861-1862), consisted of a series of battles leading to a culminating clash (the Seven Days or Pea Ridge). I. First, make sure that you have a good grasp of basic events, people, and issues. You should be able to discuss comfortably (when, where, why, how, what) the fol ...
... the Trans-Mississippi West in 1861-1862), consisted of a series of battles leading to a culminating clash (the Seven Days or Pea Ridge). I. First, make sure that you have a good grasp of basic events, people, and issues. You should be able to discuss comfortably (when, where, why, how, what) the fol ...
Civil War 150 — KidsPost and Puzzles
... and was preparing to defend itself. • The Confederate states took over all U.S. government property inside their borders except for three forts off Florida’s coast and Fort Sumter in South Carolina’s Charleston Harbor. Lincoln — and everyone else — knew his election had caused these things ...
... and was preparing to defend itself. • The Confederate states took over all U.S. government property inside their borders except for three forts off Florida’s coast and Fort Sumter in South Carolina’s Charleston Harbor. Lincoln — and everyone else — knew his election had caused these things ...
UNIT 3: THE CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION
... • Confederate President Jefferson Davis made good on his promise • As the Union ships entered Charleston, South Carolina, Davis ordered an attack • The Union responded in self defense • These became the first shots of the Civil War Free powerpoint template: www.brainybetty.com ...
... • Confederate President Jefferson Davis made good on his promise • As the Union ships entered Charleston, South Carolina, Davis ordered an attack • The Union responded in self defense • These became the first shots of the Civil War Free powerpoint template: www.brainybetty.com ...
Ch 20 Packet
... almost unanimous support for the North. b. support for the South among the upper classes and for the North among the working classes. c. almost unanimous support for the South. d. support for the South in France and Spain and for the North in Britain and Germany. e. support for the North in the larg ...
... almost unanimous support for the North. b. support for the South among the upper classes and for the North among the working classes. c. almost unanimous support for the South. d. support for the South in France and Spain and for the North in Britain and Germany. e. support for the North in the larg ...
Chapter 20 - Newton Public Schools
... b. Confederate agents continued to use Canada as a safe base for raids into the North. c. the British did not withdraw their support for French intervention in Mexico. d. the British aristocracy continued to express public support for the Confederacy. e. the British government delivered the Laird ra ...
... b. Confederate agents continued to use Canada as a safe base for raids into the North. c. the British did not withdraw their support for French intervention in Mexico. d. the British aristocracy continued to express public support for the Confederacy. e. the British government delivered the Laird ra ...
18R-Civil_War_Politics_and_Economics
... Confederates fought for self-determination, its culture, its homeland and freedoms (for whites) C. The Confederate army had superb military officers 1. Robert E. Lee: one of greatest military leaders in U.S. history a. Ironically, he was opposed to slavery and spoke against secession in January 18 ...
... Confederates fought for self-determination, its culture, its homeland and freedoms (for whites) C. The Confederate army had superb military officers 1. Robert E. Lee: one of greatest military leaders in U.S. history a. Ironically, he was opposed to slavery and spoke against secession in January 18 ...
REV: Wexler on McPherson, `War on the Waters: The Union - H-Net
... Confederate ports and smaller rivers and inlets. Du Pont’s November 1861 capture of Port Royal provided the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron a forward base situated between Savannah and Charleston to allow their ships to remain on station without returning North for resupply. The acquisition and c ...
... Confederate ports and smaller rivers and inlets. Du Pont’s November 1861 capture of Port Royal provided the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron a forward base situated between Savannah and Charleston to allow their ships to remain on station without returning North for resupply. The acquisition and c ...
Civil War Jeopardy
... African Americans fought in both Confederate and Union armies. The Confederacy often used slaves as naval crew members and soldiers. The Union moved to enlist African American sailors early in the war. African Americans soldiers were paid less that white soldiers. African American soldiers ...
... African Americans fought in both Confederate and Union armies. The Confederacy often used slaves as naval crew members and soldiers. The Union moved to enlist African American sailors early in the war. African Americans soldiers were paid less that white soldiers. African American soldiers ...
Guide to Civil War Intelligence - Association of Former Intelligence
... war, refugees, Southern newspapers, and documents retrieved from battlefield corpses. Sharpe’s spies counted tents to estimate troop numbers, approximate cannon numbers by the length of the artillery train, and counted guards at forts and ammunition dumps. In May 1863, with information from Sharpe’s ...
... war, refugees, Southern newspapers, and documents retrieved from battlefield corpses. Sharpe’s spies counted tents to estimate troop numbers, approximate cannon numbers by the length of the artillery train, and counted guards at forts and ammunition dumps. In May 1863, with information from Sharpe’s ...
Union Combined Operations in the Civil War (review)
... Unfortunately the early Union seacoast operations were designed simply to secure coastal enclaves for coaling, supply, and repair facilities to support the blockade of the Confederate coastline, itself the major Union naval effort of the war. As a result, the locations picked by the so-called Blocka ...
... Unfortunately the early Union seacoast operations were designed simply to secure coastal enclaves for coaling, supply, and repair facilities to support the blockade of the Confederate coastline, itself the major Union naval effort of the war. As a result, the locations picked by the so-called Blocka ...
President Abraham Lincoln, 1861-65
... • Republicans refused to admit any Tennessee, Arkansas, or Louisiana congressman from Congress because of these slave code laws in 1864 • 13th Amendment: “Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within ...
... • Republicans refused to admit any Tennessee, Arkansas, or Louisiana congressman from Congress because of these slave code laws in 1864 • 13th Amendment: “Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within ...
Civil War
... The Emancipa6on Proclama6on Ø September, 1862 – EmancipaJon ProclamaJon announced by Abraham Lincoln: • To take effect in 1863 (unless Southern states gave up rebellion against United States) • Seen, by Lincoln, as a necessary step to win the war • Slav ...
... The Emancipa6on Proclama6on Ø September, 1862 – EmancipaJon ProclamaJon announced by Abraham Lincoln: • To take effect in 1863 (unless Southern states gave up rebellion against United States) • Seen, by Lincoln, as a necessary step to win the war • Slav ...
The Home Front During the Civil War
... partisan companies, which often included former soldiers, were not usually formally attached to either army but sometimes worked with regular army units. Families with loved ones at the front were among the victims of guerilla violence. Petty disagreements often fueled the violence, and antagonisms ...
... partisan companies, which often included former soldiers, were not usually formally attached to either army but sometimes worked with regular army units. Families with loved ones at the front were among the victims of guerilla violence. Petty disagreements often fueled the violence, and antagonisms ...
Cornell Notes - Jessamine County Schools
... Chapter 20 Girding For War: The North and the South Brothers’ Blood and Border Blood pages 436-438 The slave states that remained in the Union – Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia after this pro-union portion of Virginia split and formed a new state – were the “crucial Border S ...
... Chapter 20 Girding For War: The North and the South Brothers’ Blood and Border Blood pages 436-438 The slave states that remained in the Union – Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia after this pro-union portion of Virginia split and formed a new state – were the “crucial Border S ...
Why did they fight article AP
... The Lincoln administration wrestled with the idea of authorizing the recruitment of black troops, concerned that such a move would prompt the border states to secede. When Gen. John C. Frémont (photo citation: 111-B-3756) in Missouri and Gen. David Hunter (photo citation: 111-B-3580) in South Caroli ...
... The Lincoln administration wrestled with the idea of authorizing the recruitment of black troops, concerned that such a move would prompt the border states to secede. When Gen. John C. Frémont (photo citation: 111-B-3756) in Missouri and Gen. David Hunter (photo citation: 111-B-3580) in South Caroli ...
Jubal Early

Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was a lawyer and Confederate general in the American Civil War. He served under Stonewall Jackson and then Robert E. Lee for almost the entire war, rising from regimental command to lieutenant general and the command of an infantry corps in the Army of Northern Virginia. He was the Confederate commander in key battles of the Valley Campaigns of 1864, including a daring raid to the outskirts of Washington, D.C. The articles written by him for the Southern Historical Society in the 1870s established the Lost Cause point of view as a long-lasting literary and cultural phenomenon.