Mechanical Properties of Metals
... • indenter material (ball, pyramid, cone) is harder than the material being tested (i.e.: tungsten carbide, diamond) • indenter is pressed at 90o • hardness is based on the depth of the impression or its crosssectional area ...
... • indenter material (ball, pyramid, cone) is harder than the material being tested (i.e.: tungsten carbide, diamond) • indenter is pressed at 90o • hardness is based on the depth of the impression or its crosssectional area ...
9. Short overview of rheology very short for 2 credit course
... Information - Zero Shear h, shear thinning Elasticity (reversible deformation) in materials MW & MWD differences Polymer Melts and Polymer solutions. Finding Yield in gelled dispersions High and Low Rate (short and long time) modulus properties. Extend time or frequency range with TTS ...
... Information - Zero Shear h, shear thinning Elasticity (reversible deformation) in materials MW & MWD differences Polymer Melts and Polymer solutions. Finding Yield in gelled dispersions High and Low Rate (short and long time) modulus properties. Extend time or frequency range with TTS ...
estimation of subsurface residual stress depth profiles via wideband
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
464_lec.pdf
... value of the material parameters within these laws. The identification of those mechanical parameters can be done based on homogeneous stress and strain fields such as those obtained in uni-axial tensile tests and simple shear tests performed in different plane material directions. Another way to id ...
... value of the material parameters within these laws. The identification of those mechanical parameters can be done based on homogeneous stress and strain fields such as those obtained in uni-axial tensile tests and simple shear tests performed in different plane material directions. Another way to id ...
chapter 11
... Chapter 11, Problem 33 A mass is oscillating with amplitude A at the end of a spring. How far (in terms of A) is this mass from equilibrium position of the spring when the elastic potential energy equals the kinetic energy? Chapter 11, Problem 34 (a)If a vibrating system has total energy E0, what w ...
... Chapter 11, Problem 33 A mass is oscillating with amplitude A at the end of a spring. How far (in terms of A) is this mass from equilibrium position of the spring when the elastic potential energy equals the kinetic energy? Chapter 11, Problem 34 (a)If a vibrating system has total energy E0, what w ...
Hints
... (a) (20%) Consider the amount of strain following the onset of yielding, but before the point of fracture. If this portion of the stress-strain curve is large relative to the elastic portion of the curve, it is a ductile material. (b) (20%) The stiffest material is the one with the greatest slope in ...
... (a) (20%) Consider the amount of strain following the onset of yielding, but before the point of fracture. If this portion of the stress-strain curve is large relative to the elastic portion of the curve, it is a ductile material. (b) (20%) The stiffest material is the one with the greatest slope in ...
The concept of frozen elastic energy as a consequence of - I
... This is the first hypoelastic micromechanical model for soft tissues introducing a limited number of physical parameters. The modeled mechanical behavior exhibits pathdependence of the response and possible frozen elastic energy remaining in the system after complete unloading. This behavior origina ...
... This is the first hypoelastic micromechanical model for soft tissues introducing a limited number of physical parameters. The modeled mechanical behavior exhibits pathdependence of the response and possible frozen elastic energy remaining in the system after complete unloading. This behavior origina ...
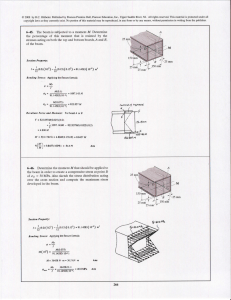
6-46. Determine the moment M that should be applied to the beam
... © 2008 by R.C. Hibbeler. Published by Pearson Prentice Hall, Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permiss ...
... © 2008 by R.C. Hibbeler. Published by Pearson Prentice Hall, Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permiss ...
Compression The mechanical properties of a ductile metal are
... 2). Failure of a ductile metal in compression only occurs owing to excessive barreling causing axial splitting around the periphery. For brittle materials, such as flake cast-iron, concrete which would not normally be used intension, the compression test is used to give quantitative mechanical prope ...
... 2). Failure of a ductile metal in compression only occurs owing to excessive barreling causing axial splitting around the periphery. For brittle materials, such as flake cast-iron, concrete which would not normally be used intension, the compression test is used to give quantitative mechanical prope ...
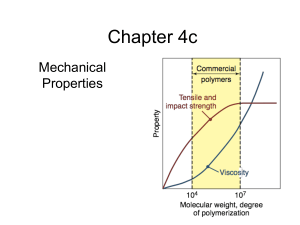
Chapter 4c - Loy Research Group
... Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microscopic cracks. Compression tests tend to be ...
... Stress-strain curves are very dependent on the test method. A modulus determined under compression is generally higher than one derived from a tensile experiment, as shown below for polystyrene. Tensile testing is most sensitive to material flaws and microscopic cracks. Compression tests tend to be ...
Poisson`s ratio
... The bulk modulus is another elastic constant that reflects the resistance of the material to an overall gain or loss of volume in conditions of hydrostatic stress ( Ph ). If the Ph increases then the volume will decrease and the volume change will be negative. If the volume increases, Ph will decrea ...
... The bulk modulus is another elastic constant that reflects the resistance of the material to an overall gain or loss of volume in conditions of hydrostatic stress ( Ph ). If the Ph increases then the volume will decrease and the volume change will be negative. If the volume increases, Ph will decrea ...
RHEOLOGY
... the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and deformation of a body of rock. The relationships regarding such behaviour include those such as elastic, viscous, viso-elastic, elastico-viscous, general line ...
... the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and deformation of a body of rock. The relationships regarding such behaviour include those such as elastic, viscous, viso-elastic, elastico-viscous, general line ...
Chap 8 Learn Obj
... 27. (a) Briefly describe the manner in which tests are performed to generate a plot of fatigue stress versus the logarithm of the number of cycles. (b) Note which three in-service conditions should be replicated in a fatigue ...
... 27. (a) Briefly describe the manner in which tests are performed to generate a plot of fatigue stress versus the logarithm of the number of cycles. (b) Note which three in-service conditions should be replicated in a fatigue ...
Chapter 9
... maximum force per unit area the material can withstand before it breaks or factures Some materials are stronger in ...
... maximum force per unit area the material can withstand before it breaks or factures Some materials are stronger in ...
Strain Rate Dependent Flow Stress Characterization
... response as shown in Fig. 2. The flow stress for compression done at high strain rate (10 sec-1) showed sharp increase of flow stress at very low strain and was followed by a plateau of relatively constant flow stress and almost no work hardening. On the other hand, specimens compressing at low stra ...
... response as shown in Fig. 2. The flow stress for compression done at high strain rate (10 sec-1) showed sharp increase of flow stress at very low strain and was followed by a plateau of relatively constant flow stress and almost no work hardening. On the other hand, specimens compressing at low stra ...
CHAPTER5
... measure of its resistance to plastic deformation. A straight line is drawn parallel to the elastic deformation part of the curve from the engineering strain value of 0.002. The stress corresponding to the intersection point of these two lines is YIELD STRENGTH. Yield strengths may range from 35 MPa ...
... measure of its resistance to plastic deformation. A straight line is drawn parallel to the elastic deformation part of the curve from the engineering strain value of 0.002. The stress corresponding to the intersection point of these two lines is YIELD STRENGTH. Yield strengths may range from 35 MPa ...
Stress Definition for a Layman
... Stress Definition for a Layman Stress is defined as the force over the area of an object. Force is related to the amount of pressure applied to an object (The American Heritage, 2006). The word stress comes from the shortening of the middle French word “destresse” to mean hardship, adversity, force, ...
... Stress Definition for a Layman Stress is defined as the force over the area of an object. Force is related to the amount of pressure applied to an object (The American Heritage, 2006). The word stress comes from the shortening of the middle French word “destresse” to mean hardship, adversity, force, ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 21: Some material science
... A nail is driven into a piece of wood with a force of 700N. What is the pressure on the wood if Anail=1 mm2? A person (weighing 700 N) is lying on a bed of such nails (his body covers 1000 nails). What is the pressure exerted by each of the nails? ...
... A nail is driven into a piece of wood with a force of 700N. What is the pressure on the wood if Anail=1 mm2? A person (weighing 700 N) is lying on a bed of such nails (his body covers 1000 nails). What is the pressure exerted by each of the nails? ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... MegaPascal=MPa= Newton/mm2 Pounds per square inch = Psi Note: 1MPa = 1 x106 Pa = 145 psi 1 kPa = 1x103 Pa, 1 MPa = 1x106Pa, 1GPa = 1x109 Pa 1 psi = 6.895kPa, 1ksi = 6.895MPa, 1 psf = 47.88 Pa ...
... MegaPascal=MPa= Newton/mm2 Pounds per square inch = Psi Note: 1MPa = 1 x106 Pa = 145 psi 1 kPa = 1x103 Pa, 1 MPa = 1x106Pa, 1GPa = 1x109 Pa 1 psi = 6.895kPa, 1ksi = 6.895MPa, 1 psf = 47.88 Pa ...
Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties
... Testing of specimens stacked one on top of another is not recommended. ...
... Testing of specimens stacked one on top of another is not recommended. ...
Suggested solutions to 2015 MEK2500 Mock Exam
... Assume a linear regime with small strains and no distinction between Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates. Consider a two-dimensional rectangular body of length a (m) and height b (m) with coordinates (x1 , x2 ) ∈ [0, a] × [0, b]. Assume that the body is isotropic and homogeneous with Lamé parameter ...
... Assume a linear regime with small strains and no distinction between Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates. Consider a two-dimensional rectangular body of length a (m) and height b (m) with coordinates (x1 , x2 ) ∈ [0, a] × [0, b]. Assume that the body is isotropic and homogeneous with Lamé parameter ...
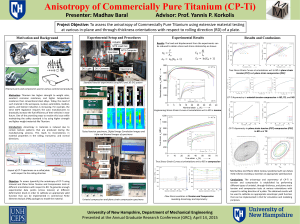
Downloadable - University of New Hampshire
... Motivation: Titanium has higher strength to weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and higher temperature resistance than conventional steel alloys. Today, the need of such material in the aerospace, nuclear, automobile, medical, sports, and fashion industries is increasing. For example, the ...
... Motivation: Titanium has higher strength to weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and higher temperature resistance than conventional steel alloys. Today, the need of such material in the aerospace, nuclear, automobile, medical, sports, and fashion industries is increasing. For example, the ...
Stress - Delta University!
... than those of low Young’s modulus values because they require much more stresses to produce the same amount of strain. It is measured by stress/strain It is measured by GPA=109 Pascal. ...
... than those of low Young’s modulus values because they require much more stresses to produce the same amount of strain. It is measured by stress/strain It is measured by GPA=109 Pascal. ...
chapter5
... t in second Example: 30% finite longitudinal strain (|e|= 0.3) is achieved in an experiment that lasts one hour (3600 s). The correspond strain rate is ė = 0.3/3600 = 8.3 x 10–5/s Now let’s see what happens to the strain rate when we change the time interval, but maintain the same amount of finite s ...
... t in second Example: 30% finite longitudinal strain (|e|= 0.3) is achieved in an experiment that lasts one hour (3600 s). The correspond strain rate is ė = 0.3/3600 = 8.3 x 10–5/s Now let’s see what happens to the strain rate when we change the time interval, but maintain the same amount of finite s ...
Viscoplasticity
Viscoplasticity is a theory in continuum mechanics that describes the rate-dependent inelastic behavior of solids. Rate-dependence in this context means that the deformation of the material depends on the rate at which loads are applied. The inelastic behavior that is the subject of viscoplasticity is plastic deformation which means that the material undergoes unrecoverable deformations when a load level is reached. Rate-dependent plasticity is important for transient plasticity calculations. The main difference between rate-independent plastic and viscoplastic material models is that the latter exhibit not only permanent deformations after the application of loads but continue to undergo a creep flow as a function of time under the influence of the applied load.The elastic response of viscoplastic materials can be represented in one-dimension by Hookean spring elements. Rate-dependence can be represented by nonlinear dashpot elements in a manner similar to viscoelasticity. Plasticity can be accounted for by adding sliding frictional elements as shown in Figure 1. In the figure E is the modulus of elasticity, λ is the viscosity parameter and N is a power-law type parameter that represents non-linear dashpot [σ(dε/dt)= σ = λ(dε/dt)(1/N)]. The sliding element can have a yield stress (σy) that is strain rate dependent, or even constant, as shown in Figure 1c.Viscoplasticity is usually modeled in three-dimensions using overstress models of the Perzyna or Duvaut-Lions types. In these models, the stress is allowed to increase beyond the rate-independent yield surface upon application of a load and then allowed to relax back to the yield surface over time. The yield surface is usually assumed not to be rate-dependent in such models. An alternative approach is to add a strain rate dependence to the yield stress and use the techniques of rate independent plasticity to calculate the response of a materialFor metals and alloys, viscoplasticity is the macroscopic behavior caused by a mechanism linked to the movement of dislocations in grains, with superposed effects of inter-crystalline gliding. The mechanism usually becomes dominant at temperatures greater than approximately one third of the absolute melting temperature. However, certain alloys exhibit viscoplasticity at room temperature (300K). For polymers, wood, and bitumen, the theory of viscoplasticity is required to describe behavior beyond the limit of elasticity or viscoelasticity. In general, viscoplasticity theories are useful in areas such as the calculation of permanent deformations, the prediction of the plastic collapse of structures, the investigation of stability, crash simulations, systems exposed to high temperatures such as turbines in engines, e.g. a power plant, dynamic problems and systems exposed to high strain rates.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑