Ohm`s Law 1
... 1. You are going to test the current passing through a set of resistors of different values. For the sake of efficiency, keep the resistors sorted and identified as you go along. Mount the resistors on a piece of paper by pushing the leads through. Decode the resistance value using the color code, a ...
... 1. You are going to test the current passing through a set of resistors of different values. For the sake of efficiency, keep the resistors sorted and identified as you go along. Mount the resistors on a piece of paper by pushing the leads through. Decode the resistance value using the color code, a ...
Chapter 16 Test Study Guide
... Resistance is measured in _______________________ and the symbol for this unit is _____________________. ...
... Resistance is measured in _______________________ and the symbol for this unit is _____________________. ...
Notes of Electricity - Sadhana Group of Institutions
... materials when rubbed on other materials. It was Gilbert who classified these materials under two headsVitreous and Resinous. They are named later as positive and negative charge. Fundamental laws of Electrostatics. a. There are two kinds of charges namely positive and negative. b. Like charges repe ...
... materials when rubbed on other materials. It was Gilbert who classified these materials under two headsVitreous and Resinous. They are named later as positive and negative charge. Fundamental laws of Electrostatics. a. There are two kinds of charges namely positive and negative. b. Like charges repe ...
How you should be thinking about electric circuits
... For an electron, the journey around a circuit is not a direct route. Rather, it is a zigzag path that results from countless collisions with fixed atoms within the conducting material. The electrons encounter resistance - a hindrance to their movement. ...
... For an electron, the journey around a circuit is not a direct route. Rather, it is a zigzag path that results from countless collisions with fixed atoms within the conducting material. The electrons encounter resistance - a hindrance to their movement. ...
Current and Resistance
... ◦ This means that there must be an electric field in the conductor. ◦ This implies a difference in potential since E=DV/d ◦ We assume that the difference in potential is small and that it can often be neglected. ◦ In this chapter, we will consider this difference and what causes it. ...
... ◦ This means that there must be an electric field in the conductor. ◦ This implies a difference in potential since E=DV/d ◦ We assume that the difference in potential is small and that it can often be neglected. ◦ In this chapter, we will consider this difference and what causes it. ...
Circuits PPT format
... Redraw the circuit – resistors in series and parallel Simplify – combine each set of series and parallel Find Req for the entire circuit Find I total – current though the battery Use Kirchoff’s Law to find other I values ...
... Redraw the circuit – resistors in series and parallel Simplify – combine each set of series and parallel Find Req for the entire circuit Find I total – current though the battery Use Kirchoff’s Law to find other I values ...
How is current electricity different from static electricity
... 12. How many amps can do damage to a person? 13. How much current runs through the wires of household circuits? 14. What safety devices are put in place in homes so the current in circuits are not overloaded and start fires? 15. A battery only makes current flow in one direction. What kind of curren ...
... 12. How many amps can do damage to a person? 13. How much current runs through the wires of household circuits? 14. What safety devices are put in place in homes so the current in circuits are not overloaded and start fires? 15. A battery only makes current flow in one direction. What kind of curren ...
Chapter 2
... • Kirchoff’s current law is based on conservation of charge • It states that the algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero. • It can be expressed as: ...
... • Kirchoff’s current law is based on conservation of charge • It states that the algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero. • It can be expressed as: ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... by using an instrument called Voltmeter. A voltmeter is connected so that it must be placed in parallel with the resister. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance so that no current will pass through it. To measure the current, the instrument is called ammeter. An ammeter is constructed so that i ...
... by using an instrument called Voltmeter. A voltmeter is connected so that it must be placed in parallel with the resister. An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance so that no current will pass through it. To measure the current, the instrument is called ammeter. An ammeter is constructed so that i ...
Chapter 2
... • Kirchoff’s current law is based on conservation of charge • It states that the algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero. • It can be expressed as: N ...
... • Kirchoff’s current law is based on conservation of charge • It states that the algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero. • It can be expressed as: N ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is ...
... The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is ...
Ohm`s Law I: Engineering Physics II
... Ohm’s Law is a rule stating that the ratio of voltage across a wire to the current flowing in it is constant as a function of applied voltage. The ratio V/I is called the electrical resistance of a material in ohms. Ohm’s Law applies to a broad range of materials and applied voltages, nevertheless, ...
... Ohm’s Law is a rule stating that the ratio of voltage across a wire to the current flowing in it is constant as a function of applied voltage. The ratio V/I is called the electrical resistance of a material in ohms. Ohm’s Law applies to a broad range of materials and applied voltages, nevertheless, ...
Lab E3
... 2) to determine the resistance of a light bulb and of a resistor, and 3) to determine if the light bulb and resistor obey Ohm’s Rule. The definition of the resistance of a material is: R = V/I where V is the voltage difference between two ends of the material and I is the current that the voltage ...
... 2) to determine the resistance of a light bulb and of a resistor, and 3) to determine if the light bulb and resistor obey Ohm’s Rule. The definition of the resistance of a material is: R = V/I where V is the voltage difference between two ends of the material and I is the current that the voltage ...
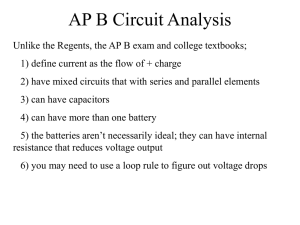
AP B Circuit Analysis
... AP B Circuit Analysis Unlike the Regents, the AP B exam and college textbooks; ...
... AP B Circuit Analysis Unlike the Regents, the AP B exam and college textbooks; ...
Study Guide for 2.3 to 2.6 Assessment: Section 2.3: Batteries
... Vocabulary- battery, wet cell, dry cell, electrode, electrolyte Concepts: Volta created the first battery by layering zinc with silver and paper soaked in salt water Luigi Galvani discovered “animal electricity” with his for leg experiment Label the parts of a wet cell (see notes) Section 2.4: ...
... Vocabulary- battery, wet cell, dry cell, electrode, electrolyte Concepts: Volta created the first battery by layering zinc with silver and paper soaked in salt water Luigi Galvani discovered “animal electricity” with his for leg experiment Label the parts of a wet cell (see notes) Section 2.4: ...