Electricity Notes I
... • To keep an electric current continually flowing in the electric circuit a voltage difference needs to be maintained in the circuit. • A battery can provide the voltage difference that is needed to keep current flowing in a circuit. • Current flows as long as there is a closed path that connects on ...
... • To keep an electric current continually flowing in the electric circuit a voltage difference needs to be maintained in the circuit. • A battery can provide the voltage difference that is needed to keep current flowing in a circuit. • Current flows as long as there is a closed path that connects on ...
C7802 Ohms Law 2005_newer
... Voltage is the force or electric pressure that allows current flow. It is measured in volts. The letter “V” (or sometimes “E”) is used to represent voltage. Resistance is the opposition to current flow. It is measured in ohms (Ω). The letter “R” is used to represent resistance. Current (I), voltage ...
... Voltage is the force or electric pressure that allows current flow. It is measured in volts. The letter “V” (or sometimes “E”) is used to represent voltage. Resistance is the opposition to current flow. It is measured in ohms (Ω). The letter “R” is used to represent resistance. Current (I), voltage ...
CSCI 2980: Introduction to Circuits, CAD, and Instrumentation
... A point of connection of two or more circuit elements. A node is one end of a circuit element together with all the perfect conductor that are attached to it. ...
... A point of connection of two or more circuit elements. A node is one end of a circuit element together with all the perfect conductor that are attached to it. ...
G:\respcare\gen_care
... where lines are attached there is a potential for current leakage. This leakage should flow down to the ground but if the patient is attached, he becomes the ground so that the current moves though him. o. Ampere: units of current p. “Macroshock”: a high current applied to the skin such as happens w ...
... where lines are attached there is a potential for current leakage. This leakage should flow down to the ground but if the patient is attached, he becomes the ground so that the current moves though him. o. Ampere: units of current p. “Macroshock”: a high current applied to the skin such as happens w ...
Document
... _____ 6. When electric current changes direction it is called a(n) a. generated current. c. alternating current. b. electromagnetic current. d. rotating current. 7. Name the four parts of a simple generator, and describe what they do. _______________________________________________________________ _ ...
... _____ 6. When electric current changes direction it is called a(n) a. generated current. c. alternating current. b. electromagnetic current. d. rotating current. 7. Name the four parts of a simple generator, and describe what they do. _______________________________________________________________ _ ...
Proportion of Voltage to Resistance in a Series Circuit
... A series circuit is shown in the diagram above. V represents the total voltage and I represents the current. The three sets of jagged lines represent resistors with resistances represented by the variables R1, R2 and R3. Resistance is measured in ohms, represented by the symbol Ω. ...
... A series circuit is shown in the diagram above. V represents the total voltage and I represents the current. The three sets of jagged lines represent resistors with resistances represented by the variables R1, R2 and R3. Resistance is measured in ohms, represented by the symbol Ω. ...
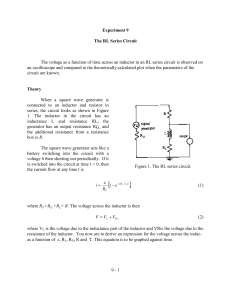
Theory
... 6) Now adjust the sweep speed on the oscilloscope (also the horizontal. magnification, if necessary) until only the first half of the trace shown in Figure 2 fills the screen. The horizontal adjustments, except for calibration, can be changed at will; however, do not change the vertical settings. 7 ...
... 6) Now adjust the sweep speed on the oscilloscope (also the horizontal. magnification, if necessary) until only the first half of the trace shown in Figure 2 fills the screen. The horizontal adjustments, except for calibration, can be changed at will; however, do not change the vertical settings. 7 ...
Chapter 16
... 2Which of the following statements about electricity is true? A. Electrical current Is not “live” until current flows. B. Electrical current flows only when there is a complete loop, out from and back to the power source. C. Electrical current always returns to its source. D. All of the above. ...
... 2Which of the following statements about electricity is true? A. Electrical current Is not “live” until current flows. B. Electrical current flows only when there is a complete loop, out from and back to the power source. C. Electrical current always returns to its source. D. All of the above. ...
Resistors Connected in Series and in Parallel
... How are resistances R2 and R3 connected in the resistance network shown at the right? They are not connected in series, because the current through R2 is not necessarily the current through R3 (why?) R2 and R3 are connected in parallel because the potential drop across R3 is the same as the potentia ...
... How are resistances R2 and R3 connected in the resistance network shown at the right? They are not connected in series, because the current through R2 is not necessarily the current through R3 (why?) R2 and R3 are connected in parallel because the potential drop across R3 is the same as the potentia ...
PHY-1020 Exam 3 Spring/Summer 2006
... a. is larger than the shorter wire. b. is smaller than the shorter wire. c. is the same as the shorter wire. d. could be more or less depending on the composition. e. could be more or less depending on the temperature. 10. Electromagnetic waves are created by a. electric charge at rest. b. magnets. ...
... a. is larger than the shorter wire. b. is smaller than the shorter wire. c. is the same as the shorter wire. d. could be more or less depending on the composition. e. could be more or less depending on the temperature. 10. Electromagnetic waves are created by a. electric charge at rest. b. magnets. ...
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
... They do not allow a single building system to be easily split into multiple sections with independent fault protection, because earthing systems are usually use common earth Rod. • As electrically leaky appliances such as some water heaters, washing machines and cookers may cause the ELCB to trip. ...
... They do not allow a single building system to be easily split into multiple sections with independent fault protection, because earthing systems are usually use common earth Rod. • As electrically leaky appliances such as some water heaters, washing machines and cookers may cause the ELCB to trip. ...
PPT - School of Engineering and Applied Science
... • Decreased supply voltage: As supply voltage is reduced, the charge stored will be small. With larger subthreshold leakage current, coupling noise etc is will be a challenge to get circuits to operate properly. • Increased role of wiring resistance, inductance and capacitance. ...
... • Decreased supply voltage: As supply voltage is reduced, the charge stored will be small. With larger subthreshold leakage current, coupling noise etc is will be a challenge to get circuits to operate properly. • Increased role of wiring resistance, inductance and capacitance. ...