damage model for brittle elastic solids with unequal tensile
... by (36) is referred to as a damage surface in stress space. The parameter R, which defines the size of the surface, is assumed to depend on the cumulative damage parameter p. The representation (36) is the simplest version of the damage criterion. It implies that during damage evolution initial dama ...
... by (36) is referred to as a damage surface in stress space. The parameter R, which defines the size of the surface, is assumed to depend on the cumulative damage parameter p. The representation (36) is the simplest version of the damage criterion. It implies that during damage evolution initial dama ...
measuring the yield stress of waxy crude oils considering its
... crude oils (Paumier-Pantet-Monnet-Touze-Foltz , 2009; Galindo-Rosales-Rubio-Hernandez , 2010). The identification of an elastic yield stress in waxy crude oils in the gelled state adds another degree of complexity to the problem. This puts this kind of material into the category of elasto-viscoplast ...
... crude oils (Paumier-Pantet-Monnet-Touze-Foltz , 2009; Galindo-Rosales-Rubio-Hernandez , 2010). The identification of an elastic yield stress in waxy crude oils in the gelled state adds another degree of complexity to the problem. This puts this kind of material into the category of elasto-viscoplast ...
330_mon.pdf
... gauges do not give enough information to calculate the residual stresses. Full field methods are required. Various optical techniques can be used, shearography or grating shearography to measure strains and ESPI or moiré interferometry to measure displacements [6-10]. To measure surface displacement ...
... gauges do not give enough information to calculate the residual stresses. Full field methods are required. Various optical techniques can be used, shearography or grating shearography to measure strains and ESPI or moiré interferometry to measure displacements [6-10]. To measure surface displacement ...
0131.PDF
... stresses. If genuine, this would suggest that the shear strength of polychloroprene (that is the offset of the Hugoniot from the hydrostat) decreases with increasing shock stress. The observation of the complex response of polymeric materials drives the experimentalist to determine techniques that c ...
... stresses. If genuine, this would suggest that the shear strength of polychloroprene (that is the offset of the Hugoniot from the hydrostat) decreases with increasing shock stress. The observation of the complex response of polymeric materials drives the experimentalist to determine techniques that c ...
Stress and Strain
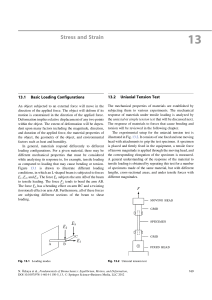
... tension tests can be used to obtain a unique curve representing the relationship between the applied load and corresponding deformation for a material. This can be achieved by dividing the applied load with the cross-sectional area (F=A) of the specimen, dividing the amount of elongation measured wi ...
... tension tests can be used to obtain a unique curve representing the relationship between the applied load and corresponding deformation for a material. This can be achieved by dividing the applied load with the cross-sectional area (F=A) of the specimen, dividing the amount of elongation measured wi ...
Review of Fluid Mechanics Terminology
... Viscosity units: Force Time/Area, ex. N s / m2. Often, viscosity is given in "poise", where 1 poise = 1 dyne s / cm2 = 0.1 N s / m2, or in centipoise (cp) where 1 cp = 0.01 poise. Usual symbol for viscosity: µ. The viscosity of liquids typically decreases with an increase in temperature, while that ...
... Viscosity units: Force Time/Area, ex. N s / m2. Often, viscosity is given in "poise", where 1 poise = 1 dyne s / cm2 = 0.1 N s / m2, or in centipoise (cp) where 1 cp = 0.01 poise. Usual symbol for viscosity: µ. The viscosity of liquids typically decreases with an increase in temperature, while that ...
elastic deformation
... interatomic bond strength. For example, virtually all aluminum alloys, regardless of how they were processed have an elastic modulus of 6.9 x 1010 N/m2. Plastic Deformation After a material has reached it's elastic limit, or yielded, further straining will result in permanent deformation. Plastic (o ...
... interatomic bond strength. For example, virtually all aluminum alloys, regardless of how they were processed have an elastic modulus of 6.9 x 1010 N/m2. Plastic Deformation After a material has reached it's elastic limit, or yielded, further straining will result in permanent deformation. Plastic (o ...
212_khr.pdf
... Plastic fracture of materials under quasistatic deformation processes is characterized by deformation and energy fracture criteria. At the same time such criteria are tightly bound among themselves as any process of plastic deformation is connected with energy dissipation. The basic problem will con ...
... Plastic fracture of materials under quasistatic deformation processes is characterized by deformation and energy fracture criteria. At the same time such criteria are tightly bound among themselves as any process of plastic deformation is connected with energy dissipation. The basic problem will con ...
Glossary
... of a material, the concept is the same, except that stress substitutes for force, and strain substitutes for displacement; see modulus of elasticity. Strain: The intensity of deformation at a point in an object. See normal strain and shear strain. Strength: A very general term that may be applied t ...
... of a material, the concept is the same, except that stress substitutes for force, and strain substitutes for displacement; see modulus of elasticity. Strain: The intensity of deformation at a point in an object. See normal strain and shear strain. Strength: A very general term that may be applied t ...
4 Constitutive Equations
... tensor. The components of the stiffness tensor C(F ) are expressions of the elastic constants which in turn depend on the actual definition of the stress rate (and thus on the deformation). Because of the properties of the rate of deformation tensor (cf. Section 2.5) hypoelastic constitutive laws do ...
... tensor. The components of the stiffness tensor C(F ) are expressions of the elastic constants which in turn depend on the actual definition of the stress rate (and thus on the deformation). Because of the properties of the rate of deformation tensor (cf. Section 2.5) hypoelastic constitutive laws do ...
Elastic-Plastic-Creep Analyses of Brazed Carbon
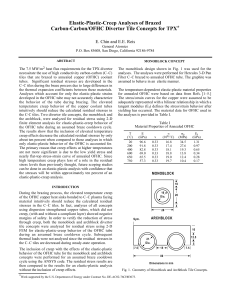
... The 7.5 MW/m 2 heat flux requirements for the TPX divertor necessitate the use of high conductivity carbon-carbon (C–C) tiles that are brazed to annealed copper (OFHC) coolant tubes. Significant residual stresses are developed in the C–C tiles during the braze process due to large differences in the ...
... The 7.5 MW/m 2 heat flux requirements for the TPX divertor necessitate the use of high conductivity carbon-carbon (C–C) tiles that are brazed to annealed copper (OFHC) coolant tubes. Significant residual stresses are developed in the C–C tiles during the braze process due to large differences in the ...
A QUASI-LINEAR VISCOELASTIC RHEOLOGICAL MODEL FOR
... in the case of small strains and static loadings, nevertheless it fails for large strains and dynamic loadings when damping and strain rate sensitivity becomes a significant factor. The most popular theory which allows for taking the rheological effects into account is the linear viscoelasticity based ...
... in the case of small strains and static loadings, nevertheless it fails for large strains and dynamic loadings when damping and strain rate sensitivity becomes a significant factor. The most popular theory which allows for taking the rheological effects into account is the linear viscoelasticity based ...
lecture 10-12 mechanical failure
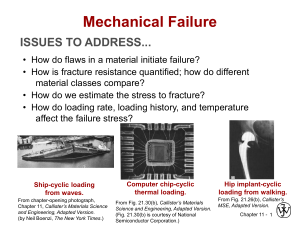
... centrifugal stresses, and high-pressure steam lines). Deformation under such circumstances is termed creep. It could be defined as the time-dependent and permanent deformation of materials when subjected to a constant load or stress. Creep is normally an undesirable phenomenon and is often the lim ...
... centrifugal stresses, and high-pressure steam lines). Deformation under such circumstances is termed creep. It could be defined as the time-dependent and permanent deformation of materials when subjected to a constant load or stress. Creep is normally an undesirable phenomenon and is often the lim ...
A micro-mechanical investigation of bifurcation in granular materials
... Other failure modes may be encountered as well before the plastic limit is reached (as for the failure mode occurring at point M, in Fig. 1). The detection of these failure modes requires a novel framework to be developed, which should lead to a different criterion other than that given in Eq. (1). ...
... Other failure modes may be encountered as well before the plastic limit is reached (as for the failure mode occurring at point M, in Fig. 1). The detection of these failure modes requires a novel framework to be developed, which should lead to a different criterion other than that given in Eq. (1). ...
Analysis of a Feder - Acta Periodica Duellatorum
... external pressure, or friction). Any strain (deformation) of a solid material generates an internal elastic stress, analogous to the reaction force of a spring, that tends to restore the material to its original undeformed state. The relation between mechanical stress, deformation, and the rate of c ...
... external pressure, or friction). Any strain (deformation) of a solid material generates an internal elastic stress, analogous to the reaction force of a spring, that tends to restore the material to its original undeformed state. The relation between mechanical stress, deformation, and the rate of c ...
Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity
... nearest neighbors. The atoms are held together by interatomic forces that can be modeled as tiny springs. If we try to change the interatomic distance the resulting force is proportional to the atom displacement from the equilibrium position. The spring constants are large and thus the lattice is re ...
... nearest neighbors. The atoms are held together by interatomic forces that can be modeled as tiny springs. If we try to change the interatomic distance the resulting force is proportional to the atom displacement from the equilibrium position. The spring constants are large and thus the lattice is re ...
Constitutive Laws
... Appropriate laws must be used for fluid mixture under consideration Come ...
... Appropriate laws must be used for fluid mixture under consideration Come ...
a new frontier for deposit stress measurement
... = Stress in megapascals, MPa. Note: MPa x 145 = PSI. L = Length of substrate on which the deposit is applied in mm. For Deposit Stress Analyzer test strips, this value is 76.2 mm. t = Deposit average thickness in millimeters. M = Correction for modulus of elasticity difference between the deposit ...
... = Stress in megapascals, MPa. Note: MPa x 145 = PSI. L = Length of substrate on which the deposit is applied in mm. For Deposit Stress Analyzer test strips, this value is 76.2 mm. t = Deposit average thickness in millimeters. M = Correction for modulus of elasticity difference between the deposit ...
Solids and Fluids
... • So far, we have assumed that solids always retain their original shape and cannot be deformed (“rigid bodies”) • However, the stretching, squeezing, and twisting of real objects when forces are applied are often too important to ignore (causing deformations) • Stress characterizes the strength of ...
... • So far, we have assumed that solids always retain their original shape and cannot be deformed (“rigid bodies”) • However, the stretching, squeezing, and twisting of real objects when forces are applied are often too important to ignore (causing deformations) • Stress characterizes the strength of ...
Bild 1 - Division of Solid Mechanics
... Modelling of the constitutive behaviour of Inconel 718 at intermediate temperatures, Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 133, Issue 9 ...
... Modelling of the constitutive behaviour of Inconel 718 at intermediate temperatures, Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 133, Issue 9 ...
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY • Conditions
... Therefore, the pivot must supply an upward force so that the net force on the board is zero, i.e., F − (28 kg)g + (40 kg)g = 0 ∴F = (68 kg)g = 666.4 N. Define ccw torques as positive and taking torques about the pivot point we have: (28 kg)g × (2 m) − (40 kg)g × d = 0 56 kg ⋅ m ∴d = = 1.40 m. ...
... Therefore, the pivot must supply an upward force so that the net force on the board is zero, i.e., F − (28 kg)g + (40 kg)g = 0 ∴F = (68 kg)g = 666.4 N. Define ccw torques as positive and taking torques about the pivot point we have: (28 kg)g × (2 m) − (40 kg)g × d = 0 56 kg ⋅ m ∴d = = 1.40 m. ...
Cellular materials made of stacked tubes : influence of the
... observed strain rate dependency for other Inconel® materials. Whereas Young's modulus, E is not dependent on the strain, both the yield and ultimate stresses, σy and σu, increase significantly and gradually with the strain rate. Results show that the material behaviour of the Inco600BM base material ...
... observed strain rate dependency for other Inconel® materials. Whereas Young's modulus, E is not dependent on the strain, both the yield and ultimate stresses, σy and σu, increase significantly and gradually with the strain rate. Results show that the material behaviour of the Inco600BM base material ...
At what grain diameter will the lower yield point be 310 Mpa?
... Kc that relates the critical stress for crack propagation and geometry of the crack: ...
... Kc that relates the critical stress for crack propagation and geometry of the crack: ...
Paper 6a.3_publicati..
... semiconductor device fabrication; metal thin film stress can cause undesirable surface cracking during deposition. Depending on the severity of stress, the surface cracking can lead to buckling and peeling of the film. This buckled or curled film can perform as a micro-mask during further metal depo ...
... semiconductor device fabrication; metal thin film stress can cause undesirable surface cracking during deposition. Depending on the severity of stress, the surface cracking can lead to buckling and peeling of the film. This buckled or curled film can perform as a micro-mask during further metal depo ...
Viscoplasticity
Viscoplasticity is a theory in continuum mechanics that describes the rate-dependent inelastic behavior of solids. Rate-dependence in this context means that the deformation of the material depends on the rate at which loads are applied. The inelastic behavior that is the subject of viscoplasticity is plastic deformation which means that the material undergoes unrecoverable deformations when a load level is reached. Rate-dependent plasticity is important for transient plasticity calculations. The main difference between rate-independent plastic and viscoplastic material models is that the latter exhibit not only permanent deformations after the application of loads but continue to undergo a creep flow as a function of time under the influence of the applied load.The elastic response of viscoplastic materials can be represented in one-dimension by Hookean spring elements. Rate-dependence can be represented by nonlinear dashpot elements in a manner similar to viscoelasticity. Plasticity can be accounted for by adding sliding frictional elements as shown in Figure 1. In the figure E is the modulus of elasticity, λ is the viscosity parameter and N is a power-law type parameter that represents non-linear dashpot [σ(dε/dt)= σ = λ(dε/dt)(1/N)]. The sliding element can have a yield stress (σy) that is strain rate dependent, or even constant, as shown in Figure 1c.Viscoplasticity is usually modeled in three-dimensions using overstress models of the Perzyna or Duvaut-Lions types. In these models, the stress is allowed to increase beyond the rate-independent yield surface upon application of a load and then allowed to relax back to the yield surface over time. The yield surface is usually assumed not to be rate-dependent in such models. An alternative approach is to add a strain rate dependence to the yield stress and use the techniques of rate independent plasticity to calculate the response of a materialFor metals and alloys, viscoplasticity is the macroscopic behavior caused by a mechanism linked to the movement of dislocations in grains, with superposed effects of inter-crystalline gliding. The mechanism usually becomes dominant at temperatures greater than approximately one third of the absolute melting temperature. However, certain alloys exhibit viscoplasticity at room temperature (300K). For polymers, wood, and bitumen, the theory of viscoplasticity is required to describe behavior beyond the limit of elasticity or viscoelasticity. In general, viscoplasticity theories are useful in areas such as the calculation of permanent deformations, the prediction of the plastic collapse of structures, the investigation of stability, crash simulations, systems exposed to high temperatures such as turbines in engines, e.g. a power plant, dynamic problems and systems exposed to high strain rates.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑