Document
... • requires a complete circuit • path cannot be only resistance cannot be only potential drops in direction of current flow Electromotive Force (EMF) • provides increase in potential E • converts some external form of energy into electrical energy Single emf and a single resistor: emf can be thou ...
... • requires a complete circuit • path cannot be only resistance cannot be only potential drops in direction of current flow Electromotive Force (EMF) • provides increase in potential E • converts some external form of energy into electrical energy Single emf and a single resistor: emf can be thou ...
Static Electricity The Laws of Electrical Charges Current Electricity
... of electricity from chemical reactions within the cell. Dry Cells - The electricity-producing cells, which are referred to as ‘batteries’, are called dry cells. They are 'dry' because the chemicals used are in a paste. The chemical reaction in a cell releases free electrons, which travel from the ne ...
... of electricity from chemical reactions within the cell. Dry Cells - The electricity-producing cells, which are referred to as ‘batteries’, are called dry cells. They are 'dry' because the chemicals used are in a paste. The chemical reaction in a cell releases free electrons, which travel from the ne ...
Lesson 5 Magnetism and Electricity Notes
... When electric current flows in only one direction, it is called direct current, or DC. ...
... When electric current flows in only one direction, it is called direct current, or DC. ...
Circuits
... way that the electric current through each of them is the same. • Parallel Circuit- Electric circuit with two or more devices connected in such a way that the same voltage acts across each one and any single one completes the circuit independently of the others. ...
... way that the electric current through each of them is the same. • Parallel Circuit- Electric circuit with two or more devices connected in such a way that the same voltage acts across each one and any single one completes the circuit independently of the others. ...
CSCI 2980: Introduction to Circuits, CAD, and Instrumentation
... Example 6.2: The voltage across a 5 μF capacitor has the waveform shown in (a). Determine the current waveform. ...
... Example 6.2: The voltage across a 5 μF capacitor has the waveform shown in (a). Determine the current waveform. ...
An Introduction to Circuits Excited with an AC Potential
... either a sine function or a cosine function. Once the selection is made it is necessary that related signals be treated consistently. That is, they must all be properly related to the reference. ...
... either a sine function or a cosine function. Once the selection is made it is necessary that related signals be treated consistently. That is, they must all be properly related to the reference. ...
16.4 Series Circuits
... Series Circuits Eventually the electrons move all the way around the circuit. A break anywhere in the path results in an open circuit, and the flow of electrons ceases. Burning out of one of the lamp filaments or simply opening the switch could cause such a break. ...
... Series Circuits Eventually the electrons move all the way around the circuit. A break anywhere in the path results in an open circuit, and the flow of electrons ceases. Burning out of one of the lamp filaments or simply opening the switch could cause such a break. ...
Operational_Amplifiers
... non-inverting and inverting inputs; use operational amplifiers which require a single power supply, i.e. 3140 IC; use an operational amplifier as a comparator and an inverting amplifier; know how to limit the gain of an operational amplifier by using an input resistor and a feedback resistor (negati ...
... non-inverting and inverting inputs; use operational amplifiers which require a single power supply, i.e. 3140 IC; use an operational amplifier as a comparator and an inverting amplifier; know how to limit the gain of an operational amplifier by using an input resistor and a feedback resistor (negati ...
Voltage Amplifier
... When Vin=0,Volt is NOT 0 due to mismatch of transistors in real circuit design. It is more meaningful to specify input-referred offset voltage, defined as Vos,in=Vos,out / A. Offset voltage may causes a DC shift of later stages, also causes limited precision in signal comparison. ...
... When Vin=0,Volt is NOT 0 due to mismatch of transistors in real circuit design. It is more meaningful to specify input-referred offset voltage, defined as Vos,in=Vos,out / A. Offset voltage may causes a DC shift of later stages, also causes limited precision in signal comparison. ...
RC SNUBBERS (SMPS) - Illinois Capacitor
... RC SNUBBERS (SMPS) Snubbers are energy-absorbing circuits used to suppress the voltage spikes caused by the circuit's inductance when a switch, electrical or mechanical, opens. The most common snubber circuit is a capacitor and resistor connected in series across the switch (transistor). ...
... RC SNUBBERS (SMPS) Snubbers are energy-absorbing circuits used to suppress the voltage spikes caused by the circuit's inductance when a switch, electrical or mechanical, opens. The most common snubber circuit is a capacitor and resistor connected in series across the switch (transistor). ...
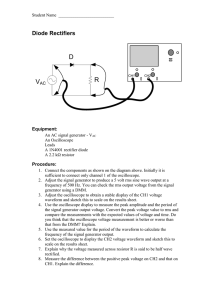
Diode Rectifiers
... between VAC and R. 10. Measure and sketch the new voltage waveform across R to scale. Comment on the peak value of the new voltage waveform. 11. Suggest a reason why the bridge rectifier output voltage might be considered an improvement on the output from the half wave rectifier. ...
... between VAC and R. 10. Measure and sketch the new voltage waveform across R to scale. Comment on the peak value of the new voltage waveform. 11. Suggest a reason why the bridge rectifier output voltage might be considered an improvement on the output from the half wave rectifier. ...
Chapter 18 Electric Current and Circuits
... 4. In a liquid, a current is set up between points A and B. Positive ions are going from A to B moving 6.0 coulombs of positive charge per second and negative charges are moving from B to A moving 2.0 coulombs of negative charge per second. What is the current from A to B? A. 8.0 A B. -8.0 A C. 4.0 ...
... 4. In a liquid, a current is set up between points A and B. Positive ions are going from A to B moving 6.0 coulombs of positive charge per second and negative charges are moving from B to A moving 2.0 coulombs of negative charge per second. What is the current from A to B? A. 8.0 A B. -8.0 A C. 4.0 ...
12 electric current support
... charge passing through it, and so it is also measured in volts (V). The energy transferred (or dissipated), ΔE, in a component is equal to the work done, W and is measured in joules (J). ...
... charge passing through it, and so it is also measured in volts (V). The energy transferred (or dissipated), ΔE, in a component is equal to the work done, W and is measured in joules (J). ...
STD840DN40
... Modified PTOT and RthJA values in Table 2 and Table 3 on page 2. Minor text changes. ...
... Modified PTOT and RthJA values in Table 2 and Table 3 on page 2. Minor text changes. ...
current - Courses
... The supply will not provide an infinite current: current will be limited at any particular voltage. The limiting current is adjustable with this knob. ...
... The supply will not provide an infinite current: current will be limited at any particular voltage. The limiting current is adjustable with this knob. ...
Opto-electronics - Electrical Revision Page
... chemical composition of the semiconductor material. Light ranging all the way from the infrared region of the spectrum up to the ultraviolet region can be produced. ...
... chemical composition of the semiconductor material. Light ranging all the way from the infrared region of the spectrum up to the ultraviolet region can be produced. ...