* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
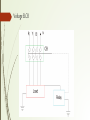
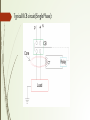
By: 47.M.B.J.Varma 48.Mallikarjuna Abhilash 49.Maraka Kulateja 50.Prajakta Mategadikar 51.Medepalli Nikhil Raj An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is a device used to directly detect currents leaking to earth from an installation with high earth impedance to prevent shock. HISTORY Voltage ELCBs were first introduced about sixty years ago and current ELCB was first introduced about forty years ago. For many years, the voltage operated ELCB and the differential current operated ELCB were both referred to as ELCBs because it was a simpler name to remember. IEC decided to apply the term residual current device (RCD) to differential-current-operated ELCBs. Residual current refers to any current over and above the load current. ELCB Manufacturers: Legrand Havells ABB (ASEA Brown Boveri) Crabtree Siemens AG Schneider Electric Vguard The main purpose of Earth leakage protectors is to prevent injury to humans and animals due to electric shock. ELCBs were mainly used on TT earthing systems. 1. Voltage ELCB 2. Current ELCB Voltage ELCB: One terminal of the relay coil is connected to the metal body of the equipment to be protected against earth leakage and other terminal is connected to the earth directly. If any insulation failure occurs or live phase wire touches the metal body, of the equipment, there must be a voltage difference appears across the terminal of the coil connected to the equipment body and earth. This voltage difference produces a current to flow the relay coil. If the voltage difference crosses, a predetermined limit(gnerally 50V), the current through the relay becomes sufficient to actuate the relay for tripping the associated circuit breaker to disconnect the power supply to the equipment Voltage ELCB Voltage ELCB Advantages: Less sensitive to faulty conditions. Nuisance tripping especially during thunder storms(When an installation has two connections to earth, a nearby high current lightning strike will cause a voltage gradient in the soil, presenting the ELCB sense coil with enough voltage to cause it to trip). If the installation’s earth rod is placed close to the earth rod of a neighboring building, a high earth leakage current in the other building can raise the local ground potential and cause a voltage difference across the two earths, again tripping the ELCB. Voltage ELCB Disadvantages: They do not allow a single building system to be easily split into multiple sections with independent fault protection, because earthing systems are usually use common earth Rod. • As electrically leaky appliances such as some water heaters, washing machines and cookers may cause the ELCB to trip. • They do not detect faults that don’t pass current through the CPC to the earth rod. What is the use of TEST button on ELCB? The test facility provided on the home ELCB will only confirm the health of the ELCB unit That test facility does not confirm that the ELCB will trip when an electric shock hazard does occur. Current ELCB: Current-operated ELCBs are generally known as Residual-current devices (RCD). These also protect against earth leakage. Both circuit conductors (supply and return) are run through a sensing coil; any imbalance of the currents means the magnetic field does not perfectly cancel. The device detects the imbalance and trips the contact. When the term ELCB is used it usually means a voltage-operated device. Similar devices that are current operated are called residual-current devices. RCCB is more sensitive than ELCB. Typical RCB circuit(Single Phase): Current ELCB Working: The polarity of the phase winding and neutral winding on the core is so chosen that, in normal condition mmf of one winding opposes that of another. As it is assumed that, in normal operating conditions the current goes through the phase wire will be returned via neutral wire if there's no leakage in between. As both currents are same, the resultant mmf produced by these two currents is also zero-ideally. The relay coil is connected with another third winding wound on the CT core as secondary. The terminals of this winding are connected to a relay system. Current ELCB Working: In normal operating condition there would not be any current circulating in the third winding as here is no flux in the core due to equal phase and neutral current. When any earth leakage occurs in the equipment, there may be part of phase current passes to the earth, through the leakage path instead of returning via mental wire. Hence the magnitude of the neutral current passing through the RCCB is not equal to phase current passing through it. Typical RCB circuit(Three Phase): This relay causes tripping of the associated circuit breaker to disconnect the power supply to the equipment under protection Residual current circuit breaker is sometimes also referred as residual current device (RCD) when we consider the device by disassociating the circuit breaker attached to RCCB. The entire parts of RCCB except circuit breaker are referred as RCD. Sensitivity of RCB: Medium sensitivity (MS): 100- 300- 500- 1000 mA (for fire protection) Low sensitivity (LS): 3- 10- 30 A (typically for protection of machine) Break time of RCB: G (general use) for instantaneous RCDs (i.e. without a time delay) Minimum break time: immediate Maximum break time: 200 ms for 1x IΔn S (selective) or T (time delayed) for RCDs with a short time delay (typically used in circuits containing surge suppressors) Minimum break time: 130 ms for 1x IΔn Maximum break time: 500 ms for 1x IΔn No JOLT From VOLT Almost 12 people die due to electrocution every day(Source-NCRB) -42% of total fires occur due to electrical sources(Source-OISD) -8% deaths that occur in factories are due to electricity. - At present to prevent electrical shock three wire system with protective multiple earthing is used. Installation of ELCB ELCB needs effective earth to trip the power else require a secondary path for current to unbalance in ELCB to operate and protect. ELCB should be tested once in a month for a better protection. Earth Loop Voltage Detector: Generally called as ELVD An intelligent sensor in the ELVD senses and compares the voltage of the neutral and the earth terminals (Body) of the appliance. If the voltage level or fault signal exceeds 75V, a positive signal is sent to the circuit breaker to cut the power only to the faulty appliance. All other lights and electrical appliances in the home continue to function normally. All that needs to be done to restore power to the appliance is to restart it after rectifying the fault in the appliance. ELVD is far more better than conventional circuit breakers which has delayed reaction presenting hazard. The operating time of ELCB is <40 milliseconds where as of ELVD is <10 milliseconds Until the fault in the appliance has been fixed, the ELVD will not allow the device to be powered.