Chapter 18: Electric Current and Circuits
... While the capacitor is charging S2 is open. After the capacitor is fully charged S1 is opened at the same time S2 is closed: this removes the battery from the circuit. Current will now flow in the right hand loop only, discharging the capacitor. ...
... While the capacitor is charging S2 is open. After the capacitor is fully charged S1 is opened at the same time S2 is closed: this removes the battery from the circuit. Current will now flow in the right hand loop only, discharging the capacitor. ...
Download T3100 Datasheet
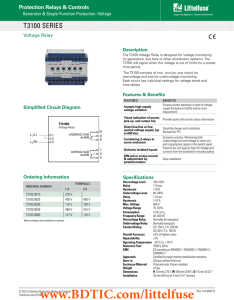
... on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3100 will signal when the voltage is out of limits for a preset time period. The T3100 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage monitoring. Each circuit has individual settings for voltage levels and ti ...
... on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3100 will signal when the voltage is out of limits for a preset time period. The T3100 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage monitoring. Each circuit has individual settings for voltage levels and ti ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... In this problem a resistor circuit is given, and we want to determine the z parameters of this two-port circuit. Firstly, let’s label the terminal variables. For port 1, we have voltage variable V1 and current variable I1. For port 2, we have V2 and I2. We can use two equations to relate the four va ...
... In this problem a resistor circuit is given, and we want to determine the z parameters of this two-port circuit. Firstly, let’s label the terminal variables. For port 1, we have voltage variable V1 and current variable I1. For port 2, we have V2 and I2. We can use two equations to relate the four va ...
File
... When a wire is doubled on it, its length would become half and area of cross-section would double. T So, a wire of length l and area of cross-section A becomes of length l/2 And area of cross section 2A. we have R = ρ(l/A) R1 = ρ((l/A) / 2A) where R1 is the new resistance. Therefore, R1/R = ρ((l/A)/ ...
... When a wire is doubled on it, its length would become half and area of cross-section would double. T So, a wire of length l and area of cross-section A becomes of length l/2 And area of cross section 2A. we have R = ρ(l/A) R1 = ρ((l/A) / 2A) where R1 is the new resistance. Therefore, R1/R = ρ((l/A)/ ...
اﻟﻔﯾزﯾﺎء ( ﺑﺎﻟﻟﻐﺔ اﻻﻧﺟﻟﯾزﯾﺔ
... 1) The number of bonds broken per second will be equal to the number of bonds mended per second in a semiconductor crystal. 2) The scale deflection per unit current intensity passing through the galvanometer coil. 3) The value of the direct current that generates the same rate of thermal effect in a ...
... 1) The number of bonds broken per second will be equal to the number of bonds mended per second in a semiconductor crystal. 2) The scale deflection per unit current intensity passing through the galvanometer coil. 3) The value of the direct current that generates the same rate of thermal effect in a ...
Chapter 18: Electric Current and Circuits
... While the capacitor is charging S2 is open. After the capacitor is fully charged S1 is opened at the same time S2 is closed: this removes the battery from the circuit. Current will now flow in the right hand loop only, discharging the capacitor. ...
... While the capacitor is charging S2 is open. After the capacitor is fully charged S1 is opened at the same time S2 is closed: this removes the battery from the circuit. Current will now flow in the right hand loop only, discharging the capacitor. ...
12.1 Electricity at Home (Pages 485
... • Electrical energy is always generated from another source of energy. • In direct current, charged particles travel through a circuit in only one direction. In alternating current, electrons move back and forth in a circuit. • Alternating current is generated when a magnet and a coil of wire are mo ...
... • Electrical energy is always generated from another source of energy. • In direct current, charged particles travel through a circuit in only one direction. In alternating current, electrons move back and forth in a circuit. • Alternating current is generated when a magnet and a coil of wire are mo ...
EE 4BD4 Lecture 28
... • (1) Use a DC-DC converter to give high voltage source to drive circuit Fig 3.8 slide 21 • (2) Replace load in Fig 3.8 by the input coil of a pulse transformer • If output current to electrodes is to be e.g. 40 ma, the input current must be 480 ma if transformer ratio is 1:12 • May then replace tra ...
... • (1) Use a DC-DC converter to give high voltage source to drive circuit Fig 3.8 slide 21 • (2) Replace load in Fig 3.8 by the input coil of a pulse transformer • If output current to electrodes is to be e.g. 40 ma, the input current must be 480 ma if transformer ratio is 1:12 • May then replace tra ...
V - UW Canvas
... The potential drop across each resistor is the same as that across a single equivalent resistor. The total current is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor. In general, for n resistors in parallel, the equivalent resistance can be calculated with ...
... The potential drop across each resistor is the same as that across a single equivalent resistor. The total current is equal to the sum of the current through each resistor. In general, for n resistors in parallel, the equivalent resistance can be calculated with ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... A. Series Circuit 1) definition 2) voltage drop 3) current flow 4) total resistance B. Parallel Circuit 1) definition 2) electrical chrematistics a) voltage b) current 3) resistance a) equal resistors b) two resistors c) unequal resistors C. Series-Parallel circuits 1) ...
... A. Series Circuit 1) definition 2) voltage drop 3) current flow 4) total resistance B. Parallel Circuit 1) definition 2) electrical chrematistics a) voltage b) current 3) resistance a) equal resistors b) two resistors c) unequal resistors C. Series-Parallel circuits 1) ...
electric circuit
... The Ss analyze and summarize the results of your experiment, they list any questions you still have about your experiment and they describe what they have learned about electric circuits from the worksheets. ...
... The Ss analyze and summarize the results of your experiment, they list any questions you still have about your experiment and they describe what they have learned about electric circuits from the worksheets. ...
Effects of electric and domestic circuits
... In region OA the positive ions in the tube are attracted to the negative electrode and the electrons move towards the positive electrode once a p.d. is applied, as number of ions crossing the tube increases so does the current. In region AB all the ions in the tube cross without recombination so no ...
... In region OA the positive ions in the tube are attracted to the negative electrode and the electrons move towards the positive electrode once a p.d. is applied, as number of ions crossing the tube increases so does the current. In region AB all the ions in the tube cross without recombination so no ...
MATHEMATICS
... Fluids: pressure, hydrostatics, Euler and Lagrange variables of a continuum, continuity equation, Euler equation of motion. Thermodynamics: first law, internal energy, work, heat. Reversible and irreversible processes, second law, Carnot cycles. Equations of state, change of phase, ideal gases, chem ...
... Fluids: pressure, hydrostatics, Euler and Lagrange variables of a continuum, continuity equation, Euler equation of motion. Thermodynamics: first law, internal energy, work, heat. Reversible and irreversible processes, second law, Carnot cycles. Equations of state, change of phase, ideal gases, chem ...
Grade 9 Academic Science – Unit 4 Electricity
... Draw a circuit diagram with five lights in series. The Potential Difference (i.e., total voltage) in the circuit is 120 V. The total resistance (R) of the lights is 40 (Recall: = ohms). What is the current through each lamp? HINT: Use Ohm’s Law formula I = V/R Voltage across a Load in Series ...
... Draw a circuit diagram with five lights in series. The Potential Difference (i.e., total voltage) in the circuit is 120 V. The total resistance (R) of the lights is 40 (Recall: = ohms). What is the current through each lamp? HINT: Use Ohm’s Law formula I = V/R Voltage across a Load in Series ...
Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t) - Rose
... Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t). The capacitor is fully discharged at time 0. We want to find the ideal op amp’s output voltage. For ideal op amp, the voltages of the input terminals are equal. The inverted terminal is grounded, so it’s at 0 V. This means that the non-invertin ...
... Here the input voltage to the circuit is given by v(t). The capacitor is fully discharged at time 0. We want to find the ideal op amp’s output voltage. For ideal op amp, the voltages of the input terminals are equal. The inverted terminal is grounded, so it’s at 0 V. This means that the non-invertin ...
muddiest points Week 1
... in a circuit when they hit a resistance and how this produces the difference in potential (voltage) across the component. I thought the electrons were slowed or "held up" by the resistance, but in this case how is the current the same (in series) after the component slows the electrons? The internet ...
... in a circuit when they hit a resistance and how this produces the difference in potential (voltage) across the component. I thought the electrons were slowed or "held up" by the resistance, but in this case how is the current the same (in series) after the component slows the electrons? The internet ...
Charging System
... A sign of a bad charging system is when the headlight blinks or strobes at idle or when there is a marked increase in headlight intensity when you gun the motor. All bikes show some increase in headlight intensity with higher RPM’s but if it goes from dim to bright it is probably the charging system ...
... A sign of a bad charging system is when the headlight blinks or strobes at idle or when there is a marked increase in headlight intensity when you gun the motor. All bikes show some increase in headlight intensity with higher RPM’s but if it goes from dim to bright it is probably the charging system ...