EE302 Lesson 1: Introduction
... This positive region created by separating the free electron from the basic atomic structure is called a positive ion. In general, every source of voltage is established by simply creating a separation of positive and negative ...
... This positive region created by separating the free electron from the basic atomic structure is called a positive ion. In general, every source of voltage is established by simply creating a separation of positive and negative ...
Ohm`s Law
... component and the SI unit of resistance, ohm, is defined as one volt per ampere (1Ω=1V/A). It is important to understand that the real content of Ohm's Law is the direct linear proportionality of V to I. One has to note that equation [1] defines resistance R for any conductor, whether it obeys Ohm's ...
... component and the SI unit of resistance, ohm, is defined as one volt per ampere (1Ω=1V/A). It is important to understand that the real content of Ohm's Law is the direct linear proportionality of V to I. One has to note that equation [1] defines resistance R for any conductor, whether it obeys Ohm's ...
examination of marine engineer officer
... 1. A single-phase transformer has 1000 turns on the primary and 200 turns on the secondary. The no load current is 3A at 0.2 power factor lag when the secondary current is 280A at a power factor of 0.8 lagging. Assume the voltage drop in the winding to be negligible. Find the current taken by the pr ...
... 1. A single-phase transformer has 1000 turns on the primary and 200 turns on the secondary. The no load current is 3A at 0.2 power factor lag when the secondary current is 280A at a power factor of 0.8 lagging. Assume the voltage drop in the winding to be negligible. Find the current taken by the pr ...
EECS 215: Introduction to Circuits
... connecting two metals with different thermal conductivities, relative to a reference temperature T1. • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circuit that generates a voltage equal to that expected from a reference j ...
... connecting two metals with different thermal conductivities, relative to a reference temperature T1. • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circuit that generates a voltage equal to that expected from a reference j ...
Data Sheet 1
... o This data sheet is applied for Block Type EMIFILr used for General Electronics equipment for your design. ...
... o This data sheet is applied for Block Type EMIFILr used for General Electronics equipment for your design. ...
Electric Current - bridgingthegap09
... Supplies energy to an electric circuit When positive and negative terminals are connected in a circuit, the electric potential energy is increased Supplies energy by converting chemical energy to electric potential energy ...
... Supplies energy to an electric circuit When positive and negative terminals are connected in a circuit, the electric potential energy is increased Supplies energy by converting chemical energy to electric potential energy ...
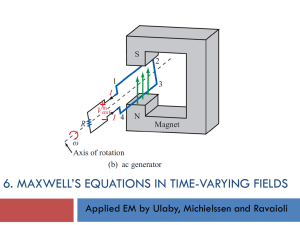
Electro-magnetic flow meters
... Postscript: Time to wave goodbye It was deduced in 1862 by James Clerk Maxwell that the converse happens: that a changing E-field produces a magnetic field. Put the two together, that a change in one gives the other and vice-versa, and you might wonder where it all ends. In fact it ends with a dance ...
... Postscript: Time to wave goodbye It was deduced in 1862 by James Clerk Maxwell that the converse happens: that a changing E-field produces a magnetic field. Put the two together, that a change in one gives the other and vice-versa, and you might wonder where it all ends. In fact it ends with a dance ...
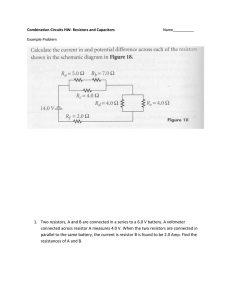
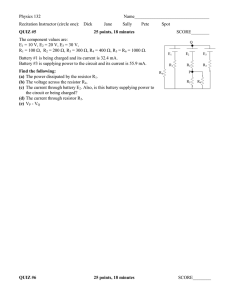
Loop Currents [pdf]
... currents. Recall the two physical laws that are introduced in Section 1.10: Ohm's Law: The voltage drop across a resistor is V=RI, where the voltage drop V is measured in volts, the resistance R is measured in ohms, and the current flow I is measured in amperes. Kirchoff's Voltage Law: The algebraic ...
... currents. Recall the two physical laws that are introduced in Section 1.10: Ohm's Law: The voltage drop across a resistor is V=RI, where the voltage drop V is measured in volts, the resistance R is measured in ohms, and the current flow I is measured in amperes. Kirchoff's Voltage Law: The algebraic ...
Basic definitions
... its energy. Some of the energy is converted into heat every time it is transferred. The voltage will drop as the energy is transferred over long distances. Thus a long wire has a higher resistance than a short wire. ...
... its energy. Some of the energy is converted into heat every time it is transferred. The voltage will drop as the energy is transferred over long distances. Thus a long wire has a higher resistance than a short wire. ...
Risistor
... A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an ...
... A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an ...
Powerpoint
... material, L is the wire length, and A its cross-sectional area. This makes sense: a longer wire or higher-resistivity wire should have a greater resistance. A larger area means more “space” for electrons to get through, hence lower resistance. ...
... material, L is the wire length, and A its cross-sectional area. This makes sense: a longer wire or higher-resistivity wire should have a greater resistance. A larger area means more “space” for electrons to get through, hence lower resistance. ...
Electric Charge How does an object get a charge (must gain or lose
... Define VOLTAGE: (potential difference) The difference in energy per unit of charge between one point in the circuit and another point in the circuit (this causes the PUSH or FORCE to get electrons moving). Voltage is also referred to as POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE (two words). What is the SYMBOL for voltag ...
... Define VOLTAGE: (potential difference) The difference in energy per unit of charge between one point in the circuit and another point in the circuit (this causes the PUSH or FORCE to get electrons moving). Voltage is also referred to as POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE (two words). What is the SYMBOL for voltag ...
Sc9 - D 2.3 (teacher notes)
... The same voltage is applied to parallel devices, different voltages to series devices. If the series portion is broken, current stops flowing in the entire circuit. If a parallel branch is broken, current continues flowing in the series portion and the remaining ...
... The same voltage is applied to parallel devices, different voltages to series devices. If the series portion is broken, current stops flowing in the entire circuit. If a parallel branch is broken, current continues flowing in the series portion and the remaining ...
ppt_ch03
... Multiply by hours: (Assume it runs half the day) energy = 4.8 kW × 12 hours = 57.6 kWh Multiply by rate: (Assume a rate of $0.08/ kWh) cost = 57.6 × $0.08 = $4.61 per day ...
... Multiply by hours: (Assume it runs half the day) energy = 4.8 kW × 12 hours = 57.6 kWh Multiply by rate: (Assume a rate of $0.08/ kWh) cost = 57.6 × $0.08 = $4.61 per day ...
Chapter 26
... an E-field electrons move randomly with no net motion random speeds 106 m/s Drift Speed Vd : in the presence of an E-field electrons move randomly with net motion in the direction opposite to E field Drift speeds 10-5 - 10-4 m/s ...
... an E-field electrons move randomly with no net motion random speeds 106 m/s Drift Speed Vd : in the presence of an E-field electrons move randomly with net motion in the direction opposite to E field Drift speeds 10-5 - 10-4 m/s ...
SNC1P - MsKhan
... In a series circuit, loads are connected so that there is only ___________ path for electrons to flow. In a parallel circuit, loads are connected so that there are ___________ or more paths for electrons to flow. **Do questions #1,2,4,5 on page 554** 13.3 - Electric Current Electric current (I) is t ...
... In a series circuit, loads are connected so that there is only ___________ path for electrons to flow. In a parallel circuit, loads are connected so that there are ___________ or more paths for electrons to flow. **Do questions #1,2,4,5 on page 554** 13.3 - Electric Current Electric current (I) is t ...
What is a Thyristor Surge Protective Device?
... on-state, then on to restoration. Minimum holding current values typically range from 50mA to 250mA @ 25oC (depending on device surge current rating) and decrease by 60% at 100oC, so ambient temperatures must be considered in selecting a device. This feature may limit use for some applications. TSPD ...
... on-state, then on to restoration. Minimum holding current values typically range from 50mA to 250mA @ 25oC (depending on device surge current rating) and decrease by 60% at 100oC, so ambient temperatures must be considered in selecting a device. This feature may limit use for some applications. TSPD ...






![Loop Currents [pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008842970_1-01a5ba3b42e0c1c0e0ac30ac3785fc89-300x300.png)