Electric Circuits EE316
... Use the above values and the measured value of Is to calculate different voltages by Ohm's law, and compare them with the values ...
... Use the above values and the measured value of Is to calculate different voltages by Ohm's law, and compare them with the values ...
1.3.3a DC Electrical methods All the EM methods are described
... Only two means are available for causing current to flow in the ground: in the first current is injected by means of a current source, a wire and two electrodes (Figure 1.3.3a) the sum of which is called an electric bipole. Since current is conserved the current in the ground is the same as the cur ...
... Only two means are available for causing current to flow in the ground: in the first current is injected by means of a current source, a wire and two electrodes (Figure 1.3.3a) the sum of which is called an electric bipole. Since current is conserved the current in the ground is the same as the cur ...
electricity and electronics
... The movement of electrons in a wire causes collisions and the increase of temperature of the wire. The heat produced by an electric current is called JOULE EFFECT. An example of application of this effect are RADIATORS and ...
... The movement of electrons in a wire causes collisions and the increase of temperature of the wire. The heat produced by an electric current is called JOULE EFFECT. An example of application of this effect are RADIATORS and ...
Quiz 16.2–AP–Simple Circuits w- multi battery loop
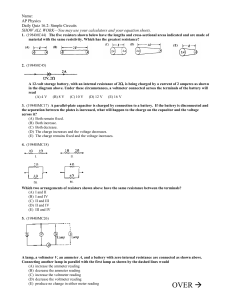
... SHOW ALL WORK—You may use your calculators and your equation sheets. 1. (1984MC44) The five resistors shown below have the lengths and cross-sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same resistivity. Which has the greatest resistance? ...
... SHOW ALL WORK—You may use your calculators and your equation sheets. 1. (1984MC44) The five resistors shown below have the lengths and cross-sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same resistivity. Which has the greatest resistance? ...
CHM 151
... conclusion of this course students should be able to: 1. Use Ohm’s law to determine voltage, current, or resistance. (2b) 2. Calculate power in a circuit. (2b) 3. Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law and Kirchhoff’s current law. (2b) 4. Use a series circuit as a voltage divider. (3a) 5. Analyze series-para ...
... conclusion of this course students should be able to: 1. Use Ohm’s law to determine voltage, current, or resistance. (2b) 2. Calculate power in a circuit. (2b) 3. Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law and Kirchhoff’s current law. (2b) 4. Use a series circuit as a voltage divider. (3a) 5. Analyze series-para ...
Basic Electricity for Computer Scientists
... Current can be carried by… Electrons moving from source to destination – as in a vacuum tube or CRT; Electrons moving railroad-car style, which means that an electron enters at one end, pushes all the other electrons along a short distance, and a different electron comes out at the other end – as in ...
... Current can be carried by… Electrons moving from source to destination – as in a vacuum tube or CRT; Electrons moving railroad-car style, which means that an electron enters at one end, pushes all the other electrons along a short distance, and a different electron comes out at the other end – as in ...
1 - School-Portal.co.uk
... If an object becomes highly charged then the potential difference between then object and the ground increases and the objects will discharge. When a charged object discharges (goes to ground) then a spark might occur. This is the electrons jumping from the object to the earthed conductor. ...
... If an object becomes highly charged then the potential difference between then object and the ground increases and the objects will discharge. When a charged object discharges (goes to ground) then a spark might occur. This is the electrons jumping from the object to the earthed conductor. ...
Условие - Reshaem
... 2. The plates of a variable capacitor can be moved. 3. The insulation resistance of any installation should be regularly controlled by means of measuring devices. 4. To make an electric current flow continuously along a wire, a continuous supply of electrons must be available at one end and a contin ...
... 2. The plates of a variable capacitor can be moved. 3. The insulation resistance of any installation should be regularly controlled by means of measuring devices. 4. To make an electric current flow continuously along a wire, a continuous supply of electrons must be available at one end and a contin ...
Solar Powered Phone Charger
... The objective of the project is to develop a Solar Charging Circuit to Charge a Cell Phone through Ni-Cd or Lead Acid Battery. The charge produced by the 12V Solar panel is fed to the 6V, 4.5Ah Rechargeable Battery through the Voltage Regulator LM 317. The charger has voltage and current regulation ...
... The objective of the project is to develop a Solar Charging Circuit to Charge a Cell Phone through Ni-Cd or Lead Acid Battery. The charge produced by the 12V Solar panel is fed to the 6V, 4.5Ah Rechargeable Battery through the Voltage Regulator LM 317. The charger has voltage and current regulation ...
Intro to Physics Lab
... connected in series, parallel, and series/parallel. You will be familiar with operation of an ohmmeter and learn how to hook-up electrical circuit. Equivalent Resistance Resistors can be connected in series or in parallel in electric circuits. When resistors are connected in series, they share the s ...
... connected in series, parallel, and series/parallel. You will be familiar with operation of an ohmmeter and learn how to hook-up electrical circuit. Equivalent Resistance Resistors can be connected in series or in parallel in electric circuits. When resistors are connected in series, they share the s ...
Lecture 5
... the conductor. When currents flow through two parallel conductors in the same direction, the magnetic fields cause the conductors to attract each other; when the flows are in opposite directions, they repel each other. The magnetic field caused by the current in a single loop or wire is such that t ...
... the conductor. When currents flow through two parallel conductors in the same direction, the magnetic fields cause the conductors to attract each other; when the flows are in opposite directions, they repel each other. The magnetic field caused by the current in a single loop or wire is such that t ...
Lecture 36
... I0 is called the reverse saturation current. It sets the overall scale for the I-V characteristic, and –I0 is the observed current once the reverse bias voltage exceeds a small fraction of a volt. Reverse bias raises the barrier and suppresses the diffusion current, so the –I0 is entirely due to the ...
... I0 is called the reverse saturation current. It sets the overall scale for the I-V characteristic, and –I0 is the observed current once the reverse bias voltage exceeds a small fraction of a volt. Reverse bias raises the barrier and suppresses the diffusion current, so the –I0 is entirely due to the ...
Electric current
... difference in (electric) potential is required. Simon Ohm (1787-1854) Experimentally determined that I V Exactly how much current flows depends on voltage and resistance to the flow of electrons Resistance How much a conductor impedes the flow of electrons Unit: ohm () ...
... difference in (electric) potential is required. Simon Ohm (1787-1854) Experimentally determined that I V Exactly how much current flows depends on voltage and resistance to the flow of electrons Resistance How much a conductor impedes the flow of electrons Unit: ohm () ...
hw05
... Slight differences will be obtained in the final answer depending on the branch used, due to rounding. For example, using the bottom branch, we get the following. Vad Vd Va E1 I 2 21 80 V 2.58 A 21 25.8 V (b) For the 80-V battery, the terminal voltage is the potential di ...
... Slight differences will be obtained in the final answer depending on the branch used, due to rounding. For example, using the bottom branch, we get the following. Vad Vd Va E1 I 2 21 80 V 2.58 A 21 25.8 V (b) For the 80-V battery, the terminal voltage is the potential di ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
Voltage in Electrical Systems
... Define electric potential, or voltage. Differentiate between AC and DC. Identify the most common source of DC voltage. Describe how to connect DC voltage sources so that ...
... Define electric potential, or voltage. Differentiate between AC and DC. Identify the most common source of DC voltage. Describe how to connect DC voltage sources so that ...