3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES – SAFETY MOMENT
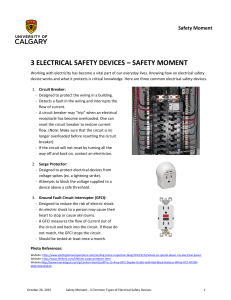
... Working with electricity has become a vital part of our everyday lives. Knowing how an electrical safety device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in ...
... Working with electricity has become a vital part of our everyday lives. Knowing how an electrical safety device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in ...
Chapter 11 - Test Study Guide
... http://zion.redemptivehistory.org/6grade (Use the online study guides to help you review!) ...
... http://zion.redemptivehistory.org/6grade (Use the online study guides to help you review!) ...
Part - Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering
... 9. What is Brewster angle? 10. What is the skin effect? 11. What is slepian vector? Part –B Unit-I 1. State and explain Coulomb’s law and the equation of force b/w two point charges indicating clearly the units of the quantities in the equation of force (10) 2. Derive an expression for the electric ...
... 9. What is Brewster angle? 10. What is the skin effect? 11. What is slepian vector? Part –B Unit-I 1. State and explain Coulomb’s law and the equation of force b/w two point charges indicating clearly the units of the quantities in the equation of force (10) 2. Derive an expression for the electric ...
VU Meter Me
... There are 2 trimmer potentiometers that you can use to calibrate how much volume you want reflected in your VU meter. By adjusting these with a normal Phillips screwdriver, you can change where the light starts and how many lights are lit up as the volume changes + and – in the middle of the board i ...
... There are 2 trimmer potentiometers that you can use to calibrate how much volume you want reflected in your VU meter. By adjusting these with a normal Phillips screwdriver, you can change where the light starts and how many lights are lit up as the volume changes + and – in the middle of the board i ...
Ohm`s Law
... Exercises – Ohm’s Law Given a circuit with a power source V = 9V,find the loop current if the resistance is 100 Ohm ...
... Exercises – Ohm’s Law Given a circuit with a power source V = 9V,find the loop current if the resistance is 100 Ohm ...
File
... 3. The total voltage lost on the three resistors would be 6.0 V. 4. (a) Increases (b) Decreases 5. The voltage is the same on both of the resistors. TR 3-50 MHR • Characteristics of Electricity 6. (a) The total current leaving the junction point must equal the current entering the junction point. (b ...
... 3. The total voltage lost on the three resistors would be 6.0 V. 4. (a) Increases (b) Decreases 5. The voltage is the same on both of the resistors. TR 3-50 MHR • Characteristics of Electricity 6. (a) The total current leaving the junction point must equal the current entering the junction point. (b ...
CircuitI_exp111411499998
... 3- Write down the time functions (instantaneous representation) for the voltages and currents in Table 3. 4- Draw the phasor diagram, showing all the voltages and currents, based on the experimental values. 5- Discuss the sources of discrepancies between the theoretical and experimental values. ...
... 3- Write down the time functions (instantaneous representation) for the voltages and currents in Table 3. 4- Draw the phasor diagram, showing all the voltages and currents, based on the experimental values. 5- Discuss the sources of discrepancies between the theoretical and experimental values. ...
CT VT CVT
... • Since CT normally has much more turns in secondary compared to the primary, the voltage generated on the open-circuited CT will be much more than the system volts,leading to flashovers. ...
... • Since CT normally has much more turns in secondary compared to the primary, the voltage generated on the open-circuited CT will be much more than the system volts,leading to flashovers. ...
Resistivity of various materials
... • In an isolated conductor, charge carriers move randomly in all directions. • When an external potential is applied across the conductor, it creates an electric field inside which produces a force on the electron. • Electrons however still have quite a random path. • As they travel through the mate ...
... • In an isolated conductor, charge carriers move randomly in all directions. • When an external potential is applied across the conductor, it creates an electric field inside which produces a force on the electron. • Electrons however still have quite a random path. • As they travel through the mate ...
EGN 3373 Week 4 – Caps and Ind Explained - Help-A-Bull
... Capacitors in parallel Capacitors in a parallel configuration each have the same applied voltage. Their capacitances are added. Charge is apportioned among them by size. ...
... Capacitors in parallel Capacitors in a parallel configuration each have the same applied voltage. Their capacitances are added. Charge is apportioned among them by size. ...
Tap 416-5: Transformers - Teaching Advanced Physics
... would you expect between VpIp and VsIs? What would this predict for the ratio Ip/Is? Comment on how closely your values match these ‘ideal’ predictions, and explain any discrepancies. ...
... would you expect between VpIp and VsIs? What would this predict for the ratio Ip/Is? Comment on how closely your values match these ‘ideal’ predictions, and explain any discrepancies. ...
Nodal Analysis
... 2. Label the voltage at the other nodes 3. Label the currents flowing through each of the components in the circuit 4. Use Kirchoff’s Current Law 5. Use Ohm’s Law to relate the voltages at each node to the currents flowing in and out of them. 6. Solve for the node voltage 7. Once the node voltages a ...
... 2. Label the voltage at the other nodes 3. Label the currents flowing through each of the components in the circuit 4. Use Kirchoff’s Current Law 5. Use Ohm’s Law to relate the voltages at each node to the currents flowing in and out of them. 6. Solve for the node voltage 7. Once the node voltages a ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... • The flow of electricity around a circuit is called CURRENT and runs from negative to positive Current is the amount of electrons passing a given point in one second I want you to come up with an analogy for Current (some real life example which is similar, e.g. An analogy for the Heart is a pum ...
... • The flow of electricity around a circuit is called CURRENT and runs from negative to positive Current is the amount of electrons passing a given point in one second I want you to come up with an analogy for Current (some real life example which is similar, e.g. An analogy for the Heart is a pum ...
File
... • The flow of electricity around a circuit is called CURRENT and runs from negative to positive. Current is the amount of electrons passing a given point in one second. I want you to come up with an analogy for Current (some real life example which is similar, e.g. An analogy for the Heart is a p ...
... • The flow of electricity around a circuit is called CURRENT and runs from negative to positive. Current is the amount of electrons passing a given point in one second. I want you to come up with an analogy for Current (some real life example which is similar, e.g. An analogy for the Heart is a p ...
Test Procedure for the LV5683PGEVB Evaluation Board SANYO Semiconductors
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
... Line regulation is defined as the maximum change in output voltage as the input voltage is varied through the specified range. It is measured by changing the input voltage and measuring the minimum/maximum voltage of the output. Line regulation is defined as the difference between maximum and minimu ...
Exam 2
... The next two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a positive point charge A of 2nC and a negative point charge B of -2nC at a distance of 3.0 m apart. The point P is directly above the charge B and is 4.0 m away from it. The point Q is midway between the charges. ...
... The next two questions refer to the diagram below, which shows a positive point charge A of 2nC and a negative point charge B of -2nC at a distance of 3.0 m apart. The point P is directly above the charge B and is 4.0 m away from it. The point Q is midway between the charges. ...
June 1999 - Vicphysics
... 2.5 x 10-4 W/m2 Inverse Square Law. Distance increases by 4, so Intensity decreases by 1/16 (1). Intensity = (1/16) x 4.0 x 10-3. A, B or C The reflected sound adds to the original sound because the reflection from the surface is irregular producing a random phase in the reflected wave. B could be a ...
... 2.5 x 10-4 W/m2 Inverse Square Law. Distance increases by 4, so Intensity decreases by 1/16 (1). Intensity = (1/16) x 4.0 x 10-3. A, B or C The reflected sound adds to the original sound because the reflection from the surface is irregular producing a random phase in the reflected wave. B could be a ...
Instructor`s Guide - The Described and Captioned Media Program
... complex circuit: A circuit with hundreds or thousands of parts, and that combines series and parallel circuits. They are used in items such as televisions and computers. conductor: A material (like a metal) through which electricity and heat flow easily. current: The flow of electricity, commonly me ...
... complex circuit: A circuit with hundreds or thousands of parts, and that combines series and parallel circuits. They are used in items such as televisions and computers. conductor: A material (like a metal) through which electricity and heat flow easily. current: The flow of electricity, commonly me ...
BSX1-80/200/250IOV1HA
... BYD Microelectronics Co., Ltd. (short for BME) exerts the greatest possible effort to ensure high quality and reliability. Nevertheless, semiconductor devices in general can malfunction or fail due to their inherent electrical sensitivity and vulnerability to physical stress. It is the responsibilit ...
... BYD Microelectronics Co., Ltd. (short for BME) exerts the greatest possible effort to ensure high quality and reliability. Nevertheless, semiconductor devices in general can malfunction or fail due to their inherent electrical sensitivity and vulnerability to physical stress. It is the responsibilit ...
ELECTRONIC COMPONENT
... • A LDR or light dependent resistor is a resistor that varies its resistance according to the light that falls in its surface. If the light increases the resistance decreases • Application-This is used to turn on the street light At night ...
... • A LDR or light dependent resistor is a resistor that varies its resistance according to the light that falls in its surface. If the light increases the resistance decreases • Application-This is used to turn on the street light At night ...
Multilayer Varistor Application Note
... Metal Oxide Varistors MOVs are made of oxidized zinc grains and small amounts of other metal oxides between two metal electrode plates (see Figure 1). These large adjacent grains form diode junctions that allow current to flow in only one direction. These “diode junctions” arrange themselves in such ...
... Metal Oxide Varistors MOVs are made of oxidized zinc grains and small amounts of other metal oxides between two metal electrode plates (see Figure 1). These large adjacent grains form diode junctions that allow current to flow in only one direction. These “diode junctions” arrange themselves in such ...